Abstract
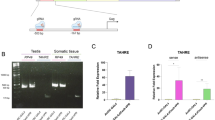
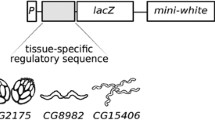
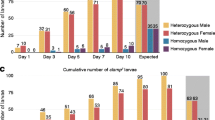
The Ychromosome of Drosophila melanogasteraccounts for approximately 13% of a normal male genome and is entirely heterochromatic. It carries six genes required exclusively for spermatogenesis. Here we report a novel activity of the Ychromosome that regulates gene expression in primary spermatocytes. By examining the expression of a reporter gene in X/Yand X/0males, we show that a specific region of the Ylong arm carries a trans-activator that regulates transcription in spermatogenesis. In the absence of the Ytrans-activator, the level of the reporter expression is greatly reduced in primary spermatocytes and the expression pattern is restricted to young primary spermatocytes. Further analysis shows that the Ytrans-activator is dispersed in the h1-h10 region on the Ylong arm and is functionally redundant, indicating involvement of the repetitive sequences on the Ychromosome. In addition, the Ytrans-activator appears to act in a tissue-specific manner, functioning only in the male germ line. We propose that the Ytrans-activator plays an important role in regulating gene expression during spermatogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appels, R. & W.J. Peacock, 1978. The arrangement and evolution of highly repeated (satellite) DNA sequences with special reference to Drosophila. Int. Rev. Cytol. (Suppl.) 8: 69–126.
Bonaccorsi, S. & A. Lohe, 1991. Fine mapping of satellite DNA sequences along the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster: relationship between satellite sequences and fertility factors. Genetics 129: 177–189.
Bonaccorsi, S., M. Gatti, C. Pisano & A. Lohe, 1990. Transcription of a satellite DNA on two Y chromosome loops of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 99: 260–266.
Bonaccorsi, S., C. Pisano, F. Puoti & M. Gatti, 1988. Y chromosome loops in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 120: 1015– 1034.
Bourgouin, C., S.E. Lundgren & J.B. Thomas, 1992. Apterous is a DrosophilaLIM domain gene required for the development of a subset of embryonic muscles. Neuron 9: 549–561.
Casadaban, M.J., A. Martinez-Arias, S.K. Shapira & J. Chou, 1983. Beta-galactosidase gene fusions for analyzing gene expression in Escherichia coliand yeast. Methods Enzymol. 100: 293–308.
Castrillon, D., P. Gonczy, S. Alexander, R. Rawson, C. Eberhart, S. Viswanathan, S. DiNardo & S.A. Wasserman, 1993. Towards a molecular genetic analysis of spermatogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: characterization of male-sterile mutants generated by single P element mutagenesis. Genetics 135: 489–505.
Castrillon, D.H. & S.A. Wasserman, 1994. Diaphanous is required for cytokinesis in Drosophilaand shares domains of similarity with the products of the limb deformity gene. Development 120: 3367–3377.
Clemson, C., J. McNeil, H. Willard & J. Lawrence, 1996. Xist RNA paints the inactive X chromosome at interphase: evidence for novel RNA involved in nuclear/chromosome structure. J. Cell Biol. 132: 259–275.
Csink, A.K. & S. Henikoff, 1998. Something from nothing: the evolution and utility of satellite repeats. Trends Genet. 14: 200-204.
Dietzel, S., H. Niemann, B. Bruckner, C. Maurange & R. Paro, 1999. The nuclear distribution of Polycomb during Drosophila melanogasterdevelopment shown with a GFP fusion protein. Chromosoma 108: 83–94.
Dimitri, P. & C. Pisano, 1989. Position effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster: relationship between suppression effect and the amount of Y chromosome. Genetics 122: 793–800.
Elgin, S.C.R. 1996. Heterochromatin and gene regulation in Drosophila. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 6: 193–202.
Fuller, M., 1993. Spermatogenesis, pp. 71–147 in The Development of Drosophila melanogaster, edited by M. Bate & A. Martinez. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Gatti, M. & S. Pimpinelli, 1983. Cytological and genetic analysis of the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Organization of the fertility factors. Chromosoma 88: 349–373.
Gatti, M. & S. Pimpinelli, 1992. Functional elements in Drosophila melanogasterheterochromatin. Ann. Rev. Genet. 26: 239–275.
Gepner, J. & T. Hays, 1993. A fertility region on the Y chromosome of D. melanogasterencodes a dynein microtubule motor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 11132-11136.
Goldstein, L., R. Hardy & D.L. Lindsley, 1982. Structural genes on the Y chromosome of D. melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79: 7405–7409.
Hackstein, J.H.P., 1987. Spermatogenesis in Drosophila, pp. 63–116 in Spermatogenesis: Genetic Aspects. Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation, Vol. 15, edited W. Hennig. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York.
Hardy, R.W., K.T. Tokuyasu & D.L. Lindsley, 1981. Analysis of spermatogenesis in Drosophila melanogasterbearing deletions for Y-chromosome fertility genes. Chromosoma 88: 593–617.
Hardy, R.W., D.L. Lindsley, K.J. Livak, B. Lewis, A.L. Sivertsen, G.L. Joslyn, J. Edwards & S. Bonaccorsi, 1984. Cytogenetic analysis of a segment of the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 107: 591–610.
Hazelrigg, T., P. Fornili & T. Kaufman, 1982. A cytogenetic analysis of X-ray induced male sterile on the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 87: 535–559.
Heatwole, V.M. & S.R. Haynes, 1996. Association of RB97D, an RRM protein required for male fertility, with a Y chromosome lampbrush loop in Drosophilaspermatocytes. Chromosoma 105: 285–292.
Karpen, G.H. & A.C. Spradling, 1992. Analysis of subtelomeric heterochromatin in a Drosophilaminichromosome by single P element insertional mutagenesis. Genetics 132: 737–753.
Karsch-Mizrachi, I. & S.R. Haynes, 1993. The Rb97D gene encodes a potential RNA-binding protein required for spermatogenesis in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 9: 2229–2235.
Kassis, J.A., 1990. Spatial and temporal control elements of the Drosophilaengrailed gene. Genes Dev. 4: 433–443.
Kennison, J.A., 1981. The genetic & cytological organization of the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 98: 529–548.
Lin, T., S. Viswanathan, C. Wood, P. Wilson, N. Wolf & M. Fuller, 1996. Coordinate developmental control of the meiotic cell cycle and spermatid differentiation in Drosophilamales. Development 122: 1331–1341.
Lindsley, D. & K.T. Tokuyasu, 1980. Spermatogenesis, pp. 225–294 in Genetics and Biology in Drosophila, 2nd edition, edited M. Ashburner & T. Wright. Academic Press, New York.
Lohe, A., A. Hilliker & P. Roberts, 1993. Mapping simple repeated DNA sequences in heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 134: 1149–1174.
Marsh, J.L. & E. Wieschaus, 1978. Is sex determination in germ line and soma controlled by separate genetic mechanisms? Nature 272: 249–251.
Meller, V.H., K.H. Wu, G. Roman, M.I. Kuroda & R.L. Davis, 1997. roX1 RNA paints the X chromosome of male Drosophilaand is regulated by the dosage compensation system. Cell 88:445–457.
Mlodzik, M. & Y. Hiromi, 1992. The enhancer trap method in Drosophila: its application to neurobiology, pp. 397–414 in Gene Expression in Neural Tissues (Methods in Neuroscience 9), edited P.M. Cann. Academic Press, Orlando, Florida.
Montell, D.J., P. Rorth & A.C. Spradling, 1992. slow border cells, a locus required for a developmentally regulated cell migration during oogenesis, encodes a DrosophilaC/EBP homolog. Cell 71: 51–62.
Pak, D.T., M. Pflumm, I. Chesnokov, D.W. Huang, R. Kellum, J. Marr, P. Romanowski & M.R. Botchan, 1998. Association of the origin recognition complex with heterochromatin and HP1 in higher eukaryotes. Cell 91: 311–323.
Pimpinelli, S., M. Berloco, L. Fanti, P. Dimitri, S. Bonaccorsi, E. Marchetti, R. Caizzi, C. Caggese & M. Gatti, 1995. Transposable elements are stable structural components of Drosophila melanogasterheterochromatin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 3804–3808.
Platero, J., A. Csink, A. Quintanilla & S. Henikoff, 1998. Changes in chromosomal localization of heterochromatin-binding proteins during the cell cycle in Drosophila. J. Cell Biol. 140: 1297–1306.
Santel, A., Winhauer, T., Blumer, N. & R. Renkawitz-Pohl, 1997. The Drosophila don juan (dj)gene encodes a novel sperm specific protein component characterized by an unusual domain of a repetitive amino acid motif. Mech. Dev. 64: 19–30.
Spofford, J.B., 1976. Position-effect variegation in Drosophila, pp. 955–1018 in The Genetics and Biology of Drosophila, Vol. 1c, edited by M. Ashburner & E. Novitiski. Academic Press, New York.
Tautz, D. & C. Pfeifle, 1989. A non-radioactive in situhybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophilaembryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma 98: 81–85.
White-Cooper, H., M. Schäfer, L. Alphey & M. Fuller, 1998. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control mechanisms coordinate the onset of spermatid differentiation with meiosis I in Drosophila. Development 125: 125–134.
Wallrath, L., 1998. Unfolding the mysteries of heterochromatin. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 8: 147–153.
Zhang, P. & A.C. Spradling, 1994. Insertional mutagenesis of Drosophila heterochromatinwith single P elements. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 3539–3542.
Zhang, P. & R.L. Stankiewicz, 1998. Y-linked male sterile mutations induced by P element in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 150: 735–744.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Timakov, B., Stankiewicz, R.L. et al. A Trans-Activator on the Drosophila Y Chromosome Regulates Gene Expression in the Male Germ Line. Genetica 109, 141–150 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026504721067
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026504721067