Abstract
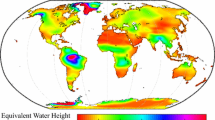
The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment, GRACE , will enable the recovery of monthly estimates of changes in water storage, on land and in the ocean, averaged over arbitrary regions having length scales of a few hundred km and larger. These data will allow the examination of changes in the distribution of water in the ocean, in snow and ice on polar ice sheets, and in continental water and snow storage. Extracting changes in water storage from the GRACE dataset requires the use of averaging kernels which can isolate a particular region. To estimate the accuracy to which continental water storage changes in a few representative regions may be recovered, we construct a synthetic GRACE dataset from global, gridded models of surface-mass variability. We find that regional changes in water storage can be recovered with rms error less than 1 cm of equivalent water thickness, for regions having areas of 4 × 105 km2 and larger. Signals in smaller regions may also be recovered; however, interpretations of such results require a careful consideration of model resolution, as well as the nature of the averaging kernel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dukowicz, J.K., and R.D. Smith: 1994, Implicit free-surface method for the Bryan-Cox-Semtner ocean model, J. Geophys. Res. 99, 7991-8014.
Entin, J., A. Robock, K. Vinnikov, S. Hollinger, S. Liu, and A. Namkhai: 2000, Temporal and spatial scales of observed soil moisture variations in the extratropics, J. Geophys. Res. 105(D9), 11,865-11,877.
GRACE Science and Mission Requirements Document: 2001, GRACE 327-200, JPL Publ. D-15928, Rev. D.
Milly, P.C.D., and A.B. Shmakin: 2001, Global modeling of land water and energy balances: 1. The Land Dynamics (LaD) Model, submitted to Journal of Hydrometeorology.
Swenson, S., and J. Wahr: 2002, Methods for inferring regional surface-mass anomalies from GRACE measurements of time-variable gravity, J. Geophys. Res. 107(B9), 2193, doi:10.1029/2001JB000576.
Swenson, S., and J. Wahr: 2002, Estimated effects of the vertical structure of atmospheric mass on the time-variable geoid, J. Geophys. Res. 107(B9), 2194, doi:10.1029/2000JB000024.
Velicogna, I., J. Wahr, and H. van den Dool: 2001, Can surface pressure be used to remove atmospheric contributions from GRACE data with sufficient accuracy to recover hydrological signals?, J. Geophys. Res. 106(B8), 16,415-16,434.
Wahr, J., M. Molenaar, and F. Bryan: 1998, Time variability of the Earth's gravity field: Hydrological and oceanic effects and their possible detection using GRACE, J. Geophys. Res. 103(B12), 30,205-30,229.
Watkins, M. M., W.M. Folkner, B. F. Chao, and B. D. Tapley: 1999, The Proposed NASA EX-5 Mission: A Laser Interferometery Successor to GRACE, Eos Trans. AGU 80(46), Nov. 16, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swenson, S., Wahr, J. Monitoring Changes in Continental Water Storage with GRACE. Space Science Reviews 108, 345–354 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026135627671
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026135627671