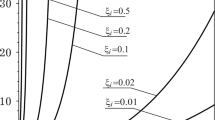
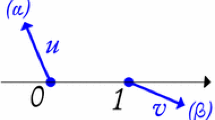
Abstract
The paper proposes a method for the construction of C 2 quasi-interpolating functions with tension properties. The constructed quasi-interpolant is a parametric cubic curve and its shape can be easily controlled via tension parameters which have an immediate geometric interpretation. Numerical examples are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Akima, A new method of interpolation and smooth curve fitting based on local procedures, J. Assoc. Comput. Mach. 17 (1970) 589–602.
W. Boehm, Curvature continuous curves and surfaces, Comput. Aided Geom. Design 2 (1985) 313–323.
R.E. Carlson and F.N. Fritsch, Monotone piecewise bicubic interpolation, SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 22 (1985) 386–400.
C.K. Chui, H. Diamond and L. Raphael, Shape-preserving quasi-interpolation and interpolation by box spline surfaces, J. Comput. Appl. Math. 25 (1989) 169–198.
C. Conti and R. Morandi, A bivariate shape-preserving quasi-interpolant method with positive compactly supported bases, J. C. A. A. A. (2001) to appear.
C. Conti, R. Morandi and C. Rabut, Shape-preserving quasi-interpolating univariate cubic splines, in: Mathematical Methods for Curves and Surfaces, Vol. II, eds. M. Dæhlen, T. Lyche and L.L. Schumaker, Lillehammer, 1997 (Vanderbilt Univ. Press, Nashville, 1998) pp. 550–62.
C. Conti, R. Morandi and C. Rabut, P1-reproducing shape-preserving quasi-interpolant using positive quadratic splines with local support, J. Comput. Appl. Math. 104 (1999) 111–122.
P. Costantini, Curve and surface construction using variable degree polynomial splines, Comput. Aided Geom. Design 17 (2000) 419–446.
N. Dyn, A. Edelman and C.A. Micchelli, On locally supported basis functions for the representation of geometrically continuous curves, Analysis 7 (1987) 313–341.
G. Farin, D. Hansford and A. Worsey, The singular cases for γ-spline interpolation, Comput. Aided Geom. Design 7 (1990) 533–546.
T.N.T. Goodman, Total positivity and the shape of curves, in: Total Positivity and its Applications, eds. M. Gasca and C.A. Micchelli (Kluwer, Dordrecht, 1996) pp. 157–186.
T.N.T. Goodman, Shape preserving interpolation by curves, in: Proc. of the 4th Internat. Symposium on Algorithms for Approximation, Huddersfield, 15-20 July 2001, to appear.
J. Hoschek and D. Lasser, Fundamentals of Computer Aided Geometric Design (A.K. Peters,_ Wellesley,_ MA, 1993).
P.E. Koch and T. Lyche, Exponential B-splines in tension, in: Approximation Theory, Vol. VI, eds. C.K. Chui, L.L. Schumaker and J.D. Ward (Academic Press, New York, 1989) pp. 361–364.
P.E. Koch and T. Lyche, Construction of exponential tension B-splines of arbitrary order, in: Curves and Surfaces, eds. P.J. Laurent, A. Le Méhauté and L.L. Schumaker (Academic Press, New York, 1991) pp. 255–258.
P.E. Koch and T. Lyche, Interpolation with exponential B-splines in tension, Geometric Modelling, Comput. Suppl. 8 (1993) 173–190.
B.I. Kvasov, Shape preserving spline approximation via local algorithms, in: Advanced Topics in Multivariate Approximation, eds. F. Fontanella, K. Jetter and P.J. Laurent, Ser. Approx. Decomposition, Vol. 8 (World Science, River Edge, 1996) pp. 181–196.
B.I. Kvasov, Algorithms for shape preserving local approximation with automatic selection of tension parameters, Comput. Aided Geom. Design 17 (2000) 17–37.
B.I. Kvasov and P. Sattayatham, GB-splines of arbitrary order, J. Comput. Appl. Math. 104 (1999) 63–88.
P. Lamberti and C. Manni, Shape preserving C 2 functional interpolation via parametric cubics, Numer. Algorithms 28 (2001) 229–254.
T. Lyche and L.L. Schumaker, Local spline approximation methods, J. Approx. Theory 15 (1975) 294–325.
C. Manni, C 1 comonotone Hermite interpolation via parametric cubics, J. Comput. Appl. Math. 69 (1996) 143–157.
C. Manni, On shape preserving C 2 Hermite interpolation, BIT 41 (2001) 127–148.
G.M. Nielson, Some piecewise polynomial alternatives to spline under tension, in: Computer Aided Geometric Design, eds. R.E. Barnill and R.F. Riesenfeld (Academic Press, New York, 1974) pp. 209–235.
C. Rabut, B-splines polyharmoniques cardinales: Interpolation, quasi-interpolation, filtrage, Thèse No. 1413, Université Paul Sabatier, Toulouse (1990).
I.J. Schoenberg, Contribution to the problem of approximation of equidistant data by analytic functions. Part A. On the problem of smoothing or graduation. A first class of analytic approximation formulae, Quart. Appl. Math. 4 (1946) 45–99.
D.G. Schweikert, An interpolation curve using a spline in tension, J. Math. Phys. 45 (1966) 312–317.
R.J. Walker, Algebraic Curves (Dover, New York, 1962).
Z.M. Wu and R. Schaback, Shape preserving properties and convergence of univariate multiquadric quasi-interpolation, Acta Math. Appl. Sinica (English Ser.) 10(4) (1994) 441–446.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamberti, P., Manni, C. Tensioned Quasi-Interpolation Via Geometric Continuity. Advances in Computational Mathematics 20, 105–127 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025823221346
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025823221346