Abstract
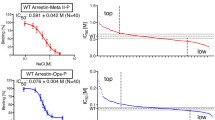
A combination of intrinsic fluorescence and circular dichroic (CD) spectroscopy has been used to characterize the complexes formed between bovine retinal arrestin and heparin or phytic acid, two ligands that are known to mimic the structural changes in arrestin attending receptor binding. No changes in the CD spectra were observed upon ligand binding, nor did the degree of tryptophan fluorescence quenching change significantly in the complexes. These data argue against any large-scale changes in protein secondary or tertiary structure accompanying ligand binding. The change in tyrosine fluorescence intensity was used to determine the dissociation constants for the heparin and phytic acid complexes of arrestin. The only change observed was a saturable diminution of tyrosine fluorescence signal from the protein. For both ligands, the data suggest two distinct binding interactions with the protein—a high-affinity interaction with K d between 200 and 300 nM, and a lower affinity interaction with K d between 2 and 8 μM. Study of collisional quenching of tyrosine fluorescence in free arrestin and the ligand-replete complexes indicates that 10 of the 14 tyrosine residues of the protein are solvent-exposed in the free protein; this value drops to between 5 and 6 solvent-exposed residues in the high-affinity complexes of the two ligands. These data suggest that ligand binding leads to direct occlusion of between 4 and 5 tyrosine residues on the solvent-exposed surface of the protein, but not to any large-scale changes in protein structure. The large activation energy previously reported to be associated with arrestin–receptor interactions may therefore reflect localized movements of the N- and C-termini of arrestin, which are proposed to interact in the free protein through electrostatic interactions. Binding of the anionic ligands heparin, phytic acid, or phosphorylated rhodopsin may compete with the C-terminus of arrestin for these electrostatic interactions, thus allowing the C-terminus to swing out of the binding region.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Akama, K., Sato, H., Furihata-Yamauchi, M., Komatsu, Y., Tobita, T., and Nakano, M. (1996). J. Biochem. 119, 448–455.
Ashikawa, I., Nishimura, Y., Tsuboi, M. Watanabe, K., and Iso, K. (1982). J. Biochem. 91, 2047–2055.
Attramadal, H., Arriza, J. L., Aoki, C., Dawson, T. M., Codina, J., Kwatra, M. M., Snyder, S. H., Caron, M. G., and Lefkowitz, R. J. (1992). J. Biol. Chem. 267, 17882–17890.
Bradford, M. (1976). Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254.
Copeland, R. A. (1994). Methods for Protein Analysis: A Practical Guide to Lab Protocols, Chapman and Hall, New York, pp. 161–198.
Copeland, R. A., Ji, H., Halfpenny, A., Williams, R., Thompson, K., Herber, W., Thomas, K., Bruner, M., Ryan, J., Marquis-Omer, D., Sanyal, G., Sitrin, R., Yamazaki, S., and Middaugh, R. (1991). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 289, 53–61.
Craft, C. M., Whitmore, D. H., and Wiechmann, A. F. (1994). J. Biol. Chem. 269, 4613–4619.
Creighton, T. E. (1993). Proteins: Structures and Molecular Properties, W. H. Freeman & Co., New York, pp. 368–370.
Feldman, H. A. (1972). Anal. Biochem. 48, 317–338.
Gurevich, V. V., and Benovic, J. L. (1993). J. Biol. Chem. 268, 11628–11638.
Gurevich, V., Chen, C. Y., Kim, C. M., and Benovic, J. L. (1994). J. Biol. Chem. 269, 8721–8724.
Halfman, C., and Nishida, T. (1972). Biochemistry 11, 3493–3498.
Kim, Y. T., Tabor, S., Bortner, C., Griffeth, J. D., and Richardson, C. C. (1992). J. Biol. Chem. 267, 15022–15031.
Kotake, S., Hey, P., Mirmira, R., and Copeland, R. A. (1991). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 285, 126–133.
Kowalczykowski, S. C., Lonberg, N., Newport, J. W., and von Hippel, P. H. (1981). J. Mol. Biol. 145, 75–104.
Kramm, C. M., Korf, H.-W., Czerwionka, M., Schachenmayr, W., and de Grip, J. W. (1991). Acta Neuropathol. 81, 296–302.
Lakowitz, J. (1983). Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, Plenum Press, New York.
Lehrer, S. S. (1971). Biochemistry 10, 3254–3263.
Lindberg, G., Kowalczykowski, S. C., Rist, J. K., Sugino, A., and Rothman-Denes, L. (1989). J. Biol. Chem. 264, 12700–12708.
Mayer, R., Toulme, F., Montenay-Garestier, T., and Helene, C. (1979). J. Biol. Chem. 254, 75–82.
Ohguro, H., Johnson, R. S., Ericsson, L. H., Walsh, K. A., Palczewski, K. (1994). Biochemistry 33, 1023–1028.
Palczewski, K., Buczylko, J., Imami, N. R., McDowell, J. H., and Hargrave, P. A. (1991a). J. Biol. Chem. 266, 15334–15339.
Palczewski, K., Pulvermüller, A., Buczylko, J., and Hofmann, K. P. (1991b). FEBS Lett. 295, 195–199.
Palczewski, K., Pulvermüller, A., Buczylko, J., and Hofmann, K. P. (199c). J. Biol. Chem. 266, 18649–18654.
Parma, J., Duprez, L., Van Sande, J., Cochaux, P., Gervy, C., Mockel, J., Dumont, J. and Vassart, G. (1993). Nature 365, 649–651.
Parruti, G., Peracchia, F., Sallcse, M., Ambrosini, G., Masini, M., Rotilio, D., and DeBlasi, A. (1993). J. Biol. Chem. 268, 9753–9761.
Raming, K., Frietag, J., Krieger, J., and Breer, H. (1993). Cell. Signal. 5, 69–80.
Rapoport, B., Kaufman, K. D., and Chazenbalk, G. D. (1992). Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 84, R39–R43.
Schleicher, A., Kühn, H., and Hofmann, K. P. (1989). Biochemistry 28, 1770–1775.
Schnarr, M., Durand, M., and Maurizot, J. C. (1983). Biochemistry 22, 3563–3570.
Smith, W. C., Milam, A. H., Dugger, D., Arendt, A., Hargrave, P. A., and Palczewski, K. (1994). J. Biol. Chem. 269, 15407–15410.
Sterne-Marr, R., Gurevich, V. V., Goldsmith, P., Bodine, R. C., Sanders, C., Donoso, L. A., and Benovic, J. L. (1993). J. Biol. Chem. 268, 15640–15648.
Tsuda, M., Kikuchi, T., Yamaki, K., and Shinohara, T. (1991). Eur. J. Biochem. 200, 95–101.
Ungerer, M., Parruti, G., Böhm, M., Puzicha, M., DeBlasi, A., Erdmann, E., and Lohse, M. J. (1994). Circ. Res. 74, 206–213.
Wacker, W. B., Donoso, L. A., Kalsow, C. M., Yankeelov, J. A., Jr., and Organisciak, D. T. (1977). J. Immunol. 119, 1949–1958.
Wilden, U., Wüst, E., Weyand, I., and Kühn, H. (1986). FEBS Lett. 207, 292–295.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilson, C.J., Copeland, R.A. Spectroscopic Characterization of Arrestin Interactions with Competitive Ligands: Study of Heparin and Phytic Acid Binding. J Protein Chem 16, 755–763 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026311832660
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026311832660