Abstract
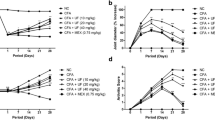
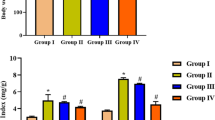
The aim of this study was to determine therapeutic effects of complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) on the progression and relapsing of pristine-induced arthritis (PIA) and investigate the mechanism involved. Chronic relapsing arthritis was induced by pristine in LEW rats. After onset of arthritis, rats were intradermally injected CFA and rats in control group were injected the same volume of PBS. Arthritis was monitored visually, and joint pathology was examined histologically. Cytokine mRNA expression in inguinal lymph nodes was assessed by RT-PCR. The levels of nitric oxide (NO) in serum were measured by colorimetric assay. The results showed that CFA significantly suppressed the progression and relapsing of PIA. Relapsing rate of PIA in CFA-treated group was 12.5% and it was 85.7% in PBS-control group (P < 0.005). CFA markedly inhibited the infiltration of inflammatory cells and cartilage damage in the joints of CFA-treated rats and promoted the increases of IFN-γ mRNA and NO levels. The present study provided an implication that adjuvant therapy may be a new strategy for the treatments of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and other chronic inflammatory diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brooks, P. 1993. Clinical management of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 341:286–290.
Bresnihan, B., J. M. Alvaro-Gracia, M. Cobby, M. Doherty, Z. Domljan, P. Emery, et al. 1998. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Arthritis Rheum. 41:2196–2204.
Elliott, M., R. N. Maini, M. Feldmann, A. Long-Fox, P. Charles, H. Biji, et al. 1994. Repeated therapy with monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor-α (cA2) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 344:1125–1127.
Van Roon, J. A., F. P. Lafeber, and J. W. Bijlsma. 2001. Synergistic activity of interleukin-4 and interleukin-10 in suppression of inflammation and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 44:3–12.
Cobelens, P. M., C. J. Heijnen, E. E. Nieuwenhuis, P. P. Kramer, R. van der Zee, W. van Eden, et al. 2000. Treatment of adjuvant-induced arthritis by oral administration of mycobacterial Hsp 65 during disease. Arthritis Rheum. 43:2694–2702.
Muto, Y., J. Satoh, G. Muto, T. Msuda, M. Sagara, M. Fukuzawa, et al. 1997. Effect of long-term treatment with complete Freund's adjuvant on kk-ay mouse, a model of non-dependent diabetes mellitus. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 83:53–59.
Shehadeh, N., F. Calcinaro, B. J. Bradley, I. Bruchlim, and K. J. Lafferty. 1994. Effect of adjuvant therapy on development of diabetes in mouse and man. Lancet 343:706–707.
Kahn, G., M. G. Buzzi, U. Sabatini, E. Giugni, S. Bastianello, F. Viselli, et al. 1999. Use of bacilli calmette-guerin (BCG) in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 53:1588–1589.
Kahn, D., D. C. Archer, D. P. Gold, and C. J. Kelly. 2001. Adjuvant immunotherapy is dependent on inducible nitric oxide synthase. J. Exp. Med. 193:1261–1267.
Balagon, M. V., D. S. Walsh, P. L. Tan, R. V. Cellona, R. M. Abalos, E. V. Tan, et al. 2000. Improvement in psoriasis after intradermal administration of heat-killed mycobacterium vaccae. Int. Dermatol. 39:51–58.
Wooley, P., S. Sud, J. D. Whalen, and S. Nasser. 1998. Pristane-induced arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 41:2022–2031.
Vingsbo, C., P. Sahlstrand, J. G. Brun, R. Jonsson, T. Saxne, and R. Halmdahl. 1996. Pristane-induced arthritis in rats: A new model for rheumatoid arthritis with a chronic disease course influenced by both major histocompatibility complex and non-major histocompatibility complex genes. Am. J. Pathol. 149:1675–1683.
Wooley, P., J. R. Seibold, J. D. Whalen, and J. M. Chapdelaine. 1989. Pristane-induced arthritis: The immunologic and genetic features of an experimental murine model of autoimmune disease. Arthritis Rheum. 32:1022–1030.
Staiuk, L. M., M. Choraishian, J. Elson, and S. J. Thompson. 1997. Pristane-induced arthritis is CD4+T cell dependent. Immunology 90:81–86.
Trentham, D.E., A. S. Townes, and A. H. Kang. 1997. Autoimmunity to type II collagen: An experiment model of arthritis. J. Exp. Med. 146:857–868.
Tso, J. Y., X. H. Sun, T. H. Kao, K. S. Reece, and R. Wu. 1985. Isolation and characterization of rat human glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNA: Genomic complexity and molecular evolution of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 13:2486–2502.
Schmidt-Weber, C. B., D. Pohlers, A. Siegling, H. Schadlich, E. Buchner, H. D.y Volk, et al. 1999. Cytokinegeneactivationinsynovial membrane regional lymph nodes, spleen during the course of rat adjuvant arthritis. Cell Immunol. 195:53–65.
Zipris, T., D. L. Greiner, S. Malkani, B. Whalen, J. P. Mordes, and A. A. Rossini. 1999. Cytokine gene expression in islets and thyroids of BB rats. J. Immunol. 156:1315–1321.
Zhang, H., T. Morisaki, H. Matsunaga, N. Sato, A. Uchiyama, K. Hashizume, et al. 2000. Protein-bound polysaccharide PKS inhibits tumor invasiveness by down-regulation of TGF-b and MMPs. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 18:343–352.
Trembleau, S., T. Germann, M. K. Gately, and L. Adorini. 1995. The role of IL-2 in the induction of organ-specific autoimmune disease. Immunol. Today 16:383–386.
Cooper, S. M., S. Sriram, and G. E. Ranges. 1988. Suppression of murine collagen-induced arthritis with monoclonal anti-Ia antibodies and augmentation with IFN-γ. J. Immunol. 141:1958–1962.
Williams, R. O., D. G. Williams, M. Feldmann, and R. N. Maini. 1993. Increasedlimbinvolvementinmurinecollagen-inducedarthri-tis following treatment with anti-interferon-gamma. Clin. Exp. Immumol. 92:323–327.
Manoury-Schwartz, B., G. Chiocchia, N. Bessis, O. Abehsira-Amar, F. Batteux, S. Muller, et al. 1997. High susceptibity to collagen-induced arthritis in mice lacking IFN-γ receptors. J. Immunol. 158:5501–5506.
Wiesenberg, I., P. H. Van der Meide, H. Schellebens, and S. S. Alkan. 1989. Suppression and augmentation of rat adjuvant arthritis with monoclonal anti-interferon-gamma antibody. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 78:245–249.
Fox, S. W. and T. J. Chambers. 2000. Interferon-γ directly inhibits TRANCE-induced osteoclastogenesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 276:868–872.
Takayanayi, H., K. Ogasawara, S. Hida, T. Chiba, S. Murata, K. Sato, et al. 2000. T-cell-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis by signaling cross-talk between RANKL and IFN-γ. Nature 408:600–605.
Alvaro-Gracia, J. M., N. J. Zvaifler, and G. S. Firestein. 1990. Cytokines in chronic inflammatory arthritis. V: Mutual antagonism between interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on HLA-DR expression, proliferation, collagenase production, and granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor production by rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. J. Clin. Invest. 86:1790–1798.
Guedez, Y. B., K. B. Whittington, J. L. Clayton, L. B. Joosten, F. J. Van de Loo, W. B. van den Berg, and E. F. Rosloniec. 2001. Genedtic ablation of interferon-γ up-regulates interleukin-1β expression and enables the elicitation of collagen-induced arthritis in a nonsusceptible mouse strain. Arthritis Rheum. 44:2413–2424.
Sicher, S C., M. A. Vazques, and C. Y. Lu. 1994. Inhibition of macrophage Ia expression by nitric oxide. J. Immunol. 153:1293–1300.
Tavares-Murta, B. M., J. S. Machado, S. H. Ferreira, and F. Q. Cunha. 2001. Nitric oxide mediates the inhibition of neutrophil migration induced by systemic administration of LPS. Inflammation 25:247–253.
De Caterina, R. P., P. Libby, H. B. Ping, V. J. Thannickal, T. B. Rajavsahisth, M. A. Gimbrone, et al. 1995. Nitric oxide decreased cytokine-induced endothelial activation: Nitric oxide selectively reduces endothelial expression of adhesion molecules and proinflammatory cytokines. J. Clin. Invest. 96:60–68.
Sandi, C., and C. Gauza. 1995. Evidence for nitric oxide in the corticotropin-releasing factor release induced by interleukin-1β. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 274:17–23.
Arnett, A. A., R. P. Hellendall, G. K. Matsushima, K. Suzuki, V. E. Laubach, P. Sherman, et al. 2002. The protective role of nitric oxide in a neurotoxicant-induced demyelinating model. J. Immunol. 168:427–433.
Veihelmann, A., J. Landes, A. Hofbauer, M. Dorger, H. J. Refior, K. Messmer, et al. 2001. Exacerbation of antigen-induced arthritis in inducible nitric oxide synthase-deficient mice. Arthritis Rheum. 44:1420–1427.
Billigham, M. E. 1995. Mechanism and models in rheumatoid arthritis. ISBN 0–12–340440–1384–409.
Tsukano, M., Y. Nawa, and M. Kotani. 1983. Characterization of low dose induced suppressor cells in adjuvant arthritis in rats. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 53:60–66.
Qin, H. Y., M. W. Sadelain, C. Hitchon, J. Lauzon, and B. Shigh. 1993. Complete Freund's adjuvant-induced T cells prevent the development and adoptive transfer of diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. J. Immunol. 150:2072–2080.
Zheng, C. L., M. A. Hossiain, A. Kukita, K. Ohki, T. Satoh, and O. Kohashi. 2002. Complete Freund's adjuvant suppresses the development and progression of pristane-induced arthritis in rats. Clin Immunol 103:204–209.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, CL., Ohki, K., Hossain, M.A. et al. Complete Freund's Adjuvant Promotes the Increases of IFN-γ and Nitric Oxide in Suppressing Chronic Arthritis Induced by Pristane. Inflammation 27, 247–255 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025092615584
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025092615584