Abstract
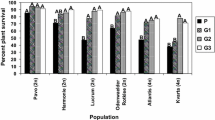
Resistance to bacterial soft rot caused by Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora is a quantitative trait. The narrow-sense heritability was from 42% to 60% in the studied populations. Griffing's diallel analysis and generation mean analysis indicated that additive genetic effects were most significant, and the resistant sources involved in this study appeared to have different genes or alleles. Recurrent phenotypic selection was used for improving the resistance level by combining different resistance genes from the selected genotypes of Chinese cabbage. After 3 cycles of recurrent selection, the level of resistance increased markedly. When the cycle 3 population was compared with the cycle 0 population, the mean disease severity rating was reduced 38% from 6.3 to 3.9, and the percentage of plant survival increased from 65% to 97% based on the mean of two years experiments using mist-chamber seedling inoculation methods. The improvement of resistance was also demonstrated in field assays.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, R.J., 1978. Issues in diallel analysis. Crop Sci 18: 533–536.
Collmer, A. & N.T. Keen, 1986. The role of pectic enzymes in plant pathogenesis. Ann Rev Phytopathol 24: 383–409.
Fehr, W.R., 1987a. Recurrent selection. In: Principles of Cultivar Development, pp. 172–198. Volume 1, Theory and Technique. McGraw-Hill, Inc.
Fehr, W.R., 1987b. Heritability. In: Principles of Cultivar Development, pp. 80–94. Volume 1, Theory and Technique. McGraw-Hill, Inc.
Gamble, E.E., 1962. Gene effects in corn (Zea mays L.): I. Separation and relative importance of gene effects for yield. Can J Plant Sci 42: 339–348.
Grandclement, C., F. Laurens & G. Thomas, 1996. Genetic analysis of resistance to clubroot (Plasmodiophora brassicae Woron) in two Brassica oleracea groups (ssp. acephala and ssp. botrytis) through diallel analysis. Plant Breeding 115: 152–156.
Griffing, G., 1956. Concept of general and specific combining ability in relation to diallel crossing systems. Aust J Biol Sci 9: 463–493.
Hayman, B.I., 1958. The separation of epistatic from additive and dominance variation in generation means. Heredity 12: 371–390.
Hayman, B.I., 1960. The separation of epistatic from additive and dominance variation in generation means. II. Genetica 31: 133–146.
Ito, G.M. & J.L. Brewbaker, 1991. Genetic analysis of pericarp thickness in progenies of eight corn hybrids. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 116: 1072–1077.
Nishi, S., M. Toda, S. Umeda & T. Toyoda, 1970. Studies on the breeding of cruciferae vegetables by interspecific and intergeneric hybridization. II. Breeding of disease resistant Chinese cabbage by backcrossing to interspecific hybrids between cabbage and Chinese cabbage. Bull Hort Res Sta A9: 101–128.
Ren, J.P., 1998. Resistance to bacterial soft rot (Erwinia carotovora subsp carotovora) in Brassica rapa vegetables. PhD Dissertation. Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA.
Ren, J.P., M.H. Dickson & R. Petzoldt, 1995. Screening and identification of resistance to Erwinia carotovora in Brassica rapa crops. Eucarpia Cruciferae Newsl 17: 86–87.
Ren, J.P., R. Petzoldt & M.H. Dickson, 2000. Screening and identification of resistance to bacterial soft rot in Brassica rapa. Euphytica in press.
Sachan, J.H. & B. Singh, 1987. Generation mean analysis for flowering and maturity in Indian mustard Brassica juncea L. Czern and Coss. Theor Appl Genet 73: 571–574.
Salter, R., E. Miller-Garvin & D.R. Viands, 1994. Breeding for resistance to alfalfa root rot caused by Fusarium species. Crop Sci 34: 1213–1217.
Shimizu, S., K. Kanazawa & T. Kobayashi, 1958. Studies on the breeding of Chinese cabbage for resistance to soft rot. I. Difference of resistance among varieties under field conditions. Bull Natl Inst Agric Sci Ser E 6: 75–108.
Shimizu, S., K. Kanazawa & T. Kobayashi, 1962. Studies on the breeding of Chinese cabbage for resistance to soft rot. III. The breeding of the resistant variety ‘Hiratsuka No. 1' by interspecific crossing. Bull Hort Res Sta A1: 157–174.
Togashi, J., 1981. Studies on relationship between variety difference of Chinese cabbage in resistance to the soft rot disease and growth of the causal organism (Erwinia carotovora) in rhizosphere soils. Bull Yamagata Univ Agr Sci 8: 1–7.
Warner, J.N., 1952. A method for estimating heritability. Agronomy J 44: 427–430.
Wehner, T.C. & C.S. Cramer, 1996. Gain for pickling cucumber yield and fruit shape using recurrent selection. Crop Sci 36: 1538–1544.
Williams, P.H., 1981. Workshop on screening crucifers for multiple disease resistance, p. 105. University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, USA.
Yamagishi, H., H. Yoshikawa & S. Yui, 1990. Leaf morphology and soft rot resistance in offspring of a somatic hybrid between Chinese cabbage and kale (Cruciferae). Euphytica 47: 215–221.
Yoshikawa, H., T. Sawada, H. Yamagishi & S. Yui, 1989. Soft rot resistance of progenies of somatic hybrid: Chinese cabbage + Kale. J Japan Soc Hort Sci 58(Suppl. 1): 190–191.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, J., Petzoldt, R. & Dickson, M.H. Genetics and population improvement of resistance to bacterial soft rot in Chinese cabbage. Euphytica 117, 197–207 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026541724001
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026541724001