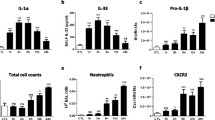
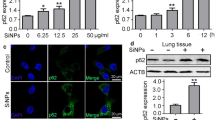
Abstract
Nitric oxide (NO), a reactive nitrogen species, plays an important role in inflammatory lung damage. In the present study, we investigated the role of NO in DNA-binding activity of NF-κB in macrophages stimulated with silica or other inflammatory stimulants. Treatment of mouse macrophages (RAW264.7 cells) with a selective inhibitor of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), L-N6-(1-iminoethyl) lysine (L-NIL), or a nonselective iNOS inhibitor, Nω-nitro-L-arginine methylester (L-NAME), resulted in inhibition of silica-induced nitric oxide production as well as silica-induced NF-κB activation. L-NIL also effectively inhibited NF-κB activation induced by other inflammatory stimulants, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or muramyl dipeptide (MDP). These inhibitory effects of L-NIL and L-NAME on silica- or LPS-induced NF-κB activation were also observed in primary rat alveolar macrophages. Furthermore, NO generating compounds, such as sodium nitroprusside (SNP) and 3-morpholinosydnonimine (SIN-1), caused a dose-dependent increase in NF-κB activation, which was positively correlated with the level of NO production. Specific inhibitors of protein tyrosine kinase, such as genistein and AG494, prevented NF-κB activation in SNP- or SIN-1 treated cells, suggesting involvement of tyrosine kinase in the NO signaling pathway leading to NF-κB activation. In contrast, inhibitors of protein kinase C or A, such as staurosporine or H89, had no inhibitory effect on SIN-1 induced NF-κB activation. Metalloporphyrins, such as tetrakis (N-methyl-4′-pyridyl) porphyrinato iron (III) (Fe-TMPyP) and Zn-TMPyP which are known to alter NO-dependent activity, markedly inhibited silica- and LPS-induced NF-κB activation. The results suggest that NF-κB activation in macrophages can be induced under certain conditions by nitric oxide and that nitric oxide produced by phagocytes exposed to inflammatory agents may up-regulate the activation of NF-κB.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Craighead JE, Kleinerman J, Abraham JL, Gibbs AR, Green FHY, Harley RA, Ruettner JR, Vallyathan V, Juliano EB: Diseases associated with exposure to silica and non-fibrous silicate minerals. Arch Pathol Lab Med 112: 673–720, 1988
Mcdonald JC: Silica and lung cancer. In: V. Castranova, V. Vallyathan, W. E. Wallace (eds). Silica and Silica-Induced Lung Diseases. CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1996, pp 383–396
Saffiotti U, Williams AO, Daniel LN, Kaighn MD, Mao Y, Shi X: Carcinogenesis by crystalline silica: Animal, cellular, and molecular studies. In: V. Castranova, V. Vallyathan, W.E. Wallace (eds). Silica and Silica-Induced Lung Diseases. CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1996, pp 345–381
Lapp NL, Castranova V: How silicosis and coal workers' pneumoconiosis develop: A cellular assessment. Occup Med: State of the Art Reviews 8: 35–56, 1993
Shi X, Castranova V, Halliwell B, Vallyathan V: Reactive oxygen species and silica-induced carcinogenesis. J Toxicol Environ Health Part B 1: 181–197, 1998
Chen F, Casranova V, Shi X, Demers LM: New insights into the role of nuclear factor-κB, a ubiquitous transcription factor in the initiation of diseases. Clin Chem 45: 7–17, 1999
Barnes PJ, Karin M: A pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. New Engl J Med 366: 1066–1071, 1997
Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D: IκB: A specific inhibitor of the NF-κB transcription factor. Science 242: 540–548, 1988
Chen F, Lu Y, Demers LM, Rojanasakul Y, Shi X, Vallyathan V, Castranova V: Role of hydroxyl radical in silica-induced NF-κB activation in macrophages. Ann Clin Lab Sci 28: 1–13, 1998
Kang JL, Go YH, Hur KC, Castranova V: Silica-induced nuclear factor-κB activation: Involvement of reactive oxygen species and protein tyrosine kinase activation. J Toxicol Environ Health: 2000 (in press)
Sacks M, Gordon J, Bylander J, Porter D, Shi XL, Castranova V, Kaczmarczyk W, Vandyke K, Reasor MJ: Silica-induced pulmonary inflammation in rats: activation of NF-kappa B and its suppression by dexamethasone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 253: 181–184, 1998
Castranova V, Antonini JM, Reasor MJ, Wu L, Vandyke K: Oxidant release from pulmonary phagocytes. In: V. Castranova, V. Vallyathan, W.E. Wallace (eds). Silica and Silica-Induced Lung Diseases. CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1996, pp 185–195
Shi X, Ding M, Dong Z, Chen F, Ye J, Wang S, Leonard SS, Castranova V, Vallyathan V: Antioxidant properties of aspirin: Characterization of the ability of aspirin to inhibit silica-induced lipid peroxidation, DNA damage, NF-κB activation and TNFα production. Mol Cell Biochem 199: 93–102, 1999
Blackford JA, Antonini JM, Castranova V, Dey RD: Intratracheal instillation of silica up-regulates inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression and increases nitric oxide production in alveolar macrophages and neutrophils. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 11: 426–431, 1994
Lee J: Inducible nitric oxide synthase mRNA expression and nitric oxide production in silica-induced acute inflammatory lung injury. Kor J Physiol Pharmacol 2: 233–239, 1998
Blackford JA, Jones W, Dey RD, Castranova V: Comparison of inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression and lung inflammation following intratracheal instillation of silica, coal, carbonyl iron, or titanium dioxide in rats. J Toxicol Environ Health 51: 203–218, 1997
Chen F, Kuhn DC, Sun SC, Gaydos LJ, Demers LM: Dependence and reversal of nitric oxide production on NF-κB in silica and lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 214: 839–846, 1995
Lander HM, Sehajpal PK, Levine DM, No vogrodsky A: Activation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells by nitric oxide-generating compounds. J Immunol 150: 1509–1516, 1993
Sweeney TD, Castranova V, Bowman L, Miles PR: Factors which affect superoxide anion release from rat alveolar macrophages. Exp Lung Res 2: 85–89, 1981
Castranova V, Jones T, Barger MW, Afshari A, Frazer DJ: Pulmonary responses of guinea pigs to consecutive exposures to cotton dust. In: R.R. Jacobs, P.J. Wakelyn, L.N. Domelsmith (eds). Proceedings of the 14th Cotton Dust Research Conference. National Cotton Council, Memphis, TN, 1990, pp 131–135
Sun SC, Elwood T, Beraud C, Greene WC: Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax activation of NF-κB/Rel involves phosphorylation and degradation of IκB and Rel A(p65)-mediated induction of the c-rel gene. Mol Cell Biol 14: 7377–7384, 1994
Huffman LJ, Judy DJ, Castranova V: Regulation of nitric oxide production by rat alveolar macrophages in response to silica exposure. J Toxicol Environ Health 53:101–118, 1998
Luo D, Vincent SR: Metalloporphyrins inhibit nitric oxide-dependent cGMP formation in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 267: 263–267, 1994
Ignarro L, Ballot B, Wood KS: Regulation of soluble guanylate cyclase activity by porphyrins and metalloporphyrins. J Biol Chem 259: 6201–6207, 1984
Misko TP, Highkin MK, Veenhunzen AW, Manning PT, Stern MK, Currie MG, Salremin D: Characterization of the cytoprotective action of peroxynitrite decomposition catalysts. J Biol Chem 273: 15646–15653, 1998
Umansky V, Hehner SP, Dumont A, Hofmann TG, Schirrmacher V, Droge W, Schmitz M.L: Co-stimulatory effect of nitric oxide on endothelial NF-kappa B implies a physiological self-amplifying mechanism. Eur J Immunol 28: 2276–2282, 1998
Schreck R, Baeuerle PA: A role for oxygen radicals as second messengers. Trends Cell Biol 1: 39–43, 1991
Lander HM, Sehajpal PK, Novogrodsky A: Nitric oxide signaling: A possible role for G proteins. J Immunol 151: 7182–7187, 1993
Lander HM, Ogiste JS, Pearce SFA, Levi R, Novogrodsky A: Nitric oxide-stimulated guanine nucleotide exchange on p21ras. J Biol Chem 270: 7017–7020, 1995
Chen F, Sun SC, Kuhn DC, Gaydos LJ, Demers LM: Essential role of NF-kappa B activation in silica-induced inflammatory mediator production in macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 214: 985–992, 1995
Raychaudhuri B, Dweik R, Connors MJ, Buhrow L, Malur A, Drazba J, Arroliga AC, Erzurum SC, Kavuru MS, Thomassen MJ: Nitric oxide blocks nuclear factor kappa B activation in alveolar macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 21: 311–316, 1999
Peng HB, Peter L, JK: Induction and stabilization of IκBa by nitric oxide mediates inhibition of NF-κB. J Biol Chem 270: 14214–14219, 1995
Matthews JR, Botting CH, Panico M, Morris HR, Hay RT: Inhibition of NF-κB DNA binding by nitric oxide. Nucl Acids Res 24: 2236–2242, 1996
Diaz-Cazorla M, Perez-sala D, Lamas S: Dual effect of nitric oxide donors on cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human mesangial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 10: 943–952, 1999
Castranova V, Huffman LJ, Judy DJ, Bylander JE, Lapp LN, Weber SL, Blackford JA, Dey RD: Enhancement of nitric oxide production by pulmonary cells following silica exposure. Environ Health Perspect 106(suppl 5): 1165–1169, 1998
Wang H, Joseph JA: Quantifying cellular oxidative stress by dichlorofluorescein assay using microplate reader. Free Rad Biol Med 27: 612–616, 1999
Kanazawa H, Hirata K, Yoshikawa J: Administration of SIN-1 induces guinea pig airway hyperresponsiveness through inactivation of airway neutral endopeptidase. Int Arch Aller Immun 120: 317–322, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, J.L., Lee, K. & Castranova, V. Nitric oxide up-regulates DNA-binding activity of nuclear factor-κB in macrophages stimulated with silica and inflammatory stimulants. Mol Cell Biochem 215, 1–9 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026581301366
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026581301366