Abstract
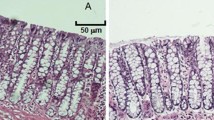
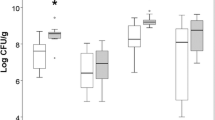
Repair of superficial damage to gastrointestinal mucosa occurs by a process called restitution, with epithelial integrity and continuity reestablished before cell proliferation occurs. The aim of the present study was to investigate the diversity of restitution in rat jejunum exposed to different concentrations of deoxycholic acid (DOC; 1.5–100 mmol/liter). Following a 30-min exposure, the intestine was allowed to recover for 15–330 minutes. DOC caused dose-dependent tissue destruction. Exfoliating epithelial cells were already observed after 5 min of exposure (1.5 mmol/liter), with simple sloughing off and resealing of the tips. Moderately affected epithelium (20 mmol/liter) demonstrated denudation of villous tips and then became covered with goblet cells. Severely affected epithelium (100 mmol/liter) also appeared to be replaced with goblet cells. These data suggest that the reversibility of mucosal damage induced by DOC is due to a variety of processes, which depend on the severity of the mucosal insult.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cameron GR, Khanna SD: Regeneration of the intestinal villi after extensive mucosal infarction. J Pathol Bacterial 77:505-510, 1959
Silen W, Ito S: Mechanisms for rapid re-epithelialization of the gastric mucosal surface. Annu Rev Physiol 47:217-229, 1985
Lacy ER: Epithelial restitution in the gastrointestinal tract. J Clin Gastroenterol 10(suppl 1):S72-S77, 1988
Paimela H, Goddard PJ, Silen W: Present views on restitution of gastrointestinal epithelium. Dig Dis Sci 40:2495-2496, 1995
Lacy ER: Rapid epithelial restitution in the stomach: An update perspective. Scand J Gastroenterol 30(suppl 210):6-8, 1995
Lacy ER, Ito S: Rapid epithelial restitution of the rat gastric mucosa after ethanol injury. Lab Invest 51:573-585, 1984
Morris GP, Wallace JL: The roles of ethanol and of acid in the production of gastric mucosa erosions in rats. Virchow's Arch (Cell Pathol) 38:23-28, 1981
Critchlow J, Magee D, Ito S, Takeuchi K, Silen W: Requirements for restitution of the surface epithelium of frog stomach after mucosal injury. Gastroenterology 88:237-249, 1985
Feil W, Klimesch S, Karner P, Wenzl E, Starlinger M, Lacy ER. Schiessel R: Importance of an alkaline microenvironment for rapid restitution of the rabbit duodenal mucosa in vitro. Gastroenterology 97:112-122, 1989
Prasad M, Goddard PJ, Carter KJ, Milbank AJ, Silen W: In vitro restitution in rat colon: Effects of butyrate and bicarbonate. Gastroenterology 104(suppl):A272, 1993
Feil W, Lacy ER, Wong Y-MM, Burger D, Wenzl E, Starlinger M, Schiessel R: Rapid epithelial restitution of human and rabbit colonic mucosa. Gastroenterology 97:685-701, 1989
Binder HJ, Metha P: Short-chain fatty acids stimulate active sodium and chloride absorption in vitro in the rat distal colon. Gastroenterology 96:989-996, 1989
Modlin IM, Hunt RH: Critical reappraisal of mucosal repair mechanisms. Scand J Gastroenterol 30(suppl 210):28-31, 1995
Dieckgraefe BK, Stenson WF, Alpers DH: Gastrointestinal epithelial response to injury. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 12:109-114, 1996
Wilson AJ, Gibson PR: Epithelial migration in the colon: filling in the gaps. Clin Sci 93:97-108, 1997
Gibson PR, Anderson RP, Mariadason JM, Wilson AJ: Protective role of the epithelium of the small intestine and colon. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2:279-302, 1996
Moore R, Carlson S, Madara JL: Villus contraction aids repair for intestinal epithelium after injury. Am J Physiol 257(Gastrointest. Liver Physiol 20):G274-G283, 1989
Moore R, Carlson S, Madara JL: Rapid barrier restitution in an in vitro model of intestinal epithelial injury. Lab Invest 60:237-244, 1989
Ikeda H, Suzuki Y, Suzuki M, Koike M, Tamura J, Tong J, Nomura M, Itoh G: Apoptosis is a major mode of cell death caused by ischaemia and ischaemia/reperfusion injury to the rat intestinal epithelium. Gut 42:530-537, 1998
Ikeda H, Yang CL, Tong J, Nishimaki H, Masuda K, Takano M, Kasai, Itoh G: Rat small intestinal goblet cell kinetics in the process of restitution of surface epithelium subjected to ischemia-reperfusion injury. Dig Dis Sci 47:590-601, 2002
Sund RB, Jacobsen DN: In vivo reversibility of the jejunal glucose and cation transport alteration caused by intraluminal surfactants in the rat. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 43:339-345, 1978
Inoue T, Osakake H: A new drying method of biological specimens for scanning electron microscopy: The t-butyl alcohol freeze-drying method. Arch Histol Cytol 51:53-59, 1988
Ichimura E, Fukuda T, Oyama T, Kashiwabara K, Sakurai S, Sano T, Nakajima T: Formalin fixation by boiling: Is it suitable for the TUNEL staining? Pathol Int 45:971-972, 1995
Matovelo JA, Landsverk T, Sund RB: Alteration of ultrastructure and of cytoplasmic filaments in remodeling rat jejunal epithelial cells during recovery from deoxycholate. APMIS 98:887-895, 1990
Matovelo JA, Landsverk T, Sund RB: Enzyme changes in remodeling epithelial cells: a histochemical study of the rat jejunum in vivo during and following exposure to deoxycholic acid. APMIS 101:369-377, 1993
Matovelo JA, Sund RB, Landsverk T: Morphological and functional recovery following exposure to deoxycholic acid. APMIS 97:798-810, 1989
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masuda, K., Ikeda, H., Kasai, K. et al. Diversity of Restitution After Deoxycholic Acid-Induced Small Intestinal Mucosal Injury in the Rat. Dig Dis Sci 48, 2108–2115 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026295014525
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026295014525