Abstract
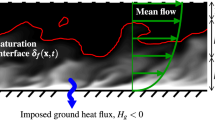
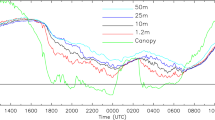
The effect of longwave radiation on the structure the clear stable boundary layer (SBL) is examined. Special emphasis is given to radiative cooling near the surface and the top of the boundary layer and its impact on the heat flux profile. Further, the formation, growth and dissipation of fog in the SBL are studied both from observations and from a one-dimensional ensemble averaged turbulence closure model. The model is compared with detailed observations that were made for both a shallow (about 30 m) radiation fog and a deep (about 200 m) fog layer at the 200-m tower at Cabauw in the Netherlands. The model describes adequately the most important mechanisms occurring during the fog evolution. In this study special attention is given to the parameterization of the vegetation, which is important for a good representation of the (minimum) air temperature. The influence of turbulence transport, longwave radiative cooling and gravitational droplet settling on the fog evolution is described. The study demonstrates the need for more accurate measurements of turbulence quantities, especially the master length scale, in a variety of SBLs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, R.: 1987: ‘Observations of the Structure of a Deep Fog’, Meteorol. Mag. 116, 329–338.
Beljaars, A. C. M. and Holtslag, A. A. M.: 1991, ‘Flux Parametrization over Land Surfaces for Atmospheric Models’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 30, 327–341.
Brutsaert, W.: 1982, Evaporation into the Atmosphere, D. Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrecht, 299 pp.
Businger, J. A., Wyngaard, J. C., Izumi, Y., and Bradley, E. F.: 1971, ‘Flux-profile Relationships in the Atmospheric Surface Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 28, 181–189.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1978, ‘Efficient Prediction of Ground Surface Temperature and Moisture, with Inclusion of a Layer of Vegetation’, J. Geophys. Res. 83, 1889–1903.
Driedonks, A. G. M. and Duynkerke, P. G.: 1989, ‘Current Problems in the Stratocumulus-Topped Atmospheric Boundary Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 46, 275–303.
Duynkerke, P. G. and Driedonks, A. G. M.: 1987, ‘A Model for the Turbulent Structure of the Stratocumulus-Topped Atmospheric Boundary Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 44, 43–64.
Duynkerke, P. G. and Driedonks, A. G. M.: 1988, ‘Turbulent Structure of a Shear Driven Stratustopped Atmospheric Boundary Layer: A Comparison of Model Results with Observations’, J. Atmos. Sci. 45, 2343–2351.
Duynkerke, P. G.: 1990, Radiation Fog: A Comparison of Model Results with Detailed Observations, 1990 Conference on Cloud Physics, San Francisco, U.S.A.
Duynkerke, P. G.: 1991a, ‘Radiation Fog: A Comparison of Model Simulation with Detailed Observations’, Mon. Wea. Rev. 119, 324–341.
Duynkerke, P. G.: 1991b, ‘Observation of a Quasi-Periodic Oscillation Due to Gravity Waves in a Shallow Radiation Fog’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 117, 1207–1224.
Duynkerke, P. G.: 1992, ‘The Roughness Length for Heat and Other Vegetation Parameters for a Surface of Short Grass’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 31, 579–586.
Elliott, W. P.: 1963, ‘The Height Variation of Vertical Heat Flux near the Ground’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 90, 260–265.
Fitzjarrald, D. R. and Lala, G. G.: 1989, ‘Hudson Valley Fog Environments’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 28, 1303–1328.
Funk, J. P.: 1960, ‘Measured Radiative Flux Divergence nNear the Ground at Night’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 86, 382–389.
Garratt, J. R.: 1992, The Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Cambridge University Press, U.K., 316 pp.
Garratt, J. R. and Brost, R. A.: 1981, ‘Radiative Cooling Effects within and above the Nocturnal Boundary Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 38, 2730–2746.
Jiusto, J. E.: 1981, ‘Fog Structure’, in P. V. Hobbs and A. Deepak (eds.), Clouds: Their Formation, Optical Properties and Effects, Academic Press, 495 pp.
Kondratyev, K. Ya.: 1969, Radiation in the Atmosphere, Academic Press, 912 pp.
Kunkel, B. A.: 1984, ‘Parameterization of Droplet Terminal Velocity and Extinction Coefficient in Fog Models’, J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 23, 34–41.
Larsson, L.: 1997, ‘Measurements and Modelling of Turbulence Characteristics in Stable Boundary Layers. IMAU-report V97–25. Obtainable from: IMAU, Princetonplein 5, 3584 CC Utrecht, The Netherlands.
Monna, W. A. A. and van der Vliet, J. G.: 1987: ‘Facilities for Research and Weather Observations on the 213 m Tower at Cabauw and at Remote Locations’, Sci. Rep. WR 87–5. Obtainable from: KNMI, PO Box 201, 3730AE, De Bilt, The Netherlands.
Musson-Genon, L.: 1987, ‘Numerical Simulation of a Fog Event with a One-Dimensional Boundary Layer Model’, Mon. Wea. Rev. 115, 592–607.
Nieuwstadt, F. T. M.: 1984: ‘The Turbulent Structure of the Stable, Nocturnal Boundary Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 41, 2202–2216.
Oncley, S. P., Friehe, C. A., Larue, J. C., Businger, J. A., Itsweire, E. C., and Chang, S. S.: 1996, ‘Surface-Layer Fluxes, Profiles, and Turbulence Measurements over Uniform Terrain under Near-Neutral Conditions’, J. Atmos. Sci. 53, 1029–1044.
Rider, N. E. and Robinson, G. D.: 1951, ‘A Study of the Transfer of Heat and Water Vapour above a Surface of Short Grass’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 77, 375–401.
Rodgers, C. D.: 1967, ‘The Use of Emissivity in Atmospheric Radiation Calculations’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 93, 43–54.
Staley, D. O. and Jurica, G. M.: 1970, ‘Flux Emissivity Tables for Water Vapor, Carbon Dioxide and Ozone’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 9, 365–372.
Turton, J. D. and Brown, R.: 1987, ‘A Comparison of a Numerical Model of Radiation Fog with Detailed Observations’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 113, 37–54.
Tjemkes, S. A. and Duynkerke, P. G.: 1989, ‘The Nocturnal Boundary Layer: Model Calculations Compared with Observations’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 28, 161–175.
Van der Avoird, E. and Duynkerke, P. G.: 1999, ‘Turbulence in a Katabatic Flow: Does it Resemble Turbulence in Stable Boundary Layers over Flat Surfaces? Boundary-Layer Meteorol., accepted.
Van Ulden, A. P. and Wieringa, J.: 1996, ‘Atmospheric Boundary Layer Research at Cabauw’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 78, 39–69.
Welch, R. and Zdunkowski, W.: 1976, ‘A Radiation Model of the Polluted Atmospheric Boundary Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 33, 2170–2184.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duynkerke, P.G. Turbulence, Radiation and fog in Dutch Stable Boundary Layers. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 90, 447–477 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026441904734
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026441904734