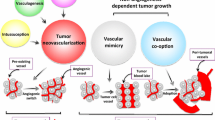
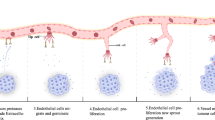
Abstract
Anti-angiogenic gene therapy may be rational approach in the treatment of solid tumors. The current state of gene therapy with regard to the abrogation of tumor vasculature is reviewed in this article and the different administration vehicles are noted. Furthermore, this article discusses the influence of vascular support cells in the tumor vasculature and choice of pre-clinical model for anti-angiogenic cancer gene therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman J: What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst 82: 4-6, 1990
Holash J, Maisonpierre PC, Compton D, Boland P, Alexander CR, Zagzag D, Yancopoulos GD, Wiegand SJ: Vessel cooption, regression, and growth in tumors mediated by angiopoietins and VEGF. Science 284: 1994-1998, 1999
Gee MS, Koch CJ, Evans SM, Jenkins WT, Pletcher CH, Moore JS, Koblish HK, Lee J, Lord EM, Trinchieri G, Lee WM: Hypoxia-mediated apoptosis from angiogenesis inhibition underlies tumor control by recombinant interleukin12. Cancer Res 59: 4882-4889, 1999
Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D, Keshet E: Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxiainitiated angiogenesis. Nature 359: 843-845, 1992
Luzzi KJ, MacDonald IC, Schmidt EE, Kerkvliet N, Morris VL, Chambers AF, Groom AC: Multistep nature of metastatic inefficiency: dormancy of solitary cells after successful extravasation and limited survival of early micrometastases. Am J Pathol 153: 865-873, 1998
Hendrix MJ, Seftor EA, Seftor RE, Kirschmann DA, Gardner LM, Boldt HC, Meyer M, Pe'er J, Folberg R: Regulation of uveal melanoma interconverted phenotype by hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF/SF). Am J Pathol 152: 855-863, 1998
Ruoslahti E, Rajotte D: An address system in the vasculature of normal tissues and tumors. Annu Rev Immunol 18: 813-827, 2000
Wickham TJ, Carrion ME, Kovesdi I: Targeting of adenovirus penton base to new receptors through replacement of its RGD motif with other receptor-specific peptide motifs. Gene Ther 2: 750-756, 1995
McDonald GA, Zhu G, Li Y, Kovesdi I, Wickham TJ, Sukhatme VP: Efficient adenoviral gene transfer to kidney cortical vasculature utilizing a fiber modified vector. J Gene Med 1: 103-110, 1999
Gross J, Azizkhan RG, Biswas C, Bruns RR, Hsieh DS, Folkman J: Inhibition of tumor growth, vascularization, and collagenolysis in the rabbit cornea by medroxyprogesterone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78: 1176-1180, 1981
O'Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Lane WS, Flynn E, Birkhead JR, Olsen BR, Folkman J: Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell 88: 277-285, 1997
O'Reilly MS, Holmgren L, Shing Y, Chen C, Rosenthal RA, Moses M, Lane WS, Cao Y, Sage EH, Folkman J: Angiostatin: a novel angiogenesis inhibitor that mediates the suppression of metastases by a Lewis lung carcinoma [see comments]. Cell 79: 315-328, 1994
O'Reilly MS, Holmgren L, Chen C, Folkman J: Angiostatin induces and sustains dormancy of human primary tumors in mice. Nat Med 2: 689-692, 1996
Boehm T, Folkman J, Browder T, O'Reilly MS: antiangiogenic therapy of experimental cancer does not induce acquired drug resistance [see comments]. Nature 390: 404-407, 1997
Griscelli F, Li H, Bennaceur-Griscelli A, Soria J, Opolon P, Soria C, Perricaudet M, Yeh P, Lu H: Angiostatin gene transfer: inhibition of tumor growth in vivo by blockage of endothelial cell proliferation associated with a mitosis arrest. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 6367-6372, 1998
Klohs WD, Hamby JM: antiangiogenic agents. Curr Opin Biotechnol 10: 544-559, 1999
Cao Y, Ji RW, Davidson D, Schaller J, Marti D, Sohndel S, McCance SG, O'Reilly MS, Llinas M, Folkman J: Kringle domains of human angiostatin. Characterization of the antiproliferative activity on endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 271: 29 461-29 467, 1996
Cao Y, Chen A, An SSA, Ji RW, Davidson D, Llinas M: Kringle 5 of plasminogen is a novel inhibitor of endothelial cell growth. J Biol Chem 272: 22 924-22 928, 1997
Ji WR, Castellino FJ, Chang Y, Deford ME, Gray H, Villarreal X, Kondri ME, Marti DN, Llinas M, Schaller J, Kramer RA, Trail PA: Characterization of kringle domains of angiostatin as antagonists of endothelial cell migration, an important process in angiogenesis. Faseb J 12: 1731-1738, 1998
Lee TH, RhimT, Kim SS: Prothrombin kringle-2 domain has a growth inhibitory activity against basic fibroblast growth factor-stimulated capillary endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 273: 28 805-28 812, 1998
Parr C, Hiscox S, Nakamura T, Matsumoto K, Jiang WG: Nk4, a newHGF/SF variant, is an antagonist to the influence of HGF/SF on the motility and invasion of colon cancer cells. Int J Cancer 85: 563-570, 2000
O'Reilly MS, Pirie-Shepherd S, Lane WS, Folkman J: antiangiogenic activity of the cleaved conformation of the serpin antithrombin. Science 285: 1926-1928, 1999
Li H, Lu H, Griscelli F, Opolon P, Sun LQ, Ragot T, Legrand Y, Belin D, Soria J, Soria C, Perricaudet M, Yeh P: Adenovirus-mediated delivery of a uPA/uPAR antagonist suppresses angiogenesis-dependent tumor growth and dissemination in mice. Gene Ther 5: 1105-1113, 1998
Kamphaus GD, Colorado PC, Panka A, Maeshima Y, Mier JW, Sukhatme VP, Kalluri R: Canstatin, a novel matrix-derived inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. J Biol Chem 275: 1209-1215, 2000
Ingber D, Fujita T, Kishimoto S, Sudo K, Kanamaru T, Brem H, Folkman J: Synthetic analogues of fumagillin that inhibit angiogenesis and suppress tumour growth. Nature 348: 555-557, 1990
Zetter BR: Angiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Annu Rev Med 49: 407-424, 1998
Darland DC, D'Amore PA: Blood vessel maturation: vascular development comes of age [comment]. J Clin Invest 103: 157-158, 1999
Hirschi KK, Rohovsky SA, Beck LH, Smith SR, D'Amore PA: Endothelial cells modulate the proliferation of mural cell precursors via platelet-derived growth factor-BB and heterotypic cell contact. Circ Res 84: 298-305, 1999
Benjamin LE, Golijanin D, Itin A, Pode D, Keshet E: Selective ablation of immature blood vessels in established human tumors follows vascular endothelial growth factor withdrawal [see comments]. J Clin Invest 103: 159-165, 1999
Nguyen JT, Wu P, Clouse ME, Hlatky L, Terwilliger EF: Adeno-associated virus-mediated delivery of antiangiogenic factors as an antitumor strategy. Cancer Res 58: 5673-5677, 1998.
Buchschacher GL Jr, Wong-Staal F: Development of lentiviral vectors for gene therapy for human diseases. Blood 95: 2499-2504, 2000
Atkins GJ, Sheahan BJ, Liljestrom P: The molecular pathogenesis of Semliki Forest virus: a model virus made useful?. J Gen Virol 80: 2287-2297, 1999
Kouraklis G, Progress in cancer gene therapy. Acta Oncol 38: 675-683, 1999
Mir LM, Bureau MF, Rangara R, Schwartz B, Scherman D: Long-term, high level in vivo gene expression after electric pulse-mediated gene transfer into skeletal muscle. C R Acad Sci III 321: 893-899, 1998
Mir LM, Bureau MF, Gehl J, Rangara R, Rouy D, Caillaud JM, Delaere P, Branellec D, Schwartz B, Scherman D: High-efficiency gene transfer into skeletal muscle mediated by electric pulses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 4262-4267, 1999
Blezinger P, Wang J, Gondo M, Quezada A, Mehrens D, French M, Singhal A, Sullivan S, Rolland A, Ralston R, Min W: Systemic inhibition of tumor growth and tumor metastases by intramuscular administration of the endostatin gene. Nat Biotechnol 17: 343-348, 1999
Chen QR, Kumar D, Stass SA, Mixson AJ: Liposomes complexed to plasmids encoding angiostatin and endostatin inhibit breast cancer in nude mice. Cancer Res 59: 3308-3312, 1999
Sauter BV, Martinet O, Zhang WJ, Mandeli J, Woo SL: Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of endostatin in vivo results in high level of transgene expression and inhibition of tumor growth and metastases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 4802-4807, 2000
Feldman AL, Restifo NP, Alexander HR, Bartlett DL, Hwu P, Seth P, Libutti SK: anti-angiogenic gene therapy of cancer utilizing a recombinant adenovirus to elevate systemic endostatin levels in mice. Cancer Res 60: 1503-1506, 2000
MacDonald NJ, Murad AC, Fogler WE, Lu Y, Sim BK: The tumor-suppressing activity of angiostatin protein resides within kringles 1 to 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 264: 469-477, 1999
Lin P, Buxton JA, Acheson A, Radziejewski C, Maisonpierre PC, Yancopoulos GD, Channon KM, Hale LP, Dewhirst MW, George SE, Peters KG: anti-angiogenic gene therapy targeting the endothelium-specific receptor tyrosine kinase Tie2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 8829-8834, 1998
Lindahl P, Hellstrom M, Kalen M, Betsholtz C: Endothelialperivascular cell signaling in vascular development: lessons from knockout mice. Curr Opin Lipidol 9: 407-411, 1998
Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S, Bartunkova S, Maisonpierre PC, Davis S, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD: Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell 87: 1171-1180, 1996
Maisonpierre PC, Suri C, Jones PF, Bartunkova S, Wiegand SJ, Radziejewski C, Compton D, McClain J, Aldrich TH, Papadopoulos N, Daly TJ, Davis S, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD: Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie2 that disrupts in vivo angiogenesis. Science 277: 55-60, 1997
Boudreau N, Andrews C, Srebrow A, Ravanpay A, Cheresh DA: Induction of the angiogenic phenotype by Hox D3. J Cell Biol 139: 257-264, 1997
Li H, Griscelli F, Lindenmeyer F, Opolon P, Sun LQ, Connault E, Soria J, Soria C, Perricaudet M, Yeh P, Lu H: Systemic delivery of anti-angiogenic adenovirus AdmATF induces liver resistance to metastasis and prolongs survival of mice. Hum Gene Ther 10: 3045-3053, 1999
Tanaka T, Manome Y, Wen P, Kufe DW, Fine HA: Viral vector-mediated transduction of a modified platelet factor 4 cDNA inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth. Nat Med 3: 437-442, 1997
Tanaka T, Cao Y, Folkman J, Fine HA: Viral vector-targeted anti-angiogenic gene therapy utilizing an angiostatin complementary DNA. Cancer Res 58: 3362-3369, 1998
Gengrinovitch S, Greenberg SM, Cohen T, Gitay-Goren H, Rockwell P, Maione TE, Levi BZ, Neufeld G: Platelet factor-4 inhibits the mitogenic activity of VEGF121 and VEGF165 using several concurrent mechanisms. J Biol Chem 270: 15 059-15 065, 1995
Perollet C, Han ZC, Savona C, Caen JP, Bikfalvi A: Platelet factor 4 modulates fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2) activity and inhibits FGF-2 dimerization. Blood 91: 3289-3299, 1998
Asselin-Paturel C, Lassau N, Guinebretiere JM, Zhang J, Gay F, Bex F, Hallez S, Leclere J, Peronneau P, Mami-Chouaib F, Chouaib S: Transfer of the murine interleukin-12 gene in vivo by a Semliki Forest virus vector induces B16 tumor regression through inhibition of tumor blood vessel formation monitored by Doppler ultrasonography. Gene Ther 6: 606-615, 1999
Coughlin CM, Salhany KE, Gee MS, LaTemple DC, Kotenko S, Ma X, Gri G, Wysocka M, Kim JE, Liu L, Liao F, Farber JM, Pestka S, Trinchieri G, Lee WM: Tumor cell responses to IFNgamma affect tumorigenicity and response to IL-12 therapy and antiangiogenesis. Immunity 9: 25-34, 1998
Klement G, Baruchel S, Rak J, Man, S, Clark K, Hicklin DJ, Bohlen P, Kerbel RS: Continuous low-dose therapy with vinblastine and VEGF receptor-2 antibody induces sustained tumor regression without overt toxicity. J Clin Invest 105: 15-24, 2000
Browder T, Butterfield CE, Kraling BM, Shi B, Marshall B, O'Reilly MS, Folkman J: anti-angiogenic scheduling of chemotherapy improves efficacy against experimental drugresistant cancer. Cancer Res 60: 1878-1886, 2000
Griscelli F, Li H, Cheong C, Opolon P, Bennaceur-Griscelli A, Vassal G, Soria J, Soria C, Lu H, Perricaudet M, Yeh P: Combined effects of radiotherapy and angiostatin gene therapy in glioma tumor model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 6698-6703, 2000
Heise C, Kirn DH: Replication-selective adenoviruses as oncolytic agents, J Clin Invest 105: 847-851, 2000.
Bergers G, Javaherian K, Lo KM, Folkman J, Hanahan D: Effects of angiogenesis inhibitors on multistage carcinogenesis in mice. Science 284: 808-812, 1999.
Hahnfeldt P, Panigrahy D, Folkman J, Hlatky L: Tumor development under angiogenic signaling: a dynamical theory of tumor growth, treatment response, and postvascular dormancy. Cancer Res 59: 4770-4775, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nesbit, M. Abrogation Of Tumor Vasculature Using Gene Therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev 19, 45–49 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026588028780
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026588028780