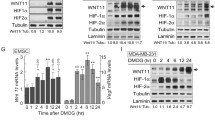
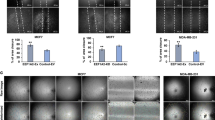
Abstract
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a potent cytokine secreted by virtually all cells plays a key role in tumor angiogenesis. Disruption of one VEGF allele in mice has revealed a dramatic lethal effect in early embryogenesis, suggesting a very tight regulation of this gene. This commentary reviews the mechanisms whereby VEGF mRNA is controlled within the tumor environment by hypoxia and the MAP kinase signaling cascades. Using hamster fibroblasts as a cellular model, we demonstrated that the Ras-mediated activation of p42/p44 MAP kinases exerts a prominent action at the transcriptional level. In normoxic conditions, p42/p44 MAPKs activate the VEGF promoter at the proximal (−88/−66) region where Sp1/AP-2 transcriptional factor complexes are recruited. At low O2 tension, the stabilized and nuclear hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) is directly phosphorylated by p42/p44 MAPKs, an action which enhances HIF-1-dependent transcriptional activition of VEGF. In addition, MAPKs activated under various cellular stresses (p38MAPK and JNK), contribute to the increased expression of this angiogenic growth and survival factor by stabilizing the VEGF mRNA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman J: What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst 82: 4-6, 1990
Folkman J, Shing Y: Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 267: 10 931-10 934, 1992
Folkman J: Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med I: 27-31, 1995
Gasparini G, Harris AL: Clinical importance of the determination of tumor angiogenesis in breast carcinoma: much more than a new prognostic tool. J Clin Oncol 13: 765-782, 1995
Leung DW, Cachianes G, Kuang WJ, Goeddel DV, Ferrara N: Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science 246: 1306-1309, 1989
Risau W: Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature 386: 671-674, 1997
Tischer E, Mitchell R, Hartman T, Silva M, Gospodarowicz D, Fiddes JC, Abraham JA: The human gene for vascular endothelial growth factor. Multiple protein forms are encoded through alternative exon splicing. J Biol Chem 266: 11 947-11 954, 1991
Berse B, Brown LF, Van deWater L, Dvorak HF, Senger DR: Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) gene is expressed differentially in normal tissues, macrophages, and tumors. Mol Biol Cell 3: 211-220, 1992
Carmeliet P, Ferreira V, Breier G, Pollefeyt S, Kieckens L, Gertsenstein M, Fahrig M, Vandenhoeck A, Harpal K, Eberhardt C, Declercq C, Pawling J, Moons L, Collen D, Risau W, Nagy A: Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single VEGF allele. Nature 380: 435-439, 1996
Ferrara N, Carver-Moore K, Chen H, Dowd M, Lu L, O'Shea KS, Powell-Braxton L, Hillan KJ, Moore MW: Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the VEGE gene. Nature 380: 439-442, 1996
Shalaby F, Rossant J, Yamaguchi TP, Gertsenstein M, Wu XF, Breitman ML, Schuh AC: Failure of bloodisland formation and vasculogenesis in Flk-1-deficient mice. Nature 376: 62-66, 1995
Fong GH, Rossant J, Gertsenstein M, Breitman ML: Role of the Flt-1 receptor tyrosine kinase in regulating the assembly of vascular endothelium. Nature 376: 66-70, 1995
Cobb MH, Goldsmith EJ: How MAP kinases are regulated. J Biol Chem 270: 14 843-14 846, 1995
Marshall MS: Ras target proteins in eukaryotic cells. Faseb J 9: 1311-1318, 1995
Pagè s G, Lenormand P, L'Allemain G, Chambard JC, Meloche S, Pouysségur J: Mitogen-activated protein kinases p42 MAPK and p44 MAPK are required for fibroblast proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 8319-8323, 1993
Waskiewicz AJ, Johnson JC, Penn B, Mahalingam M, Kimball SR, Cooper JA: Phosphorylation of the cap-binding protein eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E by protein kinase Mnk1 in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 19: 1871-1880, 1999
Pyronnet S, Imataka H, Gingras AC, Fukunaga R, Hunter T, Sonenberg N: Human eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G (eIF4G) recruits Mnk1 to phosphorylate eIF4E. Embo J 18: 270-279, 1999
Pagè s G, Guerin S, Grall D, Bonino F, Smith A, Anjuere F, Auberger P, Pouysségur J: Defective thymocyte maturation in p44 MAP kinase (Erk1) knockout mice. Science 286: 1374-1377, 1999
Graves LM, Guy HI, Kozlowski P, Huang M, Lazarowski E, Pope RM, Collins MA, Dahlstrand EN, Earp HS, Evans DR: Regulation of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase by MAP kinase. Nature 403: 328-332, 2000
Le Gall M, Chambard JC, Breittmayer JP, Grall D, Pouysségur J, Van Obberghen-Schilling E: The p42/p44 MAP kinase pathway prevents apoptosis induced by anchorage and serum removal. Mol Biol Cell 11: 1103-1112, 2000
Samuels ML, Weber MJ, Bishop JM, McMahon M: Conditional transformation of cells and rapid activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade by an estradioldependent human raf-1 protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol 13: 6241-6252, 1993
Lenormand P, McMahon M, Pouysségur J: Oncogenic Raf-1 activates p70 S6 kinase via a mitogen-activated protein kinase-independent pathway. J Biol Chem 271: 15 762-15 768, 1996
Pertovaara L, Kaipainen A, Mustonen T, Orpana A, Ferrara N, Saksela O, Alitalo K: Vascular endothelial growth factor is induced in response to transforming growth factor-beta in fibroblastic and epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 269: 6271-6274, 1994
Frank S, Hubner G, Breier G, Longaker MT, Greenhalgh DG, Werner S: Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in cultured keratinocytes. Implications for normal and impaired wound healing. J Biol Chem 270: 12 607-12 613, 1995
Grugel S, Finkenzeller G, Weindel K, Barleon B, Marme D: Both v-Ha-Ras and v-Raf stimulate expression of the vascular endothelial growth factor in NIH 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem 270: 25 915-25 919, 1995
Enholm B, Paavonen K, Ristimaki A, Kumar V, Gunji Y, Klefstrom J, Kivinen L, Laiho M, Olofsson B, Joukov V, Eriksson U, Alitalo K: Comparison of VEGF, VEGF-B, VEGF-C and Ang-1 mRNA regulation by serum, growth factors, oncoproteins and hypoxia. Oncogene 14: 2475-2483, 1997
Gille J, Swerlick RA, Caughman SW: Transforming growth factor-alpha-induced transcriptional activation of the vascular permeability factor (VPF/VEGF) gene requires AP-2-dependent DNA binding and transactivation. Embo J 16: 750-759, 1997
Mazure NM, Chen EY, Yeh P, Laderoute KR, Giaccia AJ: Oncogenic transformation and hypoxia synergistically act to modulate vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Cancer Res 56: 3436-3440, 1996
Mazure NM, Chen EY, Laderoute KR, Giaccia AJ: Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor by hypoxia is modulated by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway in Ha-ras-transformed cells through a hypoxia inducible factor-1 transcriptional element. Blood 90: 3322-3331, 1997
Rak J, Mitsuhashi Y, Sheehan C, Tamir A, Viloria-Petit A, Filmus J, Mansour SJ, Ahn NG, Kerbel RS: Oncogenes and tumor angiogenesis: differential modes of vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulation in ras-transformed epithelial cells and fibroblasts. Cancer Res 60: 490-498, 2000
Milanini J, Vinals F, Pouysségur J, Pagè s G: p42/p44 MAP kinase module plays a key role in the transcriptional regulation of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene in fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 273: 18 165-18 172, 1998
Pagè s G, Berra E, Milanini J, Levy AP, Pouysségur J: Stress activated protein kinases (c-Jun N terminal Kinase and p38/HOG) are essential for VEGF mRNA stability. J Biol Chem 902: 187-200, 2000
Levy AP, Levy NS, Wegner S, Goldberg MA: Transcriptional regulation of the rat vascular endothelial growth factor gene by hypoxia. J Biol Chem 270: 13 333-13 340, 1995
Forsythe JA, Jiang BH, Iyer NV, Agani F, Leung SW, Koos RD, Semenza GL: Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Mol Cell Biol 16: 4604-4613, 1996
Wang GL, Semenza GL: Purification and characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem 270: 1230-1237, 1995
Guillemin K, Krasnow MA: The hypoxic response: huffing and HIFing. Cell 89: 9-12, 1997
Huang LE, Arany Z, Livingston DM, Bunn HF: Activation of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor depends primarily upon redox-sensitive stabilization of its alpha subunit. J Biol Chem 271: 32 253-32 259, 1996
Gradin K, McGuire J, Wenger RH, Kvietikova I, Fhitelaw ML, Toftgard R, Tora L, Gassmann M, Poellinger L: Functional interference between hypoxia and dioxin signal transduction pathways: competition for recruitment of the Arnt transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol 16: 5221-5231, 1996
Kallio PJ, Pongratz I, Gradin K, McGuire J, Poellinger L: Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha: posttranscriptional regulation and conformational change by recruitment of the Arnt transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 5667-5672, 1997
Tian H, McKnight SL, Russell DW: Endothelial PAS domain protein 1 (EPAS1), a transcription factor selectively expressed in endothelial cells. Genes Dev 11: 72-82, 1997
Richard DE, Berra E, Pouysségur J: Angiogenesis: how a tumor adapts to hypoxia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 266: 718-722, 1999
Salceda S, Caro J: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) protein is rapidly degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system under normoxic conditions. Its stabilization by hypoxia depends on redox-induced changes. J Biol Chem 272: 22 642-22 647, 1997
Huang LE, Gu J, Schau M, Bunn HF: Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is mediated by an O2-dependent degradation domain via the ubiquitin proteasome pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 7987-7992, 1998
Kalliho PJ, Wilson WJ, O'Brien S, Makino Y, Poellinger L: Regulation of the hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 1alpha by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. J Biol Chem 274: 6519-6525, 1999
Zundel W, Schindler C, Haas-Kogan D, Koong A, Kaper F, Chen E, Gottschalk AR, Ryan HE, Johnson RS, Jefferson AB, Stokoe D, Giaccia AJ: Loss of PTEN facilitates HIF-1-mediated gene expression. Genes Dev 14: 391-396, 2000
Scheffner M, Werness BA, Huibregtse JM, Levine AJ, Howley PM: The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell 63: 1129-1136, 1990
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A, Oren M: Mdm2 promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature 387: 296-299, 1997
Kubbutat MH, Jones SN, Vousden KH: Regulation of p53 stability by Mdm2. Nature 387: 299-303, 1997
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME, Wykoff CC, Pugh CW, Maher ER, Ratcliffe PJ: The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 399: 271-275, 1999
Ravi R, Mookerjee B, Bhujwalla ZM, Sutter CH, Artemov D, Zeng Q, Dillehay LE, Madan A, Semenza GL, Bedi A: Regulation of tumor angiogenesis by p53-induced degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Genes Dev 14: 34-44, 2000
Richard DE, Berra E, Gothié E, Roux D, Pouysségur J: p42/p44 Mitogen-activated protein kinases phosphorylate hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and enhance the transcriptional activity of HIF-1. J Biol Chem 274: 32 631-32 637, 1999
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Semenza GL: Effect of protein kinase and phosphatase inhibitors on expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 216: 669-675, 1995
Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: master regulator of O2 homeostasis. Curr Opin Genet Dev 8: 588-594, 1998
Camps M, Nichols A, Gillieron C, Antonsson B, Muda M, Chabert C, Boschert U, Arkinstall S: Catalytic activation of the phosphatase MKP-3 by ERK2 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science 280: 1262-1265, 1998
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berra, E., Pagès, G. & Pouysségur, J. MAP Kinases and Hypoxia in the Control of VEGF Expression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 19, 139–145 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026506011458
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026506011458