Abstract
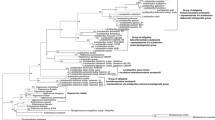
Partial gyrA sequences were determined for twelve strains belonging to Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, B. atrophaeus, B. licheniformis, B. mojavensis,B. subtilis subsp. subtilis, B. subtilissubsp. spizizenii and B. vallismortis. The average nucleotide and translated amino acid similarities for the seven type strains were 83.7 and 95.1%, respectively, whereas the corresponding value for the 16S rRNA sequences was 99.1%. All of the type strains were sharply separated; the closest relationship was found between B. atrophaeus and B. mojavensis which shared a nucleotide similarity of 95.8%. Phylogenetic trees were inferred from gyrA nucleotide sequences using the neighbor-joining, Fitch–Margoliash and maximum parsimony algorithms. The test strains were divided into four groups, which generally reflected results previously reported in restriction digest and DNA-DNA hybridization studies. It is concluded from the comparative sequence analysis that the gyrA sequences provide a firm framework for the rapid and accurate classification and identification of Bacillus subtilis and related taxa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ash C, Farrow JAE, Wallbanks S & Collins MD (1991) Phylogenetic heterogeneity of the genus Bacillus revealed by comparative analysis of small-subunit-ribosomal RNA sequences. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 13: 202–206
Chun J (1995) Computer-assisted classification and identification of actinomycetes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Newcastle, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK
Chun J & Goodfellow M (1995) A phylogenetic analysis of the genus Nocardia with 16S rRNA gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 45: 240–245
Claus D & Berkeley RCW (1986) Genus Bacillus. In: Sneath PHA, Mair NS, Sharpe ME & Holt JG (Eds) Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Vol 2 (pp 1105–1139). Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39: 783–791
Felsenstein J (1993) PHYLIP (phylogenetic inference package) version 3.5c. University of Washington, Seattle
Fitch WM (1972) Towards defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst. Zool. 20: 406–416
Fitch WM & Margoliash E (1967) Construction of phylogenetic trees. Science 155: 279–284
Fox GE, Wisotzkey JD & Jurtshuk PJ (1992) How close is close: 16S rRNA sequence identity may not be sufficient to guarantee species identity. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 42: 166–170
Fukumoto J (1943a) Studies on the production of bacterial amylase. I. Isolation of bacteria secreting potent amylase and their distribution. J. Agric. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 19: 487–503 (in Japanese)
Fukumoto J (1943b) Studies on the production of bacterial amylase. II. Bacterial and physiological nature. J. Agric. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 19: 643–650 (in Japanese)
Harwood CR (1992) Bacillus subtilis and its relatives: molecular biological and industrial workhorses. Trends Biotechnol. 10: 247–256
Jukes TH & Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro HN (Ed) Mammalian Protein Metabolism, Vol (pp 21–132). Academic Press, New York
Kasai H, Ezaki T & Harayama S (2000) Differentiation of phylogenetically related slowly growing mycobacteria by their gyrB sequences. J. Clin. Microbiol. 38: 301–308
Kim BJ, Lee SH, Lyu MA, Kim SJ, Bai GH, Chae GT, Kim EC, Cha CY & Kook YH (1999) Identification of mycobacterial species by comparative sequence analysis of the RNA polymerase gene (rpoB). J. Clin. Microbiol. 37: 1714–1720
Kunst F, Ogasawara N, Moszer I, Albertini AM, Alloni G, Azevedo V, Bertero MG, Bessieres P, Bolotin A, Borchert S, Borriss R, Boursier L, Brans A, Braun M, Brignell SC, Bron S, Brouillet S, Bruschi CV, Caldwell B, Capuano V, Carter NM, Choi SK, Codani JJ, Connerton IF, Danchin A et al. (1997) The complete genome sequence of the gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Nature 390: 249–256
Mollet C, Drancourt M & Raoult D (1997) rpoB sequence analysis as a novel basis for bacterial identification. Mol. Microbiol. 26: 1005–1011
Munakata N, Morohoshi F, Saitou M, Yamazaki N & Hayashi K (1994) Molecular characterization of thirteen gyrA mutations conferring nalidixic acid resistance in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Gen. Genet. 244: 97–103
Nakamura LK (1989) Taxonomic relationship of black-pigmented Bacillus subtilis strains and a proposal for Bacillus atrophaeus sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 39: 295–300
Nakamura LK, Roberts MS & Cohan FM (1999) Relationship of Bacillus subtilis clades associated with strains 168 and W23: a proposal for Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis subsp. nov. and Bacillus subtilis subsp. spizizenii subsp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49: 1211–1215
Priest FG, Goodfellow M, Shute LA & Berkeley RCW (1987) Bacillus amyloliquefaciens sp. nov., nom. rev. Int. J. Syst.Bacteriol. 37: 69–71
Roberts MS, Nakamura LK & Cohan FM (1994) Bacillus mojavensis sp. nov., distinguishable from Bacillus subtilis by sexual isolation, divergence in DNA sequence, and differences in fatty acid composition. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 44: 256–264
Roberts MS, Nakamura LK & Cohan FM (1996) Bacillus vallismortis sp. nov., a close relative of Bacillus subtilis, isolated from soil in Death Valley, California. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 46: 470–475
Saitou N & Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4: 406–425
Skerman VBD, McGowan V & Sneath PHA (1980) Approved Lists of Bacterial Names. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 30: 225–420
Swofford DL (1998) PAUP: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Massachusetts
Venkateswaran K, Moser DP, Dollhopf ME, Lies DP, Saffarini DA, MacGregor BJ, Ringelberg DB, White DC, Nishijima M, Sano H, Burghardt J, Stackebrandt E & Nealson KH (1999) Polyphasic taxonomy of the genus Shewanella and description of Shewanella oneidensis sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49: 705–724
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE, Stackebrandt E, Starr MP & Trüper HG (1987) Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 37: 463–464
Yamamoto S & Harayama S (1998) Phylogenetic relationships of Pseudomonas putida strains deduced from the nucleotide sequences of gyrB, rpoD and 16S rRNA genes. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 48: 813–819
Yamamoto S, Bouvet PJ & Harayama S (1999) Phylogenetic structures of the genus Acinetobacter based on gyrB sequences: comparison with the grouping by DNA-DNA hybridization. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49: 87–95
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chun, J., Bae, K.S. Phylogenetic analysis of Bacillus subtilis and related taxa based on partial gyrA gene sequences. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 78, 123–127 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026555830014
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026555830014