Abstract
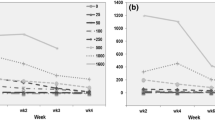
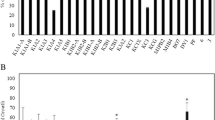
Potentially poplars and willows may be used for the in situ decontamination of soils polluted with Cd, such as pasturelands fertilised with Cd-rich superphosphate fertiliser. Poplar (Kawa and Argyle) and willow (Tangoio) clones were grown in soils containing a range (0.6–60.6 μg g−1 dry soil) of Cd concentrations. The willow clone accumulated significantly more Cd (9–167 μg g−1 dry matter) than the two poplar clones (6–75 μg g−1), which themselves were not significantly different. Poplar trees (Beaupré) sampled in situ from a contaminated site near the town of Auby, Northern France, were also found to accumulate significant quantities (up to 209 μg g−1) of Cd. The addition of chelating agents (0.5 and 2 g kg−1 EDTA, 0.5 g kg−1 DTPA and 0.5 g kg−1NTA) to poplar (Kawa) clones caused a temporary increase in uptake of Cd. However, two of the chelating agents (2 g kg−1 EDTA and 0.5 g kg−1 NTA) also resulted in a significant reduction in growth, as well as abscission of leaves. If the results obtained in these pot experiments can be realised in the field, then a single crop of willows could remove over 100 years worth of fertiliser-induced Cd contamination from pasturelands.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brooks R R 1998 Plants that Hyperaccumulate Heavy Metals: Their Role in Phytoremediation, Microbiology, Archaeology, Mineral Exploration and Phytomining. CAB International. Wallingford. UK.
Chaney R L 1983 Plant uptake of inorganic waste constituents. In Land Treatment of Hazardous Wastes. Eds. JF Parr et al. pp. 50–76. Noyes Data Corp, Park Ridge.
Chardonnens A N, Bookum W M, Kuijper L D J, Verkleij J A C and Ernst W H O 1998 Distribution of cadmium in leaves of cadmium tolerant and sensitive ecotypes of Silene vulgaris. Physiol. Plant. 104, 75–80.
Deram A 1999 Unpublished thesis, Université de Lille 1, Villeneuve d'Ascq, 59655 France.
Dickinson N M, Punshon T, Hodkinson R B and Lepp N W 1994 Metal tolerance and accumulation in willows. Willow vegetation filters for municipal wastewaters and sludges, proceedings of a study tour, conference and workshop in Uppsala Sweeden, 5- 10 June, 1994. ISBN 0282- 6267.
Felix H 1997 Field trials of the in situ decontamination of heavy metal polluted soils using crops of metal accumulating plants. Z. Pflanzenernähr Bodenkd. 160, 525–529.
Göransson A and Philippot S 1994 The use of fast growing trees as 'Metal-collectors'. In: Willow Vegetation Filters for Municipal Wastewaters and Sludges, Proceedings of a Study Tour, Conference and Workshop in Uppsala, Sweeden, 5- 10 June, 1994. ISBN 0282- 6267.
Greger M, Landberg T and Prost R 1997 Use of willow clones with high Cd accumulating properties in phytoremediation of agricultural soils with elevated Cd levels. Contaminated soils: 3rd International Conference on the Biogeochemistry of Trace Elements, Paris, France, 15- 19 May, 1995. 505–511.
Hinchman R R, Negri M C and Gatliff E G 1996 Phytoremediation: using green plants to clean up contaminated soil, groundwater and wastewater. Proc., International Topical Meeting on Nuclear and Hazardous Waste Management, Spectrum 96. Seattle WA.
Hong A P K, Li C, Banerji S K and Regmi T 1999 Extraction, recovery, and biostability of EDTA for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. J. Soil Contam. 8(1) 81–103
Huang J W and Cunningham S D 1996 Lead phytoextraction: species variation in lead uptake and translocation. New Phytol. 134, 75–84.
Huiyi H, Deming J, Chunxing Z, Youbiao Z and Zhiquing L 1991 Study on the control of cadmium-pollution in the soil by forestry ecological engineering. China Environ. Sci. 2(1), 36–45.
Landberg T and Greger M 1994 Can heavy metal tolerant clones of Salix be used as vegetation filters on heavy metal contaminated land? In: Willow Vegetation Filters for Municipal Wastewaters and Sludges, Proceedings of a Study Tour, Conference and Workshop in Uppsala, Sweden, 5- 10 June, 1994. ISBN 0282- 6267.
Loganathan P and Hedley M J 1997 Downward movement of cadmium and phosphorus from phosphatic fertilisers in a pasture soil in New Zealand. Environ. Poll. 95, 319–324.
McGrath S P, Sidoli C M D, Baker A J M and Reeves R D 1993 The potential for the use of metal-accumulating plants for the in situ decontamination of metal-polluted soils. In: Integrated Soil and Sediment Research: A Basis for Proper Protection. Eds. HJP Eijsakers and T Hamers. pp 673–676. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Means J L, Kucak T and Crerar D A 1980 Relative degradation rates of NTA, EDTA and DTPA and environmental implications. Environ. Poll. Ser. B1. 45–60.
Russel M, Colglazier E W and English M R 1991 Hazardous Waste Remediation: The task ahead. Waste Management Research and Education Institute, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, T.N.
Salt D E, Blaylock M, Kumar N P B A, Dushenov V, Ensley B, Chet I and Raskin I 1995. Phytoremediation: A novel strategy for the removal of toxic metals from the environment using plants. Bio. Tech. 13, 468–474.
Underwood E J and Suttle N F 1999. The mineral nutrition of livestock. 3rd edn. CAB International. Wallingford. UK.
Zanders J M 1998 Studies on the origin, distribution and mobility of cadmium in pastoral soils. Unpublished PhD thesis, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robinson, B.H., Mills, T.M., Petit, D. et al. Natural and induced cadmium-accumulation in poplar and willow: Implications for phytoremediation. Plant and Soil 227, 301–306 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026515007319
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026515007319