Abstract
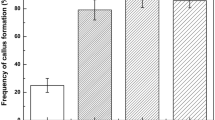
A protocol for large-scale propagation of Phragmites communis Trin. by somatic embryogenesis has been established. Plants were regenerated through somatic embryogenesis from stem segments of R5002-12, a salt-tolerant variant line of Phragmites communis Trin. Stem segment explants produced hard white callus on the semi-solid Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium supplemented with 9.05 μM 2,4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid (2,4-D) for 4 weeks. The induction frequency was 36.7%. Then, the callus was transferred to MS medium supplemented with 4.52 μM 2,4-D. After 4 weeks in culture, yellow embryogenic callus with some nodular structures was formed. When the embryogenic callus was transferred to differentiation medium (MS supplemented with 0.45 μM 2,4-D), differentiation was initiated to form small green islands on the surface of the callus after 2 weeks in culture. Within 4 weeks, a large number of somatic embryos were formed with a frequency of 86.7%. Six weeks later, they developed into strong plantlets. When the plantlets (about 1 cm in length) were cultured on propagation medium (MS supplemented with 13.31 μM BA+5.37 μM NAA), a great number of regenerated plants were obtained. After the plants were cultured on liquid 1/2 MS medium with 2.69 μM NAA added 2.46 μM IBA roots developed. The rooted plants were transferred to soil with over 85% survival. Using this methodology, more than 20000 regenerated plants of salt tolerant variant line of Phragmites communis Trin. have been produced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen KY, Ye HC, Chen JL, Gu LM & Li GF (1994) A salt tolerant variant of Phragmites communis and its cytological characteriza-tion. Acta Bot. Sin. 36: 930–933
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497
Sangwan RS & Gorenflot R (1975) In vitro culture of Phragmites tissue, callus formation, organ differentiation and cell suspension culture. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 75: 256–269
Wu GL, Ye HC, Li GF & Zhang QH (1987) Embryogenic callus formation and plantlet regeneration of Phragmites communis. Acta Bot. Sin. 29: 361–366
Ye HC, Chen JL, Gu LM, Wu GL, Li GF & Mu XJ (1990) Screening and characteristic analysis of the salt tolerant cell line of embryogenic callus of Phragmites communis. In: Hu H & Wang HL (eds) Plant Cell Engineering and Breeding, Beijing (pp. 245–252). Industrial University Press, Beijing
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, YG., Guo, YM., Guo, Y. et al. Regeneration and large-scale propagation of Phragmites communis through somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 75, 287–290 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025871015405
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025871015405