Abstract
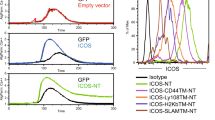
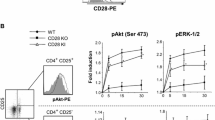
Stimulation of T cells through the T cell receptor is insufficient for optimal T cell activation. A second activation signal is necessary, being usually provided by the costimulatory molecule CD28. Recently, additional costimulatory pathways have been identified, including inducible costimulator (ICOS) and its ligand B7RP-1. We have examined the role of the B7RP-1/ICOS costimulatory pathway on antigen presentation by B cells, using the I-Ak and I-Ek-positive CH27 B cell line and several different T cell lines. We found that CH27 expressed B7RP-1 and PD-L1 whereas the T cell lines expressed ICOS and PD-1. In the presence of HEL, the T cell hybridomas C10 and 3A9 released IL-2, which is indicative of antigen-specific T cell activation by the CH27 cells. Unexpectedly, blocking antibodies for B7RP-1 and ICOS enhanced the IL-2 response in both T cells. As expected, an increase in the production of IL-2 was seen when blocking antibodies for PD-1 were used. Blocking with antibodies for I-Ak, CD28, B7.1, and B7.2 lead to a decrease in IL-2 production. Additionally we tested a Th1 and a Th2 T cell clone. Blockade of B7RP-1/ICOS lead to an increased IFN-γ response in Th1 cells (A.E7) and an increased IL-4 response in Th2 cells (D10.G4.1). Intracellular staining also showed an increase in cytokine production when the B7RP-1/ICOS pathway was blocked. In conclusion, the B7RP-1/ICOS pathway is negatively regulating T cell activation by B cells and may play a role similar to that of the PD-L1/PD-1 pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
June, C. H., J. A. Bluestone, L.M. Nadler, and C. B. Thompson. 1994. The B7 and CD28 receptor families. Immunol. Today 15:321–331.
Schwartz, R. H. 1990. A cell culture model for T lymphocyte clonal anergy. Science 248:1349–1356.
Van Parijs, L. and A. K. Abbas. 1998. Homeostasis and self-tolerance in the immune system: Turning lymphocytes off. Science 280:243–248.
Bluestone, J. A. 1997. Is CTLA-4 a master switch for peripheral T cell tolerance? J. Immunol. 158:1989–1993.
Yoshinaga, S. K., J. S. Whoriskey, S. D. Khare, U. Sarmiento, J. Guo, T. Horan, G. Shih, M. Zang, M. A. Coccia, T. Kohno, A. Tafuri-Bladt, and B. Brankow. 1999 T-cell co-stimulation through B7RP-1 and ICOS. Nature 402:827–832.
Hutloff, A., A. M. Dittrich, K. C. Beier, B. Eljaschewitsch, R. Kraft, I. Anagnostopoulos, and R. A. Kroczek. 1999. ICOS is an inducible T-cell co-stimulator structurally and functionally related to CD28. Nature 397:263–266.
Aicher, A., M. Hayden-Ledbetter, W. A. Brady, A. Pezzutto, G. Richter, D. Magaletti, S. Buckwalter, J. A. Ledbetter, and E. A. Clark. 2000. Characterization of human inducible costimulator ligand expression and function. J. Immunol. 164:4689–4696.
Mages, H. W., A. Hutloff, C. Heuck, K. Buchner, H. Himmelbauer, F. Oliveri, and R. A. Kroczek. 2000. Molecular cloning and characterization of murine ICOS and identification of B7h as ICOS ligand. Eur. J. Immunol. 30:1040–1047.
Chambers, C. A. 2001. The expanding world of co-stimulation: The two-signal model revisited. Trends Immunol. 22:217–23.
Nishimura, H. and T. Honjo. 2001. PD-1: An inhibitory immunoreceptor involved in peripheral tolerance. Trends Immunol. 22:265–268.
Ozkaynak, E., W. Gao, N. Shemmeri, C. Wang, J. C. Gutierrez-Ramos, J. Amaral, S. Qin, J. B. Rottman, A. J. Coyle, and W. W. Hancock. Importance of ICOS-B7RP-1 costimulation in acute and chronic allograft rejection. Nat. Immunol. 2:591–596.
Wahl, P., R. Schoop, G. Bilic, J. Neuweiler, M. Le Hir, S. K. Yoshinaga, and R. P. Wüthrich. 2002. Renal tubular epithelial expression of the costimulatory molecule B7RP-1 (ICOS ligand). J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 13:1517–1526.
Dong, C., U. A. Temann, and R. A. Flavell. 2001. Cutting edge: Critical role of inducible costimulator in germinal center reactions. J. Immunol. 166: 3659–3662.
Tafuri, A., A. Shahinian, F. Bladt, S. K. Yoshinaga, M. Jordana, A. Wakeham, L. M. Boucher, D. Bouchard, V. S. Chan, G. Duncan, B. Odermatt, A. Ho, A. Itie, T. Horan, J. S. Whoriskey, T. Pawson, J. M. Penninger, P. S. Ohashi, and T. W. Mak. 2001. ICOS is essential for effective T-helper-cell responses. Nature 409:105–109.
Dong, C., A. E. Juedes, U. A. Temann, S. Shresta, J. P. Allison, N. H. Ruddle, and R. A. Flavell. 2001. ICOS co-stimulatory receptor is essential for T-cell activation and function. Nature 409:97–101.
Rottman, J. B., T. Smith, J. R. Tonra, K. Ganley, T. Bloom, R. Silva, B. Pierce, J. C. Gutierrez-Ramos, E. özkaynak, and A. J. Coyle. 2001. The costimulatory molecule ICOS plays an important role in the immunopathogenesis of EAE. Nat. Immunol. 2:605–611.
Wüthrich, R. P., L. H. Glimcher, M. A. Yui, A. M. Jevnikar, S. E. Dumas, and V. E. Kelley. 1990. Generation of highly differentiated murine renal tubular epithelial cell lines MHC class II regulation, antigen presentation and tumor necrosis factor production. Kidney Int. 37:783–792.
Jevnikar, A. M., R. P. Wüthrich, F. Takei, H. W. Xu, D. C. Brennan, L. H. Glimcher, and V. E. Rubin-Kelley. 1990. Differing regulation and function of ICAM-1 and class II antigens on renal tubular cells. Kidney Int. 38:417–425.
Hagerty, D. T. and P. M. Allen. 1992. Processing and presentation of self and foreign antigens by the renal proximal tubule. J. Immunol. 148:2324–2330.
Hudson, L. and F. C. Hay. 1980. Practical Immunology, 2nd edn. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford.
Allen, P. M. and E. R. Unanue. 1984. Differential requirements for antigen processing by macrophages for lysozyme-specific T cell hybridomas. J. Immunol. 132:1077–1079.
Allen, P. M., G. R. Matsueda, E. Haber, and E. R. Unanue. 1985. Specificity of the T cell receptor: Two different determinants are generated by the same peptide and the Iak molecule. J. Immunol. 135:368–373.
Nabavi, N., Z. Ghogawala, A. Myer, I. J. Griffith, W. F. Wade, Z. Z. Chen, D. J. McKean, and L. H. Glimcher. 1989. Antigen presentation abrogated in cells expressing truncated Ia molecules. J. Immunol. 142:144–147.
Lederer, J. A., J. S. Liou, M. D. Todd, L. H. Glimcher, and A. H. Lichtman. 1994. Regulation of cytokine gene expression in T helper cell subsets. J. Immunol. 152:77–86.
Benz, P. S., X. Fan, and R. P. Wüthrich. 1996. Enhanced CD44 expression in MRL-lpr lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 50:156–163.
Mueller, D. L. 2000. T cells: A proliferation of costimulatory molecules. Curr. Biol. 10:R227-R230.
Coyle, A. J. and J. C. Gutierrez-Ramos. 2001. The expanding B7 superfamily: Increasing complexity in costimulatory signals regulating T cell function. Nat. Immunol. 2:203–209.
Swallow, M. M., J. J. Wallin, and W. C. Sha. 1999. B7h, a novel costimulatory homolog of B7.1 and B7.2, is induced by TNF alpha. Immunity 11:423–432.
Salomon, B. and J. A. Bluestone. 2001. Complexities of CD28/B7: CTLA-4 costimulatory pathways in autoimmunity and transplantation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19:225–9252.
Carter, L. L., L. A. Fauser, J. Jussif, L. Fitz, B. Deng, C. R. Wood, M. Collins, T. Honjo, G. J. Freeman, and B. M. Carreno. 2002. PD-1:PD-L inhibitory pathway affects both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and is overcome by IL-2. Eur. J. Immunol. 32: 634–643.
Freeman, G. J., A. J. Long, Y. Iwai, K. Bourque, T. Chernova, H. Nishimura, L. J. Fitz, N. Malenkovich, T. Okazaki, M. C. Byrne, H. F. Horton, L. Fouser, L. Carter, V. Ling, M. R. Bowman, B. M. Carreno, M. Collins, C. R. Wood, and T. Honjo. 2000. Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J. Exp. Med. 192:1027–1034.
Latchman, Y., C. R. Wood, T. Chernova, D. Chaudhary, M. Borde, I. Chernova, Y. Iwai, A. J. Long, J. A. Brown, R. Nunes, E. A. Greenfield, K. Bourque, V. A. Boussiotis, L. L. Carter, B. M. Carreno, N. Malenkovich, H. Nishimura, T. Okazaki, T. Honjo, A. H. Sharpe, and G. J. Freeman. 2001. PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nat. Immunol. 2:261–268.
Nishimura, H., M. Nose, H. Hiai, N. Minaro, and T. Honjo. 1999. Development of lupus-like autoimmune diseases by disruption of the PD-1 gene encoding an ITIM motif-carrying immunoreceptor. Immunity 11:141–151.
Eppihimer, M. J., J. Gunn, G. J. Freeman, E. A. Greenfield, T. Chernova, J. Erickson, and J. P. Leonard. 2002. Expression and regulation of the PD-L1 immunoinhibitory molecule on microvascular endothelial cells. Microcirculation 9:133–145.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wahl, P., Schoop, R., Horan, T.P. et al. Interaction of B7RP-1 with ICOS Negatively Regulates Antigen Presentation by B Cells. Inflammation 27, 191–200 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025032429697
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025032429697