Abstract
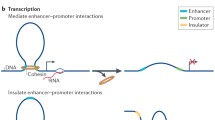
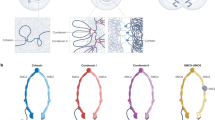
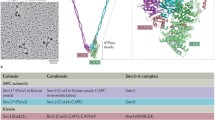
Structural chromatin proteins of the SMC (Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes) family play an important role in structural DNA reorganization in pro- and eukaryotes. Eukaryotic SMC proteins are the core components of the cohesin and condensin complexes. The cohesin complex is responsible for sister chromatid and homolog cohesion in mitosis and meiosis. The condensin complex uses ATP energy to induce positive coiled-coils in DNA, which results in compaction of the latter and formation of mitotic chromosome scaffold. In addition, the SMC proteins constitute recombination and recombination repair complexes. In hermaphrodites of nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, the SMC protein-containing complex controls dosage compensation and inactivation of the X chromosome genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Strunnikov, A.V., Larionov, V.L., and Koshland, D., SMC1: An Essential Yeast Gene Encoding a Putative Head-Rod-Tail Protein Is Required for Nuclear Division and Defines a New Ubiquitous Protein Family, J. Cell Biol., 1993, vol. 123, no. 6, part 2, pp. 1635–1648.
Chuang, P.T., Albertson, D.G., and Meyer, B.J., DPY-27: A Chromosome Condensation Protein Homolog That Regulates Caenorhabditis elegans Dosage Compensation through Association with the X Chromosome, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1994, vol. 79, no. 3, pp. 459–474.
Fousteri, M.I. and Lehmann, A.R., A Novel SMC Protein Complex in Schizosaccharomyces pombe Contains the Rad18 DNA Repair Protein, EMBO J., 2000, vol. 19, no. 7, pp. 1691–1702.
Hirano, T. and Mitchison, T.J., A Heterodimeric Coiled-Coil Protein Required for Mitotic Chromosome Condensation in Vitro, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1994, vol. 79, no. 3, pp. 449–458.
Jessberger, R., Chui, G., Linn, S., and Kemper, B., Analysis of the Mammalian Recombination Protein Complex RC-1, Mutat. Res., 1996, vol. 350, no. 1, pp. 217–227.
Lieb, J.D., Albrecht, M.R., Chuang, P.T., and Meyer, B.J., MIX-1: An Essential Component of the Caenorhabditis elegans Mitotic Machinery Executes X-Chromosome Dosage Compensation, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1998, vol. 92, no. 2, pp. 265–277.
Revenkova, E., Eijpe, M., Heyting, C., et al., Novel Meiosis-Specific Isoform of Mammalian SMC1, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2001, vol. 21, no. 20, pp. 6984–6998.
Saitoh, N., Goldberg, I.G., Wood, E.R., and Earnshaw, W.C., ScII: An Abundant Chromosome Scaffold Protein Is a Member of a Family of Putative ATPases with an Unusual Predicted Tertiary Structure, J. Cell Biol., 1994, vol. 127, no. 2, pp. 303–318.
Saka, Y., Sutani, T., Yamashita, Y., et al., Fission Yeast Cut3 and Cut14, Members of a Ubiquitous Protein Family, Are Required for Chromosome Condensation and Segregation in Mitosis, EMBO J., 1994, vol. 13, no. 20, pp. 4938–4952.
Schmiesing, J.A., Ball, A.R., Jr., Gregson, H.C., et al., Identification of Two Distinct Human SMC Protein Complexes Involved in Mitotic Chromosome Dynamics, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1998, vol. 95, no. 22, pp. 12 906–12 911.
Steffensen, S., Coelho, P.A., Cobbe, N., et al., A Role for Drosophila SMC4 in the Resolution of Sister Chromatids in Mitosis, Curr. Biol., 2001, vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 295–307.
Strunnikov, A.V., Hogan, E., and Koshland, D., SMC2, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae Gene Essential for Chromosome Segregation and Condensation, Defines a Subgroup within the SMC Family, Genes Dev., 1995, vol. 9, no. 5, pp. 587–599.
Britton, R.A., Lin, D.C., and Grossman, A.D., Characterization of a Prokaryotic SMC Protein Involved in Chromosome Partitioning, Genes Dev., 1998, vol. 12, no. 9, pp. 1254–1259.
Sultana, R., Adler, D.A., Edelhoff, S., et al., The Mouse Sb1.8 Gene Located at the Distal End of the X Chromosome Is Subject to X Inactivation, Hum. Mol. Genet., 1995, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 257–263.
Holt, C.L. and May, G.S., An Extragenic Suppressor of the Mitosis-Defective bimD6 Mutation of Aspergillus nidulans Codes for a Chromosome Scaffold Protein, Genetics, 1996, vol. 142, no. 3, pp. 777–787.
Hagstrom, K.A., Holmes, V.F., Cozzarelli, N.R., and Meyer, B.J., Caenorhabditis elegans Condensin Promotes Mitotic Chromosome Architecture, Centromere Organization, and Sister Chromatid Segregation during Mitosis and Meiosis, Genes Dev., 2002, vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 729–742.
Harvey, S.H., Krien, M.J., and O'Connell, M.J., Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes (SMC) Proteins, a Family of Conserved ATPases, Genome Biol., 2002, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 3003.1–3003.5.
Jessberger, R., The Many Functions of SMC Proteins in Chromosome Dynamics, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2002, vol. 3, no. 10, pp. 767–778.
Hirano, T., The ABCs of SMC Proteins: Two-Armed ATPases for Chromosome Condensation, Cohesion, and Repair, Genes Dev., 2002, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 399–414.
Nasmyth, K., Disseminating the Genome: Joining, Resolving, and Separating Sister Chromatids during Mitosis and Meiosis, Annu. Rev. Genet., 2001, vol. 35, pp. 673–745.
Graumann, P.L., Losick, R., and Strunnikov, A.V., Subcellular Localization of Bacillus subtilis SMC, a Protein Involved in Chromosome Condensation and Segregation, J. Bacteriol., 1998, vol. 180, no. 21, pp. 5749–5755.
Ghiselli, G., Siracusa, L.D., and Iozzo, R.V., Complete cDNA Cloning, Genomic Organization, Chromosomal Assignment, Functional Characterization of the Promoter, and Expression of the Murine Bamacan Gene, J. Biol. Chem., 1999, vol. 274, no. 24, pp. 17384–17393.
Pavlova, S.V., Nesterova, T.B., and Zakian, S.M., Genes for Structural Proteins of the SMC Family in the Common Vole Microtus arvalis, Mol. Biol. (Moscow), 2001, vol. 35, no. 3, pp. 383–390.
Jones, S. and Sgouros, J., The Cohesin Complex: Sequence Homologies, Interaction Networks and Shared Motifs, Genome Biol., 2001, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 0009.1–0009.12.
Anderson, D.E., Losada, A., Erickson, H.P., and Hirano, T., Condensin and Cohesin Display Different Arm Conformations with Characteristic Hinge Angles, J. Cell Biol., 2002, vol. 28, p. 28.
Melby, T.E., Ciampaglio, C.N., Briscoe, G., and Erickson, H.P., The Symmetrical Structure of Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes (SMC) and MukB Proteins: Long, Antiparallel Coiled Coils, Folded at a Flexible Hinge, J. Cell Biol., 1998, vol. 142, no. 6, pp. 1595–1604.
Haering, C.H., Lowe, J., Hochwagen, A., and Nasmyth, K., Molecular Architecture of SMC Proteins and the Yeast Cohesin Complex, Mol. Cell, 2002, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 773–788.
Lowe, J., Cordell, S.C., and van den Ent, F., Crystal Structure of the SMC Head Domain: An ABC ATPase with 900 Residues Antiparallel Coiled-Coil Inserted, J. Mol. Biol., 2001, vol. 306, no. 1, pp. 25–35.
Hirano, M., Anderson, D.E., Erickson, H.P., and Hirano, T., Bimodal Activation of SMC ATPase by Intra-and Intermolecular Interactions, EMBO J., 2001, vol. 20, no. 12, pp. 3238–3250.
Saitoh, N., Goldberg, I., and Earnshaw, W.C., The SMC Proteins and the Coming of Age of the Chromosome Scaffold Hypothesis, BioEssays, 1995, vol. 17, no. 9, pp. 759–766.
Peterson, C.L., The SMC Family: Novel Motor Proteins for Chromosome Condensation?, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1994, vol. 79, no. 3, pp. 389–392.
Hirano, T., Mitchison, T.J., and Swedlow, J.R., The SMC Family: From Chromosome Condensation to Dosage Compensation, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 1995, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 329–336.
Akhmedov, A.T., Frei, C., Tsai-Pflugfelder, M., et al., Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes Protein CTerminal Domains Bind Preferentially to DNA with Secondary Structure, J. Biol. Chem., 1998, vol. 273, no. 37, pp. 24 088–24 094.
Akhmedov, A.T., Gross, B., and Jessberger, R., Mammalian SMC3 C-Terminal and Coiled-Coil Protein Domains Specifically Bind Palindromic DNA, Do Not Block DNA Ends, and Prevent DNA Bending, J. Biol. Chem., 1999, vol. 274, no. 53, pp. 38 216–38 224.
Kimura, K. and Hirano, T., ATP-Dependent Positive Supercoiling of DNA by 13S Condensin: A Biochemical Implication for Chromosome Condensation, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1997, vol. 90, no. 4, pp. 625–634.
Kimura, K. and Hirano, T., Dual Roles of the 11S Regulatory Subcomplex in Condensin Functions, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2000, vol. 97, no. 22, pp. 11 972–11 977.
Losada, A. and Hirano, T., Intermolecular DNA Interactions Stimulated by the Cohesin Complex in Vitro: Implications for Sister Chromatid Cohesion, Curr. Biol., 2001, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 268–272.
Hirano, M. and Hirano, T., ATP-Dependent Aggregation of Single-Stranded DNA by a Bacterial SMC Homodimer, EMBO J., 1998, vol. 17, no. 23, pp. 7139-7148.
Guacci, V., Koshland, D., and Strunnikov, A., A Direct Link between Sister Chromatid Cohesion and Chromosome Condensation Revealed through the Analysis of MCD1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1997, vol. 91, no. 1, pp. 47–57.
Michaelis, C., Ciosk, R., and Nasmyth, K., Cohesins: Chromosomal Proteins That Prevent Premature Separation of Sister Chromatids, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1997, vol. 91, no. 1, pp. 35–45.
Losada, A., Hirano, M., and Hirano, T., Identification of Xenopus SMC Protein Complexes Required for Sister Chromatid Cohesion, Genes Dev., 1998, vol. 12, no. 13, pp. 1986–1997.
Hirano, T., Kobayashi, R., and Hirano, M., Condensins, Chromosome Condensation Protein Complexes Containing XCAP-C, XCAP-E and a Xenopus Homolog of the Drosophila Barren Protein, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1997, vol. 89, no. 4, pp. 511–521.
Schmiesing, J.A., Gregson, H.C., Zhou, S., and Yokomori, K., A Human Condensin Complex Containing hCAP-C-hCAP-E and CNAP1, a Homolog of Xenopus XCAP-D2, Colocalizes with Phosphorylated Histone H3 during the Early Stage of Mitotic Chromosome Condensation, Mol. Cell Biol., 2000, vol. 20, no. 18, pp. 6996–7006.
Gregson, H.C., Van Hooser, A.A., Ball, A.R., Jr., et al., Localization of Human SMC1 Protein at Kinetochores, Chromosome Res., 2002, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 267–277.
Ball, A.R., Jr. and Yokomori, K., The Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes (SMC) Family of Proteins in Mammals, Chromosome Res., 2001, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 85–96.
Cobbe, N. and Heck, M.M., A Review: SMCs in the World of Chromosome Biology—From Prokaryotes to Higher Eukaryotes, J. Struct. Biol., 2000, vol. 129, nos. 2-3, pp. 123–143.
Hirano, T., SMC Protein Complexes and Higher-Order Chromosome Dynamics, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 1998, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 317–322.
Hirano, T., SMC-Mediated Chromosome Mechanics: A Conserved Scheme from Bacteria to Vertebrates?, Genes Dev., 1999, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 11–19.
Hirano, T., Chromosome Cohesion, Condensation, and Separation, Annu. Rev. Biochem., 2000, vol. 69, pp. 115–144.
Jessberger, R., Frei, C., and Gasser, S.M., Chromosome Dynamics: The SMC Protein Family, Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 1998, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 254–259.
Nasmyth, K., Peters, J.M., and Uhlmann, F., Splitting the Chromosome: Cutting the Ties That Bind Sister Chromatids, Science, 2000, vol. 288, no. 5470, pp. 1379–1385.
Nasmyth, K., Segregating Sister Genomes: The Molecular Biology of Chromosome Separation, Science, 2002, vol. 297, no. 5581, pp. 559–565.
Strunnikov, A.V., SMC Proteins and Chromosome Structure, Trends Cell Biol., 1998, vol. 8, no. 11, pp. 454–459.
Strunnikov, A.V. and Jessberger, R., Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes (SMC) Proteins: Conserved Molecular Properties for Multiple Biological Functions, Eur. J. Biochem., 1999, vol. 263, no. 1, pp. 6–13.
Taylor, E.M., Moghraby, J.S., Lees, J.H., et al., Characterization of a Novel Human SMC Heterodimer Homologous to the Schizosaccharomyces pombe Rad18/Spr18 Complex, Mol. Biol. Cell, 2001, vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 1583–1594.
Uhlmann, F., Chromosome Condensation: Packaging the Genome, Curr. Biol., 2001, vol. 11, no. 10, pp. R384–R387.
Lee, J.Y. and Orr-Weaver, T.L., The Molecular Basis of Sister-Chromatid Cohesion, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 2001, vol. 17, pp. 753–777.
Donze, D., Adams, C.R., Rine, J., and Kamakaka, R.T., The Boundaries of the Silenced HMR Domain in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Genes Dev., 1999, vol. 13, no. 6, pp. 698–708.
Losada, A. and Hirano, T., Shaping the Metaphase Chromosome: Coordination of Cohesion and Condensation, BioEssays, 2001, vol. 23, no. 10, pp. 924–935.
Losada, A., Yokochi, T., Kobayashi, R., and Hirano, T., Identification and Characterization of SA/Scc3p Subunits in the Xenopus and Human Cohesin Complexes, J. Cell Biol., 2000, vol. 150, no. 3, pp. 405–416.
Toth, A., Ciosk, R., Uhlmann, F., et al., Yeast Cohesin Complex Requires a Conserved Protein, Eco1p (Ctf7), to Establish Cohesion between Sister Chromatids during DNA Replication, Genes Dev., 1999, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 320–333.
Tomonaga, T., Nagao, K., Kawasaki, Y., et al., Characterization of Fission Yeast Cohesin: Essential Anaphase Proteolysis of Rad21 Phosphorylated in the S Phase, Genes Dev., 2000, vol. 14, no. 21, pp. 2757–2770.
Sumara, I., Vorlaufer, E., Gieffers, C., et al., Characterization of Vertebrate Cohesin Complexes and Their Regulation in Prophase, J. Cell Biol., 2000, vol. 151, no. 4, pp. 749–762.
Darwiche, N., Freeman, L.A., and Strunnikov, A., Characterization of the Components of the Putative Mammalian Sister Chromatid Cohesion Complex, Gene, 1999, vol. 233, nos. 1-2, pp. 39–47.
Skibbens, R.V., Corson, L.B., Koshland, D., and Hieter, P., Ctf7p Is Essential for Sister Chromatid Cohesion and Links Mitotic Chromosome Structure to the DNA Replication Machinery, Genes Dev., 1999, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 307–319.
Ivanov, D., Schleiffer, A., Eisenhaber, F., et al., Eco1 Is a Novel Acetyltransferase That Can Acetylate Proteins Involved in Cohesion, Curr. Biol., 2002, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 323–328.
Tanaka, K., Yonekawa, T., Kawasaki, Y., et al., Fission Yeast Eso1p Is Required for Establishing Sister Chromatid Cohesion during S Phase, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2000, vol. 20, no. 10, pp. 3459–3469.
Wang, Z., Castano, I.B., De Las Penas, A., et al., Pol?: A DNA Polymerase Required for Sister Chromatid Cohesion, Science, 2000, vol. 289, no. 5480, pp. 774–779.
Mayer, M.L., Gygi, S.P., Aebersold, R., and Hieter, P., Identification of RFC (Ctf18p, Ctf8p, Dcc1p): An Alternative RFC Complex Required for Sister Chromatid Cohesion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Mol. Cell, 2001, vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 959–970.
Ciosk, R., Shirayama, M., Shevchenko, A., et al., Cohesin's Binding to Chromosomes Depends on a Separate Complex Consisting of Scc2 and Scc4 Proteins, Mol. Cell, 2000, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 243–254.
Furuya, K., Takahashi, K., and Yanagida, M., Faithful Anaphase Is Ensured by Mis4, a Sister Chromatid Cohesion Molecule Required in S Phase and Not Destroyed in G1 Phase, Genes Dev., 1998, vol. 12, no. 21, pp. 3408–3418.
Hartman, T., Stead, K., Koshland, D., and Guacci, V., Pds5p Is An Essential Chromosomal Protein Required for Both Sister Chromatid Cohesion and Condensation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, J. Cell Biol., 2000, vol. 151, no. 3, pp. 613–626.
Panizza, S., Tanaka, T., Hochwagen, A., et al., Pds5 Cooperates with Cohesin in Maintaining Sister Chromatid Cohesion, Curr. Biol., 2000, vol. 10, no. 24, pp. 1557–1564.
Tanaka, K., Hao, Z., Kai, M., and Okayama, H., Establishment and Maintenance of Sister Chromatid Cohesion in Fission Yeast by a Unique Mechanism, EMBO J., 2001, vol. 20, no. 20, pp. 5779–5790.
Neuwald, A.F. and Hirano, T., HEAT Repeats Associated with Condensins, Cohesins, and Other Complexes Involved in Chromosome-Related Functions, Genome Res., 2000, vol. 10, no. 10, pp. 1445–1452.
Blat, Y. and Kleckner, N., Cohesins Bind to Preferential Sites along Yeast Chromosome III, with Differential Regulation along Arms versus the Centric Region, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1999, vol. 98, no. 2, pp. 249–259.
Laloraya, S., Guacci, V., and Koshland, D., Chromosomal Addresses of the Cohesin Component Mcd1p, J. Cell Biol., 2000, vol. 151, no. 5, pp. 1047–1056.
Megee, P.C., Mistrot, C., Guacci, V., and Koshland, D., The Centromeric Sister Chromatid Cohesion Site Directs Mcd1p Binding to Adjacent Sequences, Mol. Cell, 1999, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 445–450.
Sumara, I., Vorlaufer, E., Stukenberg, P.T., et al., The Dissociation of Cohesin from Chromosomes in Prophase Is Regulated by Polo-like Kinase, Mol. Cell, 2002, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 515–525.
Gregson, H.C., Schmiesing, J.A., Kim, J.S., et al., A Potential Role for Human Cohesin in Mitotic Spindle Aster Assembly, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, vol. 276, no. 50, pp. 47 575–47 582.
Hoque, M.T. and Ishikawa, F., Human Chromatid Cohesin Component hRad21 Is Phosphorylated in M Phase and Associated with Metaphase Centromeres, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, vol. 276, no. 7, pp. 5059–5067.
Warren, W.D., Steffensen, S., Lin, E., et al., The Drosophila RAD21 Cohesin Persists at the Centromere Region in Mitosis, Curr. Biol., 2000, vol. 10, no. 22, pp. 1463–1466.
Sutani, T., Yuasa, T., Tomonaga, T., et al., Fission Yeast Condensin Complex: Essential Roles of Non-SMC Subunits for Condensation and Cdc2 Phosphorylation of Cut3/SMC4, Genes Dev., 1999, vol. 13, no. 17, pp. 2271–2283.
Freeman, L., Aragon-Alcaide, L., and Strunnikov, A., The Condensin Complex Governs Chromosome Condensation and Mitotic Transmission of rDNA, J. Cell Biol., 2000, vol. 149, no. 4, pp. 811–824.
Bhat, M.A., Philp, A.V., Glover, D.M., and Bellen, H.J., Chromatid Segregation at Anaphase Requires the barren Product, a Novel Chromosome-Associated Protein That Interacts with Topoisomerase II, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1996, vol. 87, no. 6, pp. 1103–1114.
Cabello, O.A., Eliseeva, E., He, W.G., et al., Cell Cycle-Dependent Expression and Nucleolar Localization of hCAP-H, Mol. Biol. Cell, 2001, vol. 12, no. 11, pp. 3527–3537.
Yoshimura, S.H., Hizume, K., Murakami, A., et al., Condensin Architecture and Interaction with DNA: Regulatory Non-SMC Subunits Bind to the Head of SMC Heterodimer, Curr. Biol., 2002, vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 508–513.
Kimura, K., Hirano, M., Kobayashi, R., and Hirano, T., Phosphorylation and Activation of 13S Condensin by Cdc2 in Vitro, Science, 1998, vol. 282, no. 5388, pp. 487–490.
Kimura, K., Cuvier, O., and Hirano, T., Chromosome Condensation by a Human Condensin Complex in Xenopus Egg Extracts, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, vol. 276, no. 8, pp. 5417–5420.
Lavoie, B.D., Hogan, E., and Koshland, D., In Vivo Dissection of the Chromosome Condensation Machinery: Reversibility of Condensation Distinguishes Contributions of Condensin and Cohesin, J. Cell Biol., 2002, vol. 156, no. 5, pp. 805–815.
Chu, D.S., Dawes, H.E., Lieb, J.D., et al., A Molecular Link between Gene-Specific and Chromosome-Wide Transcriptional Repression, Genes Dev., 2002, vol. 16, no. 7, pp. 796–805.
Ball, A.R., Jr., Schmiesing, J.A., Zhou, C., et al., Identification of a Chromosome-Targeting Domain in the Human Condensin Subunit CNAP1/hCAP-D2/Eg7, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2002, vol. 22, no. 16, pp. 5769–5781.
Hendzel, M.J., Wei, Y., Mancini, M.A., et al., Mitosis-Specific Phosphorylation of Histone H3 Initiates Primarily within Pericentromeric Heterochromatin during G2 and Spreads in an Ordered Fashion Coincident with Mitotic Chromosome Condensation, Chromosoma, 1997, vol. 106, no. 6, pp. 348–360.
MacCallum, D.E., Losada, A., Kobayashi, R., and Hirano, T., ISWI Remodeling Complexes in Xenopus Egg Extracts: Identification as Major Chromosomal Components That Are Regulated by INCENP-Aurora B, Mol. Biol. Cell, 2002, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 25–39.
Eide, T., Carlson, C., Tasken, K.A., et al., Distinct but Overlapping Domains of AKAP95 Are Implicated in Chromosome Condensation and Condensin Targeting, EMBO Rep., 2002, vol. 18, p. 18.
Steen, R.L., Cubizolles, F., Le Guellec, K., and Collas, P., A Kinase-Anchoring Protein (AKAP)95 Recruits Human Chromosome-Associated Protein (hCAP)-D2/Eg7 for Chromosome Condensation in Mitotic Extract, J. Cell Biol., 2000, vol. 149, no. 3, pp. 531–536.
Lupo, R., Breiling, A., Bianchi, M.E., and Orlando, V., Drosophila Chromosome Condensation Proteins Topoisomerase II and Barren Colocalize with Polycomb and Maintain Fab-7 PRE Silencing, Mol. Cell, 2001, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 127–136.
Sutani, T. and Yanagida, M., DNA Renaturation Activity of the SMC Complex Implicated in Chromosome Condensation, Nature, 1997, vol. 388, no. 6644, pp. 798–801.
Bazett-Jones, D.P., Kimura, K., and Hirano, T., Efficient Supercoiling of DNA by a Single Condensin Complex as Revealed by Electron Spectroscopic Imaging, Mol. Cell, 2002, vol. 9, no. 6, pp. 1183–1190.
Kimura, K., Rybenkov, V.V., Crisona, N.J., et al., 13S Condensin Actively Reconfigures DNA by Introducing Global Positive Writhe: Implications for Chromosome Condensation, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1999, vol. 98, no. 2, pp. 239–248.
Uhlmann, F. and Nasmyth, K., Cohesion between Sister Chromatids Must Be Established during DNA Replication, Curr. Biol., 1998, vol. 8, no. 20, pp. 1095–1101.
Hauf, S., Waizenegger, I.C., and Peters, J.M., Cohesin Cleavage by Separase Required for Anaphase and Cytokinesis in Human Cells, Science, 2001, vol. 293, no. 5533, pp. 1320–1323.
Jager, H., Herzig, A., Lehner, C.F., and Heidmann, S., Drosophila Separase Is Required for Sister Chromatid Separation and Binds to PIM and THR, Genes Dev., 2001, vol. 15, no. 19, pp. 2572–2584.
Jallepalli, P.V., Waizenegger, I.C., Bunz, F., et al., Securin Is Required for Chromosomal Stability in Human Cells, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 2001, vol. 105, no. 4, pp. 445–457.
Ciosk, R., Zachariae, W., Michaelis, C., et al., An ESP1/PDS1 Complex Regulates Loss of Sister Chromatid Cohesion at the Metaphase to Anaphase Transition in Yeast, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1998, vol. 93, no. 6, pp. 1067–1076.
Waizenegger, I.C., Hauf, S., Meinke, A., and Peters, J.M., Two Distinct Pathways Remove Mammalian Cohesin from Chromosome Arms in Prophase and from Centromeres in Anaphase, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 2000, vol. 103, no. 3, pp. 399–410.
Amon, A., Together until Separin Do Us Part, Nat. Cell Biol., 2001, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. E12–E14.
Alexandru, G., Uhlmann, F., Mechtler, K., et al., Phosphorylation of the Cohesin Subunit Scc1 by Polo/Cdc5 Kinase Regulates Sister Chromatid Separation in Yeast, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 2001, vol. 105, no. 4, pp. 459–472.
Chuang, P.T., Lieb, J.D., and Meyer, B.J., Sex-Specific Assembly of a Dosage Compensation Complex on the Nematode X Chromosome, Science, 1996, vol. 274, no. 5293, pp. 1736–1739.
Lieb, J.D., Capowski, E.E., Meneely, P., and Meyer, B.J., DPY-26, a Link between Dosage Compensation and Meiotic Chromosome Segregation in the Nematode, Science, 1996, vol. 274, no. 5293, pp. 1732–1736.
Carmi, I. and Meyer, B.J., The Primary Sex Determination Signal of Caenorhabditis elegans, Genetics, 1999, vol. 152, no. 3, pp. 999–1015.
Wood, W.B., Streit, A., and Li, W., Dosage Compensation: X-Repress Yourself, Curr. Biol., 1997, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 227–230.
Dawes, H.E., Berlin, D.S., Lapidus, D.M., et al., Dosage Compensation Proteins Targeted to X Chromosomes by a Determinant of Hermaphrodite Fate, Science, 1999, vol. 284, no. 5421, pp. 1800–1804.
Kuroda, M.I. and Villeneuve, A.M., Promiscuous Chromosomal Proteins: Complexes about Sex, Science, 1996, vol. 274, no. 5293, pp. 1633–1634.
Klein, F., Mahr, P., Galova, M., et al., A Central Role for Cohesins in Sister Chromatid Cohesion, Formation of Axial Elements, and Recombination during Yeast Meiosis, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1999, vol. 98, no. 1, pp. 91–103.
Watanabe, Y. and Nurse, P., Cohesin Rec8 Is Required for Reductional Chromosome Segregation at Meiosis, Nature,1999, vol. 400, no. 6743, pp. 461–464.
Prieto, I., Suja, J.A., Pezzi, N., et al., Mammalian STAG3 Is a Cohesin Specific to Sister Chromatid Arms in Meiosis I, Nat. Cell Biol., 2001, vol. 3, no. 8, pp. 761–766.
Eijpe, M., Heyting, C., Gross, B., and Jessberger, R., Association of Mammalian SMC1 and SMC3 Proteins with Meiotic Chromosomes and Synaptonemal Complexes, J. Cell Sci., 2000, vol. 113, pp. 673–682.
Jessberger, R., Podust, V., Hubscher, U., and Berg, P., A Mammalian Protein Complex That Repairs Double-Strand Breaks and Deletions by Recombination, J. Biol. Chem., 1993, vol. 268, no. 20, pp. 15 070–15 079.
Stursberg, S., Riwar, B., and Jessberger, R., Cloning and Characterization of Mammalian SMC1 and SMC3 Genes and Proteins, Components of the DNA Recombination Complexes RC-1, Gene, 1999, vol. 228, nos. 1-2, pp. 1–12.
Mengiste, T., Revenkova, E., Bechtold, N., and Paszkowski, J., An SMC-like Protein Is Required for Efficient Homologous Recombination in Arabidopsis, EMBO J., 1999, vol. 18, no. 16, pp. 4505–4512.
Lehmann, A.R., Walicka, M., Griffiths, D.J., et al., The rad18 Gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe Defines a New Subgroup of the SMC Superfamily Involved in DNA Repair, Mol. Cell. Biol., 1995, vol. 15, no. 12, pp. 7067–7080.
Yonemasu, R., McCready, S.J., Murray, J.M., et al., Characterization of the Alternative Excision Repair Pathway of UV-Damaged DNA in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Nucleic Acids Res., 1997, vol. 25, no. 8, pp. 1553–1558.
Verkade, H.M., Bugg, S.J., Lindsay, H.D., et al., Rad18 Is Required for DNA Repair and Checkpoint Responses in Fission Yeast, Mol. Biol. Cell, 1999, vol. 10, no. 9, pp. 2905–2918.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavlova, S.V., Zakian, S.M. Structural Proteins of the SMC (Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes) Family and Their Role in Chromatin Reorganization. Russian Journal of Genetics 39, 1097–1111 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026110508147
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026110508147