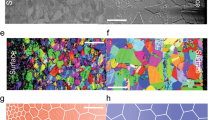
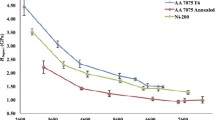
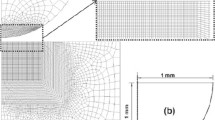
Abstract
An impact test with energy control has been developed to study the degradation phenomena generally encountered on materials submitted to complex conditions including impacts, for example during erosion. The test permits the material response to single or multiple impacts at a microscopic and a macroscopic scale to be characterized. The energy of each impact is precisely controlled and may reach a value of 100 mJ per impact. Experiments have shown that the dynamic loading duration is very short, typically between 100 and 200 μs, and deformation speeds on the impacted metals are in the order of magnitude of 103 s-1. Indenters of various tip radii have been used and a large range of impacting conditions tested. The high reproducibility of the tests confirms that it permits the simulation of damage phenomena already identified in metallic substrates submitted to erosion wear induced by hard particle impacts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Subhash, in: Mechanical Testing and Evaluation, ASM Hand-book, Vol. 8, eds. H. Kuhn and D. Medlin (ASM, Ohio, 2000), p. 519.
P. Chevallier, A. Forner and A. B. Vannes, Wear 186(1 (1995) 210.
Y. Gachon, A. B. Vannes, G. Farges, M. C. Sainte Catherine, I. Caron and G. Inglebert, Wear 233 (1999) 263.
J. P. Nobre, A. M. Dias and R. Gras, Wear 211 (1997) 226.
B. J. Koeppel and G. Subhash, Experimental Techniques, Vol. 21 (1997), p. 16.
G. J. Koeppel and G. Subhash, Wear 244 (1999) 56.
K. Wellinger and H. Breckel, Wear 13 (1969) 257.
O. Knotek, B. Bosserhoff, A. Schrey, T. Leyendecker, O. Lemmer and S. Esser, Surf. Coat. Technol. 54 (1992) 102.
K. D. Bouzakis, N. Vidakis, T. Leyendecker, O. Lemmer, H. G. Fuss and G. Erkens, Surf. Coat. Technol. 86 (1996) 549.
K. D. Bouzakis, N. Vidakis, T. Leyendecker, G. Erkens and R. Wenke, Thin Solid Films 308 (1997) 315.
C. Lalanne, Chocs Mécaniques, Hermes ed. (1999). (in French)-
D. Tabor, The Hardness of Metals, Oxford classic texts in Physical Sciences, OUP (2000).
M. Choudhri, J. Wells and A. Stephens, Phil. Mag. A43(A), (1981) 643.
G. Levy and A. A. Parry, Wear 64 (1980) 83.
K. L. Johnson, Contact Mechanics (Cambridge University Press, 1985).
E. Sauger, L. Ponsonnet, J. M. Martin and L. Vincent, Tribol. Int. 33(11) (2000) 743.
W. C. Oliver and G. M. Pharr, J. Mater. Res. 7(6) (1992).
A. C. Sekkal, Etude des transformation tribologiques de surface ou 'TTS' induites par impacts à énergie contrôlée, PhD Thesis (2000), Ecole Centrale de Lyon n° 2000–31.
Y. Bai, Res. Mechanica 31 (1990) 133.
Y. Bai, B. Dodd, Adiabatic Shear Localisation (Pergamon Press, 1992).
Y. Chen, Contribution à la physique du procédé de mécanosynthèse, PhD Thesis, Universite Paris XI, 1992.
D. R. Maurice and T. H. Courteny, Metal Trans. 21A (1990) 289.
R. M. Davis and T. H. McDeermott, Metal Trans. 19 (1988) 2869.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sekkal, A., Langlade, C. & Vannes, A. A Micro/Macro Impact Test at Controlled Energy for Erosion and Phase-Transformation Simulation. Tribology Letters 15, 265–274 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024996621189
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024996621189