Abstract
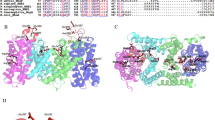
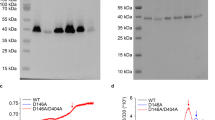
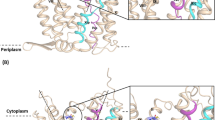
The Na+/H+ exchanger is an integral membrane protein found in the plasma membrane of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. In eukaryotes it functions to exchange one proton for a sodium ion. In mammals it removes intracellular protons while in plants and fungal cells the plasma membrane form removes intracellular sodium in exchange for extracellular protons. In this study we used the Na+/H+ exchanger of Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sod2) as a model system to study amino acids critical for activity of the protein. Twelve mutant forms of the Na+/H+ exchanger were examined for their ability to translocate protons as assessed by a cytosensor microphysiometer. Mutation of the amino acid Histidine 367 resulted in defective proton translocation. The acidic residues Asp145, Asp178, Asp266 and Asp267 were important in the proton translocation activity of the Na+/H+ exchanger. Mutation of amino acids His98, His233 and Asp241 did not significantly impair proton translocation by the Na+/H+ exchanger. These results confirm that polar amino acids are important in proton flux activity of Na+/H+ exchangers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiebe CA, DiBattista ER, Fliegel L: Functional role of amino acid residues in Na+/H+ exchangers. Biochem J 357: 1-10, 2001
Slepkov E, Fliegel L: Structure and function of the NHE1 isoform of the Na+/H+ exchanger. Biochem Cell Biol 80: 499-508, 2002
Blumwald E: Sodium transport and salt tolerance in plants. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12: 431-434, 2000
Apse MP, Aharon GS, Snedden WA, Blumwald E: Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis. Science 285: 1256-1258, 1999
Nass R, Rao R: Novel localization of a Na+/H+ exchanger in a late endosomal compartment of yeast. J Biol Chem 273: 21054-21060, 1998
Prior C, Potier S, Souciet J-L, Sychrova H: Characterization of the NHA1 gene encoding a Na+/H+-antiporter of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 387: 89-93, 1996
Banuelos MA, Sychrova H, Bleykasten-Grosshans C, Souciet JL, Potier S: The Nha1 antiporter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mediates sodium and potassium efflux. Microbiology 144: 2749-2758, 1998
Sychrova H, Ramirez J, Pena A: Involvement of Nha1 antiporter in regulation of intracellular pH in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol Lett 171: 167-172, 1999
Jia Z-P, McCullough N, Martel R, Hemmingsen S, Young PG: Gene amplification at a locus encoding a putative Na+/H+ antiporter confers sodium and lithium tolerance in fission yeast. EMBO J 11: 1631-1640, 1992
Dibrov P, Young PG, Fliegel L: Functional analysis of amino acid residues essential for activity in the Na+/H+ exchanger of fission yeast. Biochemistry 36: 8282-8288, 1998
Hahnenberger KM, Jia Z, Young PG: Functional expression of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe Na+/H+ antiporter gene, sod2, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 5031-5036, 1996
Moreno S, Klar A, Nurse P: Molecular genetic analysis of fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Meth Enzymol 194: 795-823, 1991
Toone WM, Kuge S, Samuels M, Morgan BA, Toda T, Jones N: Regulation of the fission yeast transcription factor Pap1 by oxidative stress: Requirement for the nuclear export factor Crm1 (Exportin) and the stress-activated MAP kinase Sty1/Spc1. Genes Dev 12: 1453-1463, 1998
Serrano R, Villalba JM, Palmgren MG, Portillo F, Parets-Soler A, Roldan M, Ferguson C, Montesinos C: Studies of the plasma membrane H(+)-ATPase of yeast and plants. Biochem Soc Trans 20: 562-566, 1992
Serrano R, Rodriguez-Navarro A: Ion homeostasis during salt stress in plants. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13: 399-404, 2001
Dibrov P, Smith JJ, Young P, Fliegel L: Identification and localization of the sod2 gene product in fission yeast. FEBS Lett 405: 119-124, 1997
Dibrov P, Fliegel L: Comparative molecular analysis of Na+/H+ exchangers: A unified model for Na+/H+ antiport? FEBS Lett 424: 1-5, 1998
Brett CL, Wei Y, Donowitz M, Rao R: Human Na(+)/H(+) exchanger isoform 6 is found in recycling endosomes of cells, not in mitochondria. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 282: C1031-C1041, 2002
Fliegel L, Haworth RS, Dyck JRB: Characterization of the placental brush border membrane Na+/H+ exchanger: Identification of thiol-dependent transitions in apparent molecular size. Biochem J. 289: 101-107, 1993
Williams KA: Three-dimensional structure of the ion-coupled transport protein NhaA. Nature 403: 112-115, 2000
Touret N, Poujeol P, Counillon L: Second-site revertants of a low-sodium-affinity mutant of the Na+/H+ exchanger reveal the participation of TM4 into a highly constrained sodium-binding site. Biochemistry 40: 5095-5101, 2001
Galili L, Rothman A, Kozachkov L, Rimon A, Padan E: Trans membrane domain IV is involved in ion transport activity and pH regulation of the NhaA-Na(+)/H(+) antiporter of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 41: 609-17, 2002
Claros M, von Heijne G: TopPredII: An improved software for membrane protein structure predictions. Comp Appl Biosci 10: 685-686, 1994
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiebe, C.A., Rieder, C., Young, P.G. et al. Functional analysis of amino acids of the Na+/H+ exchanger that are important for proton translocation. Mol Cell Biochem 254, 117–124 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027311916247
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027311916247