Abstract
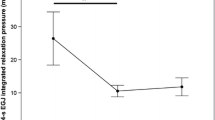
This study tests the hypothesis that eitherselective or combined destruction of the loweresophageal sphincter and the diaphragmatic crural slingshould induce reflux in the rat. Pull-through perfusion manometry was performed before and after loweresophageal myectomy, crural myotomy, or both. pHmonitoring was used to detect reflux. Unmanipulated ratsserved as controls. Paired t tests were used for comparison of pre- and postoperative pressurevalues and contingency tables with Fisher's tests forexamining the association between the interventions andthe appearance of reflux. Esophageal myectomy decreased only sphincteric pressure from 25.9± 15.5 to 9 ± 6 mm Hg (P < 0.01),whereas crural myotomy decreased only sling pressurefrom 26.2 ± 13.3 to 7.3 ± 3.9 mm Hg (P< 0.01). Simultaneous performance of both procedures decreasedsphincteric and crural pressures from 20.4 ± 7.5to 7.6 ± 4.3 mm Hg (P < 0.01) and from 45.9± 20.6 to 18.2 ± 7.4 mm Hg (P < 0.01),respectively. None of the control, myectomy, or myotomy animalsshowed reflux upon pH-metry but 5/8 rats in which bothprocedures were performed had prolonged acid exposure.No esophagitis was seen. In conclusion, normal rats do not have reflux. Selective destructionof either the sphincter or the crural sling does notinduce reflux, despite causing flattening of theirrespective manometric profiles. Conversely, combined inactivation of both components issignificantly associated with reflux.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Mittal RK, Balaban DH: The esophagogastric junction. N Engl J Med 336:924-932, 1997
Soto C, Qi B, Diez-Pardo JA, Tovar JA: Identification of the diaphragmatic crural component of the gastro-esophageal barrier in the rat. Dig Dis Sci 42:2420-2425, 1997
Montedonico S, Godoy J, Mate A, Possoegel A, Diez-Pardo JA, Tovar JA: Muscular architecture and manometric image of the gastroesophageal barrier in the rat. Dig Dis Sci (submitted)
Wang WL, Tovar JA, Eizaguirre I, Aldazabal P: Airway obstruction and gastroesophageal reflux. An experimental study of the pathogenesis of this association. J Pediatr Surg 28:995-998, 1993
Qi B, Soto C, Diez-Pardo JA, Tovar JA: An experimental study on the pathogenesis of gastroesophageal reflux after repair of diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 32:1310-1313, 1997
Ismael-Beigi F, Horton PF, Pope CE: Histological consequences of gastroesophageal reflux in man. Gastroenterology 58:163-174, 1970
Fyke FE, Code CF, Schlegel JF: The gastroesophageal sphincter in healthy human beings. Gastroenterologia (Basel) 86:135-150, 1956
Liebermann-Meffert D, Allgwer M, Schmid P, Blum AL: Muscular equivalent of the lower esophageal sphincter. Gastroenterology 76:31-38, 1979
Stein H, Liebermann-Meffert D, DeMeester T, Siewert JR: Three-dimensional pressure image and muscular structure of the human lower esophageal sphincter. Surgery 117:692-698, 1995
Boyle JT, Altschuler SM, Nixon TE, Tuchman DN, Pack AI, Cohen S: Role of the diaphragm in the genesis of lower esophageal sphincter pressure in the cat. Gastroenterology 88:723-730, 1985
Klein WA, Parkman HP, Dempsey DT, Fisher RS: Sphincterlike thoracoabdominal high pressure zone after esophagogastrectomy. Gastroenterology 105:1362-1369, 1993
Peck N, Callander N, Watson A: Manometric assessment of the effect of the diaphragmatic crural sling in gastrooesophageal reflux: Implications for surgical management. Br J Surg 82:798-801, 1995
Mittal RK: The crural diaphragm, an external lower esophageal sphincter: A definitive study (editorial). Gastroenterology 105:1565-1577, 1993
Schopf BW, Blair G, Dong S, Troger K: A porcine model of gastroesophageal reflux. J Invest Surg 10:105-114, 1997
Mittal RK, Holloway RH, Penagini R, Blackshaw LA, Dent J: Transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation. Gastroenterology 109:601-610, 1995
Mittal RK, Sivri B, Schirmer B, Heine K: Effect of crural myotomy on the incidence and mechanism of gastroesophageal reflux in cats. Gastroenterology 105:740-747, 1993
Martin CJ, Dodds WJ, Liem HH, Dantas RO, Layman RD, Dent J: Diaphragmatic contribution to gastroesophageal competence and reflux in dogs. Am J Physiol 263:G551-G557, 1992
Mittal RK, Chiarelli C, Liu J, Shaker R: Characteristics of lower esophageal sphincter relaxation induced by pharyngeal stimulation with minute amounts of water. Gastroenterology 111:378-384, 1996
Mittal RK, Holloway R, Dent J: Effect of atropine on the frequency of reflux and transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation in normal subjects. Gastroenterology 109:1547-1554, 1995
Levrat M, Lambert R, Kirshbaum G: Esophagitis produced by reflux of duodenal contents in rats. Am J Dig Dis 7:564-573, 1962
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montedonico, S., Diez-Pardo, J.A. & Tovar, J.A. Gastroesophageal Reflux After Combined Lower Esophageal Sphincter and Diaphragmatic Crural Sling Inactivation in the Rat. Dig Dis Sci 44, 2283–2289 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026665022685
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026665022685