Abstract
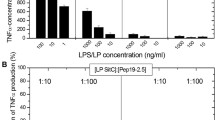
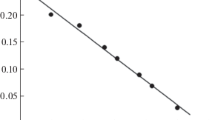
We have previously demonstrated that the detergent Tyloxapol is effective in preventing reactions to endotoxin. We studied the effects of Tyloxapol on the morbidity and mortality from endotoxemia in rabbits and on the mortality in rats with sepsis. The effects of Tyloxapol on endotoxin binding and macrophage activation were studied in the macrophage cell line RAW264.7 and CHO cells expressing CD14. Isolated human leukocytes were used to study the effects of Tyloxapol on immune reactions, leukocyte motility, and phagocytosis. Intravenous Tyloxapol (200 mg/kg), given prior to or at the time of endotoxin infusion protected rabbits from developing shock. In rats with peritoneal sepsis, a lipid-rich diet and Tyloxapol given at the time of induction of peritonitis protected them from septic death. In vitro, Tyloxapol blocked the binding of endotoxin to murine macrophages and CHO cells expressing CD14, activation of macrophages, and also some antigen–antibody immune reactions (mediated by CD2, CD4, CD22, HLA-DR). Tyloxapol may prevent the reaction to endotoxin by desensitizing endotoxin-recognizing receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serikov, V.B., Glazanova, T.V., Jerome, E.H. et al. Tyloxapol Attenuates the Pathologic Effects of Endotoxin in Rabbits and Mortality Following Cecal Ligation and Puncture in Rats by Blockade of Endotoxin Receptor–Ligand Interactions. Inflammation 27, 175–190 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025108207661
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025108207661