Abstract
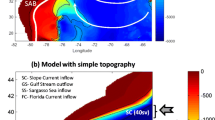
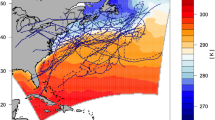
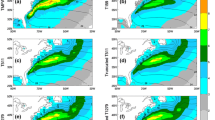
The Gulf Stream system has been numerically simulated with relatively high resolution and realistic forcing. The surface fluxes of the simulation were obtained from archives of calculations from the Eta-29 km model which is an National Center for Environment Prediction (NCEP) operational atmospheric prediction model; synoptic fields are available every 3 hour. A comparison between experiments with and without surface fluxes shows that the effect of the surface wind stress and heat fluxes on the Gulf Stream path and separation is closely related to the intensification of deep circulations in the northern region. Additionally, the separation of the Gulf Stream and the downslope movement of the Deep Western Boundary Current (DWBC) are reproduced in the model results. The model DWBC crosses under the Gulf Stream southeast of Cape Hatteras and then feeds the deep cyclonic recirculation east of the Bahamas. The model successfully reproduces the cross-sectional vertical structures of the Gulf Stream, such as the asymmetry of the velocity profile, and this structure is sustained along the downstream axis. The distribution of Root Mean Square (RMS) elevation anomaly of the model shows that the eddy activity of the Gulf Stream is realistically reproduced by the model physics. The entrainment of the upper layer slope current into the Gulf Stream occurs near cross-over; the converging cross-stream flow is nearly barotropic.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, HC., Mellor, G.L. Numerical Simulation of the Gulf Stream and the Deep Circulation. Journal of Oceanography 59, 343–357 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025520027948
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025520027948