Abstract
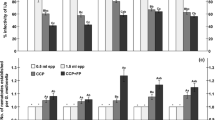
The infectivity, time to first emergence of infective juveniles (IJs), total number of IJs per insect and IJs body length of the entomopathogenic nematode Heterorhabditis megidis (strain NLH-E87.3) after development in larvae of two insect hosts, Galleria mellonella (greater wax moth) and Otiorhynchus sulcatus (vine weevil) was studied. At a dose of 30 IJs, larvae of G. mellonella show to be significantly more susceptible than O. sulcatus larvae. At a dose of one IJ, vine weevil larvae were more susceptible. The number of invading infective juveniles (IJs) increased with host size while the host mortality at a dose of one IJ decreased with the increase of host size. Time to first emergence was longer at a dose of one IJ per larva and increased with the increase of host size in both insect species. Reproduction of IJs differed between host species, host sizes and doses of nematodes. Generally, the IJs body size increased with an increasing host size. The longest infective juveniles were produced at the lowest IJ doses. Results are discussed in relation to the influence of different host species and their different sizes on the performance of H. megidis (strain NLH-E87.3) as a biological control agent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhurst, R.J. and N.E. Boemare, 1990. Biology and Taxonomy of Xenorhabdus. In: R. Gaugler and H.K. Kaya (eds), Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Biological Control. CRC Press, Boca Raton. pp. 75–87.
Barbercheck, M.E. and J. Wang, 1996. Effect of cucurbitacin D on in vitro growth of Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus spp., symbiotic bacteria of entomopathogenic nematodes. J.Invertebr.Pathol. 68: 141–145.
Barbercheck, M.E., J. Wang and I.S. Hirsh, 1995. Host plant effects on entomopathogenic nematodes. J.Invertebr.Pathol. 66: 169–177.
Boff, M.I.C., G.L. Wiegers and P.H. Smits, 2001. Host influences on the pathogenicity of Heterorhabditis megidis. BioControl (in press).
Boff, M.I.C., G.L. Wiegers, L.J.M. Gerritsen and P.H. Smits, 2000. Development of the entomopathogenic nematode Heterorhabditis megidis (strain NLH-E87.3) in Galleria mellonella. Nematology (in press).
Craig, S.M. and J.M. Webster, 1982. Influence of host nutrients on the parasitic development of Mermis nigrescens (Mermithidae). J.Nematol. 14: 398–405.
Dutky, S.R., J.V. Thompson and G.E. Cantwell, 1964. A technique for the mass propagation of the DD-136 nematode. J.Ins.Pathol. 6: 417–422.
Fuxa, J.R., A.R. Richter and F. Agudelo-Silva, 1988. Effect of host age and nematode strain on susceptibility of Spodoptera frugiperda to Steinernema feltiae. J.Nematol. 20: 91–95.
Geden, C.J., R.C. Axtell and W.M. Brooks, 1985. Susceptibility of the lesser mealworm, Alphitobius diaperinus (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) to the entomogenous nematodes Steinernema feltiae, S.glaseri (Steinernematidae) and Heterorhabditis heliothidis (Heterorhabditidae). J.Entomol.Sci. 20: 331–339.
Geden, C.J., R.C. Axtell and W.M. Brooks, 1986. Susceptibility of the house fly, Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae), to the entomogenous nematodes Steinernema feltiae, S.glaseri (Steinernematidae) and Heterorhabditis heliothidis (Heterorhabditidae). J.Med.Entomol. 23: 326–332.
Genstat Committee, 1997. Genstat 5 release 4.1 Reference Manual Supplement. Oxford.
Jansson, R.K., 1996. Infectivity and reproduction of three Heterorhabditis nematodes (Rhabditida: Heterorhabditidae) in two insect hosts. Florida Entomologist. 79: 363–373.
Kaya, H.K., 1985. Susceptibility of early larval stages of Pseudaletia unipuncta and Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to the entomogenous nematode Steinernema feltiae (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae). J.Invertebr.Pathol. 46: 58–62.
Kaya, H.K., 1990. Soil ecology. In: R. Gaugler and H.K. Kaya (eds), Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Biological Control. CRC Press, Boca Raton. pp. 93–111.
Kaya, H.K. and A.H. Hara, 1981. Susceptibility of various species of lepidopterous pupae to the entomogenous nematodes Neoaplectana carpocapsae. J.Nematol. 13: 291–294.
Lewis, E.E. and R. Gaugler, 1994. Entomopathogenic nematode (Rhabdita: Steinernematidae) sex ratio related to foraging strategy. J.Invertebr.Pathol. 64: 238–242.
Lewis, E.E., R. Gaugler and R. Harrinson, 1993. Response of cruiser and ambusher entomopathogenic nematodes (Steinernematidae) to host volatile cues. Can.J.Zool. 71: 765–769.
Mason, J.M. and W.M. Hominick, 1995. The effect of temperature on infection, development and reproduction of heterorhabditids. J.Helminthol. 69: 337–345.
Mauleon, H., S. Briand, C. Laumond and E. Bonifassi, 1993. Utilisation d'enzymes digestives pour l'étude du parasitisme des Steinernema et des Heterorhabditis envers les larves d'insectes. Fundam.Appl.Nematol. 16: 185–191.
Morgan, D.J.W. and J.D. Hare, 1997. Uncoupling physical and chemical cues: The independent roles of scale cover size and kairomone concentration on host selection by Aphytis melinus DeBach (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae). J.Insect Behav. 10: 679–694.
Murdoch, W.W., C.J. Briggs and R.M. Nisbet, 1997. Dynamical effects of host size and parasitoid state dependent attacks by parasitoids. J.Anim.Ecol. 66: 542–556.
O'Leary, S.A., C.M. Stack, M.A. Chubb and A.M. Burnell, 1998. The effect of day of emergence from the insect cadaver on the behaviour and environmental tolerances of infective juveniles of the entomopathogenic nematode Heterorhabditis megidis (strain UK211). J.Parasitol. 84: 665–672.
Schmidt, J. and J.N. All, 1978. Chemical attraction of Neoaplectana carpocapsae (Nematoda: Steinernematidae) to insect larvae. Environ.Entomol. 7: 605–607.
Selvan, S., J.F. Campbell and R. Gaugler, 1993. Density-dependent effects on entomopathogenic nematodes (Heterorhabditidae and Steinernematidae) within an insect host. J.Invertebr.Pathol. 62: 278–284.
Shapiro, D.I., J.R. Cate, J. Pena, A. Hunsberger and C.W. McCoy, 1999. Effects of temperature and host age on suppression of Diaprepes abbrevicatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) by entomopathogenic nematodes. J.Econ.Entomol. 92: 1086–1092.
Smits, P.H., J.T.M. Groenen and G. de Raay, 1991. Characterization of Heterorhabditis isolates using DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism. Revue Nematol. 14: 445–453.
Smits, P.H., G.L. Wiegers and H.J. Vlug, 1994. Selection of insect parasitic nematodes for biological control of the garden chafer, Phyllopertha horticola. Entomol.Exp.Appl. 70: 77–82.
Wang, J. and R.A. Bedding, 1996. Population development of Heterorhabditis bacteriophora and Steinernema carpocapsae in the larvae of Galleria mellonella. Fundam.Appl.Nematol. 19: 363–367.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boff, M., Wiegers, G. & Smits, P. Influences of host size and host species on theinfectivity and development of Heterorhabditismegidis (strain NLH-E87.3). BioControl 45, 469–482 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026560208285
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026560208285