Abstract
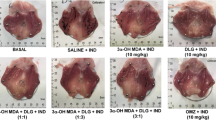
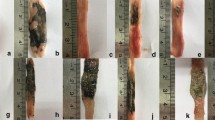
The effect of the nonsteroidal antiinflammatorydrug (NSAID) amtolmetin guacyl (AMG) on the gastricmucosa was studied in the rat by means of histologicaland functional techniques. AMG administered at 50-300 mg/kg intragastrically was virtuallydevoid of gastrolesive properties after either acute orrepeated treatment. By contrast, its metabolite,tolmetin (TOL, 15-60 mg/kg, intragastrically) caused dose-dependent gastric damage after bothtreatments. Light and electron microscopy revealed thatAMG induced minimal changes in the surface epitheliumlayer, without signs of vasocongestion or leukocytes adherence. AMG (50 mg/kg intragastrically) didnot change basal gastric potential difference (PD),whereas acetylsalicylic acid and ibuprofen induced fallsin PD of 22 and 27 mV, respectively. AMG (50 mg/kg intragastrically) reduced by 60% the fall in PDinduced by 50% ethanol; this inhibition was dependent onthe incubation time, and was maximal when AMG was given4 hr before ethanol. AMG (100 mg/kg intragastrically) induced an increase in NO synthase type 2(NOS2) activity, which was significantly different fromcontrol values, when AMG was administered 4 hr beforethe test. The metabolites of AMG, tolmetin, MED 5, and guaiacol were ineffective. Pharmacokineticanalysis of the residence time of AMG in the differentareas of the gastrointestinal tract, revealed that AMGremains in the gastrointestinal tract at least for 4 hr, the time necessary for a maximalinduction of NOS2 and for maximal protection againstethanol-induced damage. In conclusion, these dataindicate that the nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugamtolmetin guacyl is devoid of gastrolesive properties;this gastrosparing effect seems to involve theproduction of nitric oxide, which can counteract thedamaging effects due to prostaglandin inhibition. Thepresence in the stomach of the native molecule ofamtolmetin guacyl seems to be necessary for theprotective effect observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Vane JR: Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nature New Biol 231:232-235, 1971
Fromm D, Kolis M: Effects of sodium salicylate and ace tylsalicylic acid on intramural pH and ulceration of rabbit antral mucosa. Surgery 91:438-447, 1982
Szabo S, Phihan G, Trier JS: Alterations in blood vessels during gastric injury and protection. Scand J Gastroenterol 21( suppl 125):92-96, 1986
Wallace JL, Keenan CM, Granger DN: Gastric ulceration induced by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is a neutrophil-dependent process. Am J Physiol 259:G462-G467, 1990
Wallace JL: Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drug gastropathy and cytoprotection: Pathogenesis and mechanisms re-examined. Scand J Gastroenterol 27( suppl 192):3-8, 1992
Wallace JL, Reuter B, Cicala C, McKnight W, Grisham MB, Cirino G: Novel nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug derivatives with markedly reduced ulcerogenic properties in the rat. Gastroenterology 107:173-179, 1994
Wallace JL, Reuter BK, Cirino G: Nitric oxide-releasing nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: A novel approach for reducing gastrointestinal toxicity. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1:40-44, 1994
Shield MJ: Diclofenac/misoprostol: Novel findings and their clinical potential. J Rheumatol 25( suppl 51):31-41, 1998
Donnelly MT, Hawkey CJ: Review article: COX-II inhibitors—a new generation of safer NSAIDs? Aliment Pharmacol Ther 11:227-236, 1997
Wallace JL, Chin BC: New generation NSAIDs: The benefit without the risk? Drugs of today 33:371-378, 1997
Wallace JL, Chin BC: Inflammatory mediators in gastrointestinal defense and injury. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 214:192-203, 1997
Holzer P: Neural emergency system in the stomach. Gastroenterology 114:823-839, 1998
Arrigoni-Martelli E: Profile of activity of a new anti-inflammatory agent, ST 679 (MED 15). Drugs Exp Clin Res 16:63-66, 1990
Caruso A, Cutuli VM, De Bernardis E, Attaguile G, Amico-Roxas M: Pharmacological properties and toxicology of MED-15, a prodrug of tolmetin. Drugs Exp Clin Res 18:481-485, 1992
Tubaro E, Belogi L, Mezzadri CM, Ruco L, Stopacciaro A: Studies on the gastric tolerability of the new non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug amtolmetin guacyl. Arzneimittelforschung 45:1298-1302, 1995
Tavella A, Ursini G: A clinical study on the anti-inflammatory activity and gastrointestinal tolerability of amtolmetin guacyl, a new NSAID, compared with diclofenac in aged patients with osteoarticular diseases. Clin Ther 148:543-548, 1997
Silen W: Gastric mucosal defense and repair. In Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract, Vol 1, 2nd ed. LR Johnson (ed). New York, Raven Press, 1987, pp 1055-1069
Kronche KD, Fehsel K, Kolb-Bachofen V: Inducible nitric oxide synthase and its product nitric oxide, a small molecule with complex biological activities. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler 376:327-343, 1995
Alican I, Kubes P: A critical role for nitric oxide in intestinal barrier function and dysfunction. Am J Physiol 270:225-237, 1996
Moncada S, Higgs EA: Endogenous nitric oxide: Physiology, pathology and clinical relevance. Eur J Clin Invest 21:361-374, 1991
Guo FH, De Raeve HR, Rice TW, Stuehr DJ, Thunnissen FB, Erzurum SC: Continuous nitric oxide synthesis by inducible nitric oxide synthase in normal human airway epithelium in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:7809-7813, 1995
Hoffman RA, Zhang G, Nussler NC, Gleixner SL, Ford HR, Simmons RL, Watkins SC: Constitutive expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in the mouse ileal mucosa. Am J Physiol 272:383-392, 1997
Tepperman BL, Soper BD: Nitric oxide synthase induction and cytoprotection of rat gastric mucosa from injury by ethanol. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 72:1308-1312, 1994
Scarpignato C, Corradi C, Gandolfi MA, Galmiche JP: A new technique for continuous measurement and recording of gastric potential difference in the rat: Evaluation of NSAIDinduced gastric mucosal damage. J Pharmacol Toxicol Meth 34:63-72, 1995
Brown JF, Tepperman BL, Hanson PJ, Whittle BJR, Moncada S: Differential distribution of nitric oxide synthase between cell fractions isolated from the rat gastric mucosa. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 184:680-685, 1992
Mancinelli A, Bruno G, Cardace G, Morabito E, Marzo A, Arrigoni Martelli E: High-performance liquid chromatographic evaluation of MED15 and its metabolites MED 5 and tolmetin in rat plasma. J Chromatogr 553:81-86, 1991
Tarnawski A, Stachura J, Gergely H, Hollander D: Gastric microvascular endothelium: A major target for aspirin-induced injury and arachidonic acid protection. An ultrastructural analysis in the rat. Eur J Clin Invest 20:432-440, 1990
Murray HS, Strottman MP, Cooke AR: Effect of several drugs on gastric potential difference in man. Br Med J 1:19-21, 1974
Davenport HW: Salicylate damage to the gastric mucosal barrier. N Engl J Med 276:1307-1312, 1976
Whittle BJR, Lopez-Belmonte J, Moncada S: Regulation of gastric mucosal integrity by endogenous nitric oxide: Interactions with prostanoids and sensory neuropeptides in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 99:607-611, 1990
May GR, Crook P, Moore PK, Page CP: The role of nitric oxide as an endogenous regulator of platelet and neutrophil activation within the pulmonary circulation of the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol 102:759-763, 1991
Kubes P, Suzuki M, Granger DN: Nitric oxide: an endogenous modulator of leukocyte adhesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:4651-4655, 1991
Kato S, Kitamura M, Korolkiewicz RP, Takeuchi K: Role of nitric oxide in regulation of gastric acid secretion in rats: Effects of NO donors and NO synthase inhibitor. Br J Pharmacol 123:839-846, 1998
Rubanyi GM, Ho EH, Cantor EH, Lumma WC, Botelho LH: Cytoprotective function of nitric oxide: Inactivation of superoxide radicals produced by human leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 181:1392-1397, 1991
Vaananen PM, Keenan CM, Grisham MB, Wallace JL: A pharmacological investigation of the role of leukotrienes in the pathogenesis of experimental NSAID-gastropathy. Inflammation 16:227-240, 1992
MacNaughton WK, Cirino G, Wallace JL: Endotheliumderived relaxing factor (nitric oxide) has protective actions in the stomach. Life Sci 45:1869-1876, 1989
Lopez-Belmonte J, Whittle BJ, Moncada S: The actions of nitric oxide donors in the prevention or induction of injury to the rat gastric mucosa. Br J Pharmacol 108:73-78, 1993
Barrachina D, Calatayud S, Moreno L, Martinez-Cuesta A, Whittle BJ, Esplugues JV: Nitric oxide and sensory afferent neurones modulate the protective effects of low-dose endotoxin on rat gastric mucosal damage. Eur J Pharmacol 280:339-342, 1995
Mitchell JA, Larkin S, Williams TJ: Cyclooxyge nase-2: regulation and relevance in inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol 50:1535-1542, 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pisano, C., Grandi, D., Morini, G. et al. Gastrosparing Effect of New Antiinflammatory Drug Amtolmetin Guacyl in the Rat (Involvement of Nitric Oxide). Dig Dis Sci 44, 713–724 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026653623516
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026653623516