Abstract
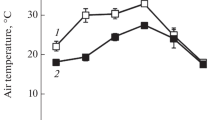
The plants of Prosopis juliflora growing in northern India are exposed to large variations of temperature, vapour pressure deficits (VPD), and photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD) throughout the year. Under these conditions P. juliflora had two short periods of leaf production, one after the winter season and second after summer, which resulted in two distinct even aged cohorts of leaves. In winter with cold nights (2–8 °C) and moderate temperatures during the day, the plants showed high rates of photosynthesis. In summer the midday temperatures often reached <45 °C and plants showed severe inhibition of photosynthesis. The leaves of second cohort appeared in July and showed typical midday depression of photosynthesis. An analysis of diurnal partitioning of the absorbed excitation energy into photochemistry showed that a smaller fraction of the energy was utilised for photochemistry and a greater fraction was dissipated thermally, further the photon utilisation for photochemistry and thermal dissipation is largely affected by the interaction of irradiance and temperature. The plants showed high photochemical efficiency of photosystem 2 (PS2) at predawn and very little photoinhibition in all seasons except in summer. The photoinhibition in summer was pronounced with very poor recovery during night. Since P. juliflora exhibited distinct pattern of senescence and production of new leaves after winter and summer stress period, it appeared that the ontogenic characteristic together with its ability for safe dissipation of excess radiant energy in P. juliflora contributes to its growth and survival.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, W.W., III, Barker, D.H.: Seasonal changes in xanthophyll cycle-dependent energy dissipation in Yucca glauca Nuttall.-Plant Cell Environ. 21: 501-511, 1998.
Adams, W.W., III, Demmig-Adams, B.: The xanthophyll cycle and sustained thermal energy dissipation activity in Vinca minor and Euonymus kiautschovicus in winter.-Plant Cell Environ. 18: 117-127, 1995.
Anderson, J.M., Park, Y.-I., Chow, W.S.: Unifying model for the photoinactivation of Photosystem II in vivo under steady-state photosynthesis.-Photosynth. Res. 56: 1-13, 1998.
Bilger, W., Björkman, O.: Role of the xanthophyll cycle in photoprotection elucidated by measurements of light-induced absorbance changes, fluorescence and photosynthesis in leaves of Hedera canariensis.-Photosynth. Res. 25: 173-185, 1990.
Demmig-Adams, B., Adams, W.W., III, Barker, D.H., Logan, B.A., Bowling, D.R., Verhoeven, A.S.: Using chlorophyll fluorescence to assess the fraction of absorbed light allocated to thermal dissipation of excess excitation.-Physiol. Plant. 98: 253-264, 1996.
Franco, A.C., Lüttge, U.: Midday depression in Savanna trees: coordinated adjustments in photochemical efficiency, photorespiration, CO2 assimilation and water use efficiency.-Oecologia 131: 356-365, 2002.
Gamon, J.A., Pearcy, R.W.: Photoinhibition in Vitis californica: interactive effects of sunlight, temperature and water status.-Plant Cell Environ. 13: 267-275, 1990.
Genty, B., Briantais, J.-M., Baker, N.R.: The relationship between the quantum yield of photosynthetic electron transport and quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence.-Biochim. biophys. Acta 990: 87-92, 1989.
Gilmore, A.M.: Mechanistic aspects of xanthophylls cycle-dependent photoprotection in higher plant chloroplasts and leaves.-Physiol. Plant. 99: 197-209, 1997.
Goel, V.L., Behl, H.M.: Fuelwood production potential of six Prosopis species on an alkaline soil site.-Biomass Bioenergy 8: 17-20, 1995.
Goel, V.L., Behl, H.M.: Growth, biomass estimations and fuel quality evaluation of coppice plants of Prosopis juliflora on sodic soil site.-J. trop. Forest Sci. 12: 139-148, 2000.
Goel, V.L., Behl, H.M.: Genetic selection and improvement of hard wood tree species for fuelwood production on sodic soil with particular reference to Prosopis juliflora.-Biomass Bioenergy 20: 9-15, 2001.
Greer, D.H., Laing, W.A.: Photoinhibition of photosynthesis in intact kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa) leaves: Recovery and its dependence on temperature.-Planta 174: 159-165, 1988.
Havaux, M., Bonfils, J.-P., Lütz, C., Niyogi, K.K.: Photodamage of the photosynthetic apparatus and its dependence on the leaf development stage in the npq1 Arabidopsis mutant deficient in the xanthophylls-cycle enzyme violaxanthin deepoxidase.-Plant Physiol. 124: 273-284, 2000.
Kitao, M., Lei, T.T., Koike, T., Tobita, H., Maruyama, Y., Matsumoto, Y., Ang, L.H.: Temperature response and photoinhibition investigated by chlorophyll fluorescence measurements for four distinct species of dipterocarp trees.-Physiol. Plant. 109: 284-290, 2000.
Krause, G.H., Virgo, A., Winter, K.: High susceptibility to photoinhibition of young leaves of tropical forest trees.-Planta 197: 583-591, 1995.
Krause, G.H., Weis, E.: Chlorophyll fluorescence and photosynthesis: the basics.-Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant mol. Biol. 42: 313-349, 1991.
Lovelock, C.E., Winter, K.: Oxygen dependent electron transport and protection from photoinhibition in leaves of tropical tree species.-Planta 198: 580-587, 1996.
Nilsen, E.T., Sharifi, M.R., Rundel, P.W., Virginia, R.A.: Influences of microclimatic conditions and water relations on seasonal leaf dimorphism of Prosopis glandulosa var. torreyana in the Sonoran Desert, California.-Oecologia 69: 95-100, 1986.
Niyogi, K.K.: Photoprotection revisited: Genetic and molecular approaches.-Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant mol. Biol. 50: 333-359, 1999.
Oliveira, G., Peñuelas, J.: Allocation of absorbed light energy into photochemistry and dissipation in a semi-deciduous and an evergreen Mediterranean woody species during winter.-Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 28: 471-480, 2001.
Oliveira, G., Peñuelas, J.: Comparative protective strategies of Cistus albidus and Quercus ilex facing photoinhibitory winter conditions.-Environ. exp. Bot. 47: 281-289, 2002.
Pathre, U., Sinha, A.K., Shirke, P.A., Sane, P.V.: Factors determining the midday depression of photosynthesis in trees under monsoon climate.-Trees 12: 472-481, 1998.
Roden, J.S., Egerton, J.J.G., Ball, M.C.: Effect of elevated [CO2] on photosynthesis and growth of snow gum (Eucalyptus pauciflora) seedlings during winter and spring.-Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 26: 37-46, 1999.
Sharifi, M.R., Nilsen, E.T., Virginia, R.A., Rundel, P.W., Jarrell, W.M.: Phenological patterns of current season shoots of Prosopis glandulosa var. torreyana in the Sonnoran Desert of California.-Flora 173: 265-277, 1983.
Shirke, P.A.: Leaf photosynthesis, dark respiration and fluorescence as influenced by leaf age in an evergreen tree, Prosopis juliflora.-Photosynthetica 39: 305-311, 2001.
Shirke, P.A.: Physiological and Biochemical Behaviour of Leaves of Prosopis juliflora in Response to Diurnal and Seasonal Variations.-Ph.D. Thesis. Dr. R.M.Lohia Avadh University, Faizabad 2002.
Valentini, R., Epron, D., de Angelis, P., Matteucci, G., Dreyer, E.: In situ estimation of net CO2 assimilation, photosynthetic electron flow and photorespiration in Turkey oak (Q. cerris L.) leaves: diurnal cycles under different levels of water supply.-Plant Cell Environ. 18: 631-640, 1995.
Verhoeven, A.S., Adams, A.A., III, Demmig-Adams, B.: Two forms of sustained xanthophylls cycle-dependent energy dissipation in overwintering Euonymus kiautschovicus.-Plant Cell Environ. 21: 893-903, 1998.
Verhoeven, A.S., Adams, W.W., III, Demmig-Adams, B.: The xanthophylls cycle and acclimation of Pinus ponderosa and Malva neglecta to winter stress.-Oecologia 118: 277-287, 1999.
Zhang, S., Gao, R.: Diurnal changes of gas exchange, chlorophyll fluorescence, and stomatal aperture of hybrid poplar clones subjected to midday light stress.-Photosynthetica 37: 559-571, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shirke, P., Pathre, U. Diurnal and Seasonal Changes in Photosynthesis and Photosystem 2 Photochemical Efficiency in Prosopis juliflora Leaves Subjected to Natural Environmental Stress. Photosynthetica 41, 83–89 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025864513663
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025864513663