Abstract
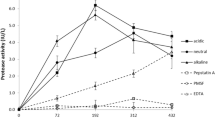
The culture liquids of three Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris strains were found to possess proteolytic activity. The culture liquid of strain B611 with the highest proteolytic activity was fractionated by salting-out with ammonium sulfate, gel filtration, and ion-exchange chromatography. The electrophoretic analysis of active fractions showed the presence of two proteases in the culture liquid of strain B611, the major of which was serine protease. The treatment of cabbage seedlings with the proteases augmented the activity of peroxidase in the cabbage roots by 28%.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Williams, P.H., Black Rot: A Continuing Threat to World Crucifer, Plant Diseases, 1980, vol. 64, pp. 736-742.
Daniels, M.J., Barber, C.E., Turner, P.C., Sawczyc, M.K., Byrde, R.J.W., and Fielding, A.H., Cloning of Genes Involved in Pathogenicity of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris Using the Broad-Host-Range Cosmid pLAFR1, EMBO J., 1984, vol. 3, pp. 3323-3328.
Dow, J.M., Clarke, B.R., Milligan, D.E., Tang, J.-L., and Daniels, M.J., Extracellular Proteases from Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris, the Black Rot Pathogen, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1990, vol. 56,no. 10, pp. 2994-2998.
Dow, J.M., Fan, M.-J., Newman, M.-A., and Daniels, M.J., Differential Expression of Conserved Protease Genes in Crucifer-Attacking Pathovars of Xanthomonas campestris, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1993, vol. 59,no. 12, pp. 3996-4003.
Manual of Methods for General Bacteriology, Gerhardt, P. et al., Eds., Washington: Am. Soc. Microbiol., 1981. Translated under the title Metody obshchei bakteriologii, Moscow: Mir, 1983, vol. 1.
Shchegolev, S.Yu. and Khlebtsov, N.G., Primenenie mikro-i mini-EVM pri opredelenii parametrov dispersionnykh sistem spektroturbidimetricheskim metodom (The Application of Micro-and Minicomputers to Determine the Parameters of Dispersed Systems by the Spectroturbidimetric Method), Saratov: Sarat. Gos. Univ., 1984.
Barbieri, P., Zanelli, T., Galli, E., and Zanetti, G., Wheat Inoculation with Azospirillum brasilense Sp6 and Some Mutants Altered in Nitrogen Fixation and Indole-3-Acetic Acid Production, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 1986, vol. 36, pp. 87-90.
Stadnik, G.I., Kalashnikova, E.E., Konnova, S.A., and Ignatov, V.V., Role of the Surface and Extracellular Substances of the Phytopathogenic Bacterium Xanthomonas campestris in Its Interactions with Cabbage Plants, Mikrobiologiya, 2001, vol. 70,no. 2, pp. 270-274.
Kelleher, P.I. and Juliano, R.L., Proteolytic Enzymes: A Practical Approach, Anal. Biochem., 1984, vol. 136, p. 470.
Laemmli, U.K., Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4, Nature (London), 1970, vol. 227, pp. 680-685.
Bradford, M.M., A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding, Anal. Biochem., 1976, vol. 72,no. 1, pp. 248-254.
Rumshinskii, L.Z., Matematicheskaya obrabotka rezul'tatov eksperimenta (Mathematical Processing of Experimental Results), Moscow: Nauka, 1971, p. 15.
Andreeva, V.A., Ferment peroksidaza: uchastie v zashchitnom mekhanizme rastenii (Peroxidase: Involvement in the Plant Defense Mechanism), Moscow: Nauka, 1988.
Ball, A.M., Ashby, A.M., Daniels, M.J., Ingram, D.S., and Johnstone, K., Evidence for the Requirement of Extracellular Protease in the Pathogenic Interaction of Pirenopeziza brassicae with Oilseed Rape, Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol., 1991, vol. 38, pp. 147-161.
Heilbronn, J., Johnstone, D.J., Dunbar, B., and Lyon, G.D., Purification of a Metalloprotease Produced by Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora and the Degradation of Potato Lectin In Vitro, Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol., 1995, vol. 47, pp. 285-292.
Dow, J.M., Davies, H.A., and Daniels, M.J., A Metalloprotease from Xanthomonas campestris That Specifically Degrades Proline-and Hydroxyproline-Rich Glycoproteins of the Plant Extracellular Matrix, Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact., 1998, vol. 11,no. 11, pp. 1085-1093.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalashnikova, E.E., Chernyshova, M.P. & Ignatov, V.V. The Extracellular Proteases of the Phytopathogenic Bacterium Xanthomonas campestris . Microbiology 72, 443–447 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025044706964
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025044706964