Abstract
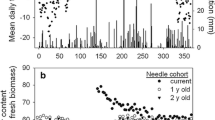
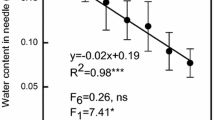
Six-year-old Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) seedlings were grown in open top chambers (OTCs) at ambient (AC) or elevated (ambient + 400 µmol mol−1; EC) CO2 concentration for three years (1996–1998). Chlorophyll (Chl) a fluorescence of current and one-year-old needles was measured in the field at two-weekly intervals in the period July–October 1998. In addition, Chl, carbon (C), and nitrogen (N) concentrations in both needle age classes were determined monthly during the same period. Chl fluorescence parameters were not significantly affected by EC, suggesting there was no response of the light reactions and the photochemical efficiency of photosystem 2. Chl concentrations were not significantly different but a reduced N concentration was observed in needles of EC treatment. Significant differences between needle age classes were observed for all parameters, but were most apparent under EC and toward the end of the growing season, possibly due to an acclimation process. As a result, significant interactions between CO2 treatment, needle age class, and season were found. This study emphasizes the importance of repeated measures including different leaf/needle age classes to assess the photosynthetic response of trees under EC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberte, R.S., McClure, P.R., Thornber, J.P.: Photosynthesis in trees. Organization of chlorophyll and photosynthetic unit size in isolated gymnosperm chloroplasts.-Plant Physiol. 58: 341-344, 1976.
Besford, R.T., Mousseau, M., Matteucci, G.: Biochemistry, physiology and biophysics of photosynthesis.-In: Jarvis, P.G. (ed.): European Forests and Global Change: The Likely Impacts of Rising CO2 and Temperature. Pp. 29-78. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1998.
Björkman, O., Demmig, B.: Photon yield of O2 evolution and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics at 77 K among vascular plants of divers origins.-Planta 170: 489-504, 1987.
Bolhàr-Nordenkampf, H.R., Öquist, G.: Chlorophyll fluorescence as a tool in photosynthesis research.-In: Hall, D.O., Scurlock, J.M.O., Bolhàr-Nordenkampf, H.R., Leegood, R.C., Long, S.P. (ed.): Photosynthesis and Production in a Changing Environment: A Field and Laboratory Manual. Pp. 193-206. Chapman &; Hall, London-Glasgow-New York-Tokyo-Melbourne-Madras 1993.
Bowes, G.: Photosynthetic responses to changing atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration.-In: Baker, N.R. (ed.): Photosynthesis and the Environment. Pp. 387-407. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht-Boston-London 1996.
Butler, W.L.: Energy distribution in the photosynthetical apparatus of photosynthesis.-Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 29: 345-378, 1978.
Ceulemans, R.: Direct impacts of CO2 and temperature on physiological processes in trees.-In: Mohren, G.M.J., Kramer, K., Sabaté, S. (ed.): Impacts of Global Change on Tree Physiology and Forest Ecosystems. Pp. 3-14. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht-Boston-London 1997.
Conroy, J.P., Smillie, R.M., Küppers, M., Bevege, D.I., Barlow, E.W.: Chlorophyll a fluorescence and photosynthetic and growth responses of Pinus radiata to phosphorus deficiency, drought stress, and high CO2.-Plant Physiol. 81: 423-429, 1986.
Cotrufo, M.F., Ineson, P., Scott, A.: Elevated CO2 reduces the nitrogen concentration of plant tissues.-Global Change Biol. 4: 43-54, 1998.
Csintalan, Z., Tuba, Z., Nagy, Z., Lichtenthaler, H.K., Grace, J.: Reconstitution of photosynthesis upon rehydratation in the desiccated leaves of the poikilochlorophyllous shrub Xerophyta scabrida at elevated CO2.-J. Plant Physiol. 148: 345-350, 1996.
Epron, D., Liozon, R., Mousseau, M.: Effects of elevated CO2 concentration on leaf characteristics and photosynthetic capacity of beech (Fagus sylvatica) during the growing season.-Tree Physiol. 16: 425-432, 1996.
Genty, B., Briantais, J.-M., Baker, N.R.: The relationship between the quantum yield of photosynthetic electron transport and quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence.-Biochim. biophys. Acta 990: 87-92, 1989.
Harbinson, J., Genty, B., Baker, N.R.: The relationship between CO2 assimilation and electron transport in leaves.-Photosynth. Res. 25: 213-224, 1990.
Hogan, K.P., Fleck, I., Bungard, R., Cheeseman, J.M., Whitehead, D.: Effect of elevated CO2 on the utilization of light energy in Nothofagus fusca and Pinus radiata.-J. exp. Bot. 48: 1289-1297, 1997.
Jach, M.E., Ceulemans, R.: Effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on phenology, growth and crown structure of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) seedlings after two years of exposure in the field.-Tree Physiol. 19: 289-300, 1999.
Jach, M.E., Ceulemans, R.: Effects of season, needle age and elevated atmospheric CO2 on photosynthesis in Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.).-Tree Physiol. 20: 145-157, 2000.
Janssens, I.A., Mousseau, M., Ceulemans, R.: Crop ecosystem responses to climatic change: tree crops.-In: Reddy, K.R., Hodges, H.F. (ed.): Climate Change and Global Crop Productivity. Pp. 245-270. CAB International, Wallingford 2000.
Kalina, J., Ceulemans, R.: Clonal differences in the response of dark and light reactions of photosynthesis to elevated atmospheric CO2 in poplar.-Photosynthetica 33: 51-61, 1997.
Kalina, J., Èajánek, M., Špunda, V., Marek, M.V.: Changes of the primary photosynthetic reactions of Norway Spruce under elevated CO2.-In: Mohren, G.M.J., Kramer, K., Sabaté, S. (ed.): Impacts of Global Change on Tree Physiology and Forest Ecosystems. Pp. 59-66. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht-Boston-London 1997.
Kellomäki, S., Wang, K.-Y.: Effects of elevated O3 and CO2 on chlorophyll fluorescence and gas exchange in Scots pine during the third growing season.-Environ. Pollut. 97: 17-27, 1997.
Krause, G.H., Weis, E.: Chlorophyll fluorescence as a tool in plant physiology II. Interpretation of fluorescence signals.-Photosynth. Res. 5: 139-157, 1984.
Lewandowska, M., Jarvis, P.G.: Quantum requirements of photosynthetic electron transport in Sitka spruce from different light environments.-Physiol. Plant. 42: 277-282, 1978.
Lewis, J.D., Tissue, D.T., Strain, B.R.: Seasonal response of photosynthesis to elevated CO2 in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) over two growing seasons.-Global Change Biol. 2: 103-114, 1996.
Littell, R.C., Milliken, G.A., Stroup, W.W., Wolfinger, R.D.: SAS System for Mixed Models.-SAS Institute, Cary 1996.
Long, S.P.: Modification of the response of photosynthetic productivity to rising temperature by atmospheric CO2 concentrations: has its importance been underestimated?-Plant Cell Environ. 14: 729-739, 1991.
Marek, M.V., Kalina, J.: Comparison of two experimental approaches used in the investigations of the long-term effects of elevated CO2 concentration.-Photosynthetica 32: 129-133, 1996.
Marek, M.V., Šprtová, M., Kalina, J.: The photosynthetic irradiance-response of Norway spruce exposed to a long-term elevation of CO2 concentration.-Photosynthetica 33: 259-268, 1997.
Norby, R.J., Wullschleger, S.D., Gunderson, C.A., Johnson, D.W., Ceulemans, R.: Tree responses to rising CO2 in field experiments: implications for the future forest.-Plant Cell Environ. 22: 683-714, 1999.
Owens, T.G.: In vivo chlorophyll fluorescence as a probe of photosynthetic physiology.-In: Alscher, R.G., Wellburn, A.R. (ed.): Plant Responses to the Gaseous Environment. Molecular, Metabolic and Physiological Aspects. Pp. 195-217. Chapman &; Hall, London 1994.
Palanisamy, K.: Interactions of elevated CO2 concentration and drought stress on photosynthesis in Eucalyptus cladocalyx F. Muell.-Photosynthetica 36: 635-638, 1999.
Porra, R.J., Thompson, W.A., Kriedemann, P.E.: Determination of accurate extinction coefficients and simultaneous equations for assaying chlorophylls a and b extracted with four different solvents: verification of the concentration of chlorophyll standards by atomic absorption spectroscopy.-Biochim. biophys. Acta 975: 384-394, 1989.
Rey, A., Jarvis, P.G.: Long-term photosynthetic acclimation to increased atmospheric CO2 concentration in young birch (Betula pendula) trees.-Tree Physiol. 18: 441-450, 1998.
Saxe, H., Ellsworth, D.S., Heath, J.: Tree and forest functioning in an enriched CO2 atmosphere.-New Phytol. 139: 395-436, 1998.
Schreiber, U., Bilger, W., Neubauer, C.: Chlorophyll fluorescence as a nonintrusive indicator for rapid assessment of in vivo photosynthesis.-In: Schulze, E.-D., Caldwell, M.M. (ed.): Ecophysiology of Photosynthesis. Pp. 49-70. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York 1994.
Seaton, G.G.R., Walker, D.A.: Chlorophyll fluorescence as a measure of photosynthetic carbon assimilation.-Proc. roy. Soc. London B 242: 29-35, 1990.
Šesták, Z. (ed.): Photosynthesis During Leaf Development.-Academia, Praha; Dr W. Junk Publishers, Dordrecht-Boston-Lancaster 1985.
Tausz, M., De Kok, L.J., Stulen, I., Grill, D.: Physiological responses of Norway spruce trees to elevated CO2 and SO2.-J. Plant Physiol. 148: 362-367, 1996.
Tissue, D.T., Griffin, K.L., Ball, J.T.: Photosynthetic adjustment in field-grown ponderosa pine trees after six years of exposure to elevated CO2.-Tree Physiol. 19: 221-228, 1999.
Tissue, D.T., Thomas, R.B., Strain, B.R.: Growth and photosynthesis of loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) after exposure to elevated CO2 for 19 months in the field.-Tree Physiol. 16: 49-59, 1996.
Tissue, D.T., Thomas, R.B., Strain, B.R.: Atmospheric CO2 enrichment increases growth and photosynthesis of Pinus taeda: a 4 year experiment in the field.-Plant Cell Environ. 20: 1123-1134, 1997.
Turnbull, M.H., Tissue, D.T., Griffin, K.L., Rogers, G.N.D., Whitehead, D.: Photosynthetic acclimation to long-term exposure to elevated CO2 concentration in Pinus radiata D. Don. is related to age of needles.-Plant Cell Environ. 21: 1019-1028, 1998.
Urban, O., Marek, M.V.: Seasonal changes of selected parameters of CO2 fixation biochemistry of Norway spruce under the long-term impact of elevated CO2.-Photosynthetica 36: 533-545, 1999.
Wang, K.-Y., Kellomäki, S.: Effects of elevated CO2 and soil-nitrogen supply on chlorophyll fluorescence and gas exchange in Scots pine, based on a branch-in-bag experiment.-New Phytol. 136: 277-286, 1997.
Wang, K.-Y., Kellomäki, S., Laitinen, K.: Effects of needle age, long-term temperature and CO2 treatments on the photosynthesis of Scots pine.-Tree Physiol. 15: 211-218, 1995.
Woodrow, I.E., Berry, J.A.: Enzymatic regulation of photosynthetic CO2 fixation in C3 plants.-Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant mol. Biol. 39: 533-594, 1988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gielen, B., Jach, M. & Ceulemans, R. Effects of Season, Needle Age, and Elevated Atmospheric CO2 on Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters and Needle Nitrogen Concentration in Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris). Photosynthetica 38, 13–21 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026727404895
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026727404895