Abstract
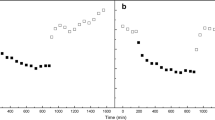
The phenomenon of rapid induction of high affinity HCO3 − uptake was investigated in two cyanobacterial species, Synechococcus strain PCC 7942 and Synechocystis strain PCC 6803. For both strains, mass spectrometric analysis of HCO3 − fluxes during steady state photosynthesis revealed that the high affinity HCO3 − uptake system was rapidly induced only in the presence of Na+. In Synechococcus there was a correlation between the capability of rapid induction of the high affinity HCO3 − uptake system and the appearance of the IctB protein. Neither fast induction of the high affinity HCO3 − uptake system nor IctB accumulation were prevented by chloramphenicol but by K252a. Inactivation of the gene dc13 upstream of ictB in Synechococcus led to the inability of the cells to rapidly induce the high affinity Na+ dependent HCO3 − uptake system although IctB was accumulated. The dc13 mutant was able to acclimate from high CO2 to 100 ppm CO2 by lowering the CO2 concentration step by step, while immediate decrease of the CO2 concentration to 100 ppm CO2 severely inhibited HCO3 − uptake. In Synechocystis the rapid induction of the Na+ dependent high affinity HCO3 − uptake system was not accompanied by an increase in sbtA RNA abundance, indicating that transcriptional regulation of sbtA is not responsible for the fast increase in substrate affinity of the HCO3 − transporter. The results are discussed in terms of post-translational modification of constitutively expressed components (e.g., SbtA)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoroso G, Sültemeyer D, Thyssen C, Fock HP (1998) Uptake of HCO3¯ and CO2 in cells and chloroplasts from the micro algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Dunaliella tertiolecta. Plant Physiol 116: 193–201
Badger MR, Palmqvist K, Yu JW (1994) Measurement of CO2 and HCO3¯ fluxes in cyanobacteria and microalgae during steadystate photosynthesis. Physiol Plant 90: 529–536
Bloye SA, Silman NJ, Mann NH, Carr, NG (1992) Bicarbonate concentration by Synechocystis PCC 6803: Modulation of protein phosphorylation and inorganic carbon transport by glucose. Plant Physiol 99: 601–606
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgramm quantities of protein utilizing the prinziple of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254
Bonfil DJ, Ronen-Tarazi M, Sültemeyer D, Lieman-Hurwitz J, Schatz D, Kaplan A (1998) A putative HCO3¯ transporter in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942. FEBS Lett 430: 236–240
Figge RM, Cassier-Chauvat C, Chauvat F, Cerff R (2001) Characterization and analysis of an NAD(P)H dehydrogenase transcriptional regulator critical for the survival of cyanobacteria facing inorganic carbon starvation and osmotic stress. Mol Microbiol 39: 455–468
Fock HP, Sültemeyer DF (1989) O2 evolution and uptake measurements in plant cells by mass spectrometer. In Liskens HF and Jackson JF (eds) Modern Methods of Plant Analysis, Vol 9: 9–18. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, Germany
Forchhammer K, Tandeau de Marsac N (1995) Functional analysis of the phosphoprotein PII (glnB gene product) in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942. J Bacteriol 177: 2033–2044
Hisbergues M, Jeanjean R, Joset F, Tandeau de Marsac N, Bédu S (1999) Protein PII regulates both inorganic carbon and nitrate uptake and is modified by a redox signal in Synechocystis PCC 6803. FEBS Lett 463: 216–220
Kaplan A, Reinhold L (1999) The CO2 concentrating mechanism in photosynthetic microorganisms. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50: 539–570
Klughammer B, Sültemeyer D, Badger MR, Price GD (1999) Involvement of NAD(P)H dehydrogenase subunits, NdhD3 and HdhF3, in high affinity CO2 uptake in Synechococcus sp. PCC7002 gives evidence for multiple NDH-1 complexes with specific roles in cyanobacteria. Mol Microbiol 32: 1305–1315
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685
Maeda SH, Badger MR, Price GD (2002) Novel gene products associated with NdhD3/D4-containing NDH-1 complexes are involved in photosynthetic CO2 hydration in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC7942. Mol Microbiol 43: 425–435
Mann NH (1994) Protein phosphorylation in cyanobacteria. Microbiology 140: 3207–3215
McKay RML, Gibbs SP, Espie GS (1993) Effect of dissolved inorganic carbon on the expression of carboxysomes, localization of Rubisco and the mode of inorganic carbon transport in cells of the cyanobacterium UTEX 625. Arch Microbiol 159: 21–29
Ogawa T, Amichay D, Gurevitz M (1994) Isolation and characterisation of the ccmM gene requiered by the cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC6803 for inorganic carbon utilization. Photosynth Res 39: 183–190
Ohkawa H, Pakrasi HB, Ogawa T (2000a) Two types of functionally distinct NAD(P)H dehydrogenases in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. J Biol Chem 275: 31630–31634
Ohkawa H, Price GD, Badger MR, Ogawa T (2000b) Mutation of ndh genes leads to inhibition of CO2 uptake rather than HCO3+ uptake in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. J Bacteriol 182: 2591–2596
Ohkawa H, Sonoda M, Shibata M, Ogawa T (2001) Localization of NAD(P)H dehydrogenase in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. J Bacteriol 183: 4938–4939
Omata T and Ogawa T (1986) Biosynthesis of a 42-kD polypeptide in the cytoplasmic membrane of the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans strain R2 during adaptation to low CO2 concentration. Plant Physiol 80: 525–530
Omata T, Price GD, Badger MR, Okamura M, Gotha S, Ogawa T (1999) Identification of an ATP-binding cassette transporter involved in bicarbonate uptake in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942. PNAS 96: 13571–13576
Omata T, Gotha S, Takahashi Y, Harano Y, Maeda S-I (2001) Involvement of a CbbR homolog in low CO2-induced activation of the bicarbonate transporter operon in cyanobacteria. J Bacteriol 183: 1891–1898
Omata T, Takahashi Y, Yamaguchi O, Nishimura T (2002) Structure, function and regulation of the cyanobacterial high-affinity bicarbonate transporter BCT1. Funct Plant Biol 29: 151–159
Porra RJ, Thompson WA, Kriedemann PE (1989) Determination of accurate extinction coefficient and simultaneous equations for assaying chlorophylls a and b extracted with four different solvents: Verification of the concentration of chlorophyll standards by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 975: 384–394
Price GD and Badger MR (1989) Expression of human carbonic anhydrase in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus PCC 7942 creates a high CO2-requiring phenotype. Plant Physiol 91: 505–513
Price GD, Sültemeyer D, Klughammer B, Ludwig M, Badger MR (1998) The functioning of the CO2 concentrating mechanism in several cyanobacterial strains: A review of general physiological characteristics, genes, proteins and recent advances. Can J Bot 76: 973–1002
Price GD, Maeda SH, Omata T, Badger MR (2002) Modes of active inorganic carbon uptake in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus PCC7942. Funct Plant Biol 29: 131–149
Salon C, Mir NA, Canvin DT (1996) Influx and efflux of inorganic carbon in Synechococcus UTEX 625 Plant Cell Environ 19: 247–259
Satoh R, Himeno M, Wadano A (1997) Carboxysomal diffusion resistence to ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate and 3-phosphoglycerate in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus PCC7942. Plant Cell Physiol 38: 769–775
Schwarz R, Reinhold L, Kaplan A (1995) Low activation state of ribulose1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in carboxysome-defective Synechococcus mutants. Plant Physiol 108: 183–190
Shibata M, Ohkawa H, Kaneko T, Fukuzawa H, Tabata S, Kaplan A, Ogawa T (2001) Distinct constitutive and low-CO2-induced CO2uptake systems in cyanobacteria: genes involved and their phylogenetic relationship with homologous genes in other organisms. PNAS 98: 11789–11794
Shibata M, Katoh H, Sonoda M, Ohkawa H, Shimoyama M, Fukuzawa H, Kaplan A, Ogawa T (2002a) Genes essential for sodiumdependent bicarbonate transport in cyanobacteria: function and phylogenetic analysis. J Biol Chem 277: 18658–18664
Shibata M, Ohkawa H, Katoh H, Shimoyama M, Ogawa T (2002b) Two CO2 uptake systems in cyanobacteria: four systems for inorganic carbon acquisition in Synechocystis PCC6803. Funct Plant Biol 29: 123–129
Smith KS, Ferry JG (2000) Prokaryotic carbonic anhydrases. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24: 335–366
Stanier RY, Kunisawa R, Mandel M, Cohen-Bazire G (1971) Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol Rev 35: 171–205
Sültemeyer D, Price GD, Yu J-W, Badger MR (1995) Characterisation of carbon dioxide and bicarbonate transport during steady-state photosynthesis in the marine cyanobacterium Synechococcus strain PCC 7002. Planta 197: 597–607
Sültemeyer D, Klughammer B, Ludwig M, Badger MR, Price GD (1997) Random insertional mutagenesis used in the generation of mutants of the marine cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7002 with an impaired CO2 concentrating mechanism. Aust J Plant Pysiol 24: 317–327
Sültemeyer D, Klughammer B, Badger MR, Price DG (1998a) Fast induction of high-affinity HCO3¯ transport in cyanobacteria. Plant Physiol 116: 183–192
Sültemeyer D, Klughammer B, Badger MR, Price GD (1998b) Protein phosphorylation and its possible involvement in the induction of the high-affinity CO2 concentrating mechanism in cyanobacteria. Can J Bot 76: 954–961
Yu JW, Price GD, Badger MR (1994) Characterisation of CO2 and HCO3¯ uptake during steady-state photosynthesis in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus strain PCC7942. Aust J Plant Physiol 21: 185–195
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amoroso, G., Seimetz, N. & Sültemeyer, D. The dc13 gene upstream of ictB is involved in rapid induction of the high affinity Na+ dependent HCO3 − transporter in cyanobacteria. Photosynthesis Research 77, 127–138 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025873718682
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025873718682