Abstract
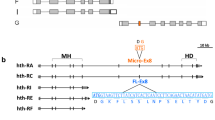
The kelch-repeat protein family is a recently found new kind of actin-binding protein. It is characterized by tandemly arranged motifs of about 50 amino acids [7]. Previous study showed that most members of the kelch-repeat family were cytoskeletal proteins implicated in various cellular processes, such as actin cytoskeleton interaction, cytoplasmic sequestration of transcription factors and cell morphology [1]. And some of the family members play important roles in tissue development, such as human ENC-1, NRP/B, etc. Another characteristic of the kelch family is that most members have another conserved BTB domain at the extreme amino terminus. The BTB domain is also found at the N-terminus of 5–10% of zinc-finger transcription factor types and is a conserved protein-protein interaction motif [15]. During the large-scale sequencing analysis of a human fetal brain cDNA library we found a novel kelch-like protein gene 5, KLHL5[11], KLHL5 has high identity with Drosophila kelch protein and many other family members. Here we report a novel splicing variants of KLHL5, named KLHL5b and the expression pattern of KLHL5b in many tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams J, Kelso R, Cooley L (2000) Trends Cell Biol. 10: 17–24
Agutter PS (1991) Biochem.Soc.Trans. 19: 1094–1098
Ahmad KF, Engel CK, Prive GG (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 95(21): 12123–12128
Ito N, Philips SEV, Yadav KDS, Knowles PF (1994) J. Mol. Biol. 238: 794–814
Adams JC, Seed B, Lawler J (1998) EMBO J. 17(17): 4964–4974
Kim TA, Lim JY, Ota S, Raja S, Rogers R, Rivnay B, Avraham H, Avraham S (1998) J. Cell. Biol. 141(3): 553–566
Kim IF, Mohammadi E, Huang RCC (1999) Gene 228: 73–83
Lauffenburger DA, Horwitz AF (1996) Cell 84: 359–369
Soltysik-Espanola M, Rogers RA, Jiang SX, Kim TA, Gaedigk R, White RA, Avraham H, Avraham S (1999) Mol.Biol.Cell 10(7): 2361–2375
Vonbulow M, Heid H, Hess H, Franke WW (1995) Exp. Cell Res. 219: 407–413
Wang S, Zhou ZX, Ying K, Tang R, Huang Y, Wu CQ, Xie Y, Mao YM (2001) Biochem. Genet. 39: 227–238
Wolff T, O'neill RE, Palese P (1998) J. Virol. 72(9): 7170–7180
Xu J, Zhuo ZX, Zeng L, Huang Y, Zhao W, Cheng C, Xu M, Xie Y, Mao YM (2001) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 91585: 1–4
Xue F, Cooley L (1993) Cell 72: 681–693
Zollman S, Godt D, Prive GG, Couderc JL, Laski FA (1994) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 91: 10717–10721
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Gu, S., Wang, S. et al. Characterization of a novel splicing variant of KLHL5 *, a member of the kelch protein family. Mol Biol Rep 30, 239–242 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026372901766
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026372901766