Abstract
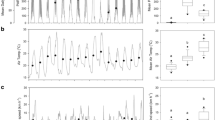
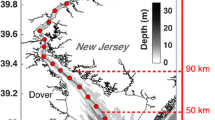
The magnitude and frequency of events leading to changes in turbidity have been studied in a large (61 km2), shallow (mean depth 3.4 m) wind-exposed lake basin at the western end of Lake Mälaren, Sweden. In this paper we couple changes in suspended particulate inorganic material (SPIM) resulting from wind driven sediment resuspension, and variations in the discharge and sediment load, to spectral variations in subsurface light and estimates of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR). To accomplish this we use a semi-analytical model which predicts the spectral variations in downwelling irradiance (E d(λ)) and the attenuation coefficient of downwelling irradiance (K d(λ)), as a function of the concentrations of chlorophyll, dissolved yellow substances, and suspended inorganic and organic particulate material. Unusually high river discharge, led to large inputs of yellow substances and large in lake yellow substance concentrations (a ys(420) ≈ 20 m−1), causing variations in yellow substance concentration to have the greatest role in influencing temporal trends in the attenuation of PAR and variations in the depth of the euphotic zone (Z eup). In spite of this, variations in SPIM could account for approximately 60% of the variation in Z eup attributed to changes in yellow substances alone. Our results show that changes in suspended sediment concentration leads to both long-term and short-term changes in the attenuation of PAR, even in the presence of high concentrations of dissolved yellow substances.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blom, G., E. H. S. Vanduin & L. Lijklema, 1994. Sediment resuspension and light conditions in some shallow Dutch lakes. Water Sci. Technol. 30: 243-252.
Buiteveld, H., 1995. A model for calculation of diffuse light attenuation (PAR) and secchi depth. Neth. J. aquat. Ecol. 29: 55-65.
Gallegos, C. L., D. L. Correll & J. W. Pierce, 1990. Modeling spectral diffuse attenuation, absorption, and scattering coefficients in a turbid estuary. Limnol. Oceanogr. 35: 1486-1502.
James, R. T., J. Martin, T. Wool & P. F. Wang, 1997. A sediment resuspension and water quality model of Lake Okeechobee. J. am. Wat. Resour. Ass. 33: 661-680.
Kirk, J. T. O., 1981. Monte carlo study of the nature of the underwater light field in, and the relationships between optical properties of, turbid yellow waters. Aust. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 32: 517-532.
Kirk, J. T. O., 1984. Dependence of relationship between inherent and apparent optical properties of water on solar altitude Limnol. Oceanogr. 29: 350-356.
Kirk, J. T. O., 1994a. Estimation of the absorption and the scattering coefficients of natural waters by use of underwater irradiance measurements. Appl. Optics 33: 3276-3278.
Kirk, J. T. O., 1994b. Light and Photosynthesis in Aquatic Ecosystems, Cambridge University Press, Melbourne.
Kirk, J. T. O., 1994c. Characteristics of the light field in highly turbid waters: a monte carlo study. Limnol. Oceanogr. 39: 702-706.
Kirk, J. T. O. & P. A. Tyler, 1986. The spectral absorption and scattering properties of dissolved and particulate components in relation to the underwater light field of some tropical Australian freshwaters. Freshwat. Biol. 16: 573-583.
Markensten, H. & D. C. Pierson, A dynamic model for flow and wind driven sediment resuspension in a shallow basin. Hydrobiologia 494 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 169): 305-311.
Mobley, C. D., 1994. Light and Water - Radiative Transfer in Natural Waters, Academic Press, San Diego.
Pierson, D. C. & N. Strömbeck, 2001. Estimation of radiance re-flectance and the concentrations of optically active substances in Lake Mälaren, Sweden, based on direct and inverse solutions of a simple model. Sci. Tot. Environ. 268: 171-188.
Reynolds, C. S., A. E. Irish & J. A. Elliott, 2001. The ecological basis for simulating phytoplankton responses to environmental change (PROTECH). Ecol. Mod. 140: 271-291.
Smith, R. C. & K. S. Baker, 1981. Optical properties of the clearest natural waters (200-800 nm). Appl. Optics 20: 177-184.
Somlyody, L. & L. Koncsos, 1991. Influence of sediment resuspension on the light conditions and algal growth in Lake Balaton. Ecol. Mod. 57: 173-192.
Strömbeck, N. 2001. Water quality and optical properties of Swedish lakes and coastal waters in relation to remote sensing PhD. Thesis Dep. of Limnology, EBC Uppsala University, Uppsala.
Strömbeck, N. & D. C. Pierson, 2001. The effects of variability in the inherent optical properties on estimations of chlorophyll by remote sensing in Swedish freshwaters. Sci. Tot. Environ. 268: 123-137.
Van Dijk, G. M. & E. P. Achterberg, 1992. Light climate in the water column of a shallow eutrophic lake (Lake Veluwe) in The Netherlands. Arch. für Hydrobiol. 125: 257-278.
Van Duin, E. H., G. Blom, L. Lijklema & M. J. M. Scholten, 1992. Aspects of modeling sediment transport and light conditions in Lake Marken. Hydrobiologia 235: 167-176.
Van Duin, E. H., G. Blom, F. J. Los, R. Maffione, R. Zimmerman, C. F. Cerco, M. Dortch & E. P. Best, 2001. Modeling underwater light climate in relation to sedimentation, resuspension, water quality and autotrophic growth. Hydrobiologia 444: 25-42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pierson, D.C., Markensten, H. & Strömbeck, N. Long and short term variations in suspended particulate material: the influence on light available to the phytoplankton community. Hydrobiologia 494, 299–304 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025455424972
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025455424972