Abstract
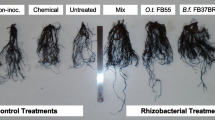
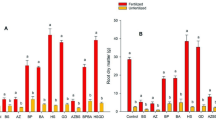
Commercial fish emulsion was evaluated as a plant growth medium and as a nutrient base to enhance radish (Raphanus sativus L. var. sativus) growth by bacterial and actinomycete isolates. Six bacterial isolates including three actinomycetes were selected from a screening of 54 bacteria (including 23 actinomycetes) based on their ability to produce plant growth regulators (PGRs) and to colonize radish roots. These isolates were tested in the presence and absence of autoclaved or non-autoclaved fish emulsion or inorganic fertilizers. The nutrient contents and types and levels of PGRs in tissues of treated plants were assayed to determine the basis of growth promotion. Fish emulsion was found to support plant growth in a sandy soil as effectively as an applied inorganic fertilizer. The plant growth promotion by bacterial and actinomycete isolates was most pronounced in the presence of autoclaved or non-autoclaved fish emulsion than in the presence of the inorganic fertilizers. The bacterial and actinomycete isolates were capable of producing auxins, gibberellins and cytokinins and appeared to use fish emulsion as a source of nutrients and precursors for PGRs. PGR levels in planta following combined treatments of the bacterial and actinomycete isolates and fish emulsion were found to be significantly enhanced over other treatments. The effect of fish emulsion appears to be more related to its role as a nutrient base for the bacterial and actinomycete isolates rather than to the increased activity of the general microflora of treated soil. This is the first report of fish emulsion as a nutrient base for plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. These results also indicate that the successful treatment can be effective and economical for horticultural production in sandy soils such as those found in the United Arab Emirates where fish emulsion is already in use as a substitute or supplement for inorganic fertilizer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad J S and Baker R 1987 Rhizosphere competence of Trichoderma harzianum. Phytopathology 77, 182–189.
Al-Desuquy H S, Mansour F A and Abo-Hamed S A 1998 Effect of the culture filtrates of Streptomyces on growth and productivity of wheat plants. Folia Microbiol. 43, 465–470.
Aung L H and Flick G J 1980 The influence of fish solubles on growth and fruiting of tomato. HortScience 15, 32–33.
Barlow S M, Bimbo A, Jensen P B and Smith G L 1981 International collaborative study of an automated method for the determination of crude protein in fish-meals. J. Sci. Food Agr. 32, 732–736.
Bentley J A 1962 Analysis of plant hormones. Methods Biochem. Anal. 9, 75–124.
Blatt C R and McRae K B 1998. Comparison of four organic amendments with a chemical fertilizer applied to three vegetables in rotation. Can. J. Plant Sci. 78, 641–646.
Bulluck L R and Ristaino J B 2002 Effect of synthetic and organic soil fertility amendments on southern blight, soil microbial communities, and yield of processing tomatoes. Phytopathology 92, 181–189.
Cheng B T 1987 Sawdust as a greenhouse growing medium. J. Plant Nutr. 10, 1437–1446.
Connick W, Jackson M A, Williams K S and Boyette C D 1997 Stability of microsclerotial inoculum of Colletotrichum truncatum encapsulated in wheat flour-kaolin granules. World J. Microb. Biot. 13, 549–554.
Cook R J and Baker K F 1983 The Nature and Practice of Biological Control of Plant Pathogens. The American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul, Minnesota, USA.
de Salamone I E G, Hynes R K and Nelson L M 2001 Cytokinin production by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and selected mutants. Can. J. Microbiol. 47, 404–411.
El-Abyad M S, El-Sayed M A, El-Shanshoury A R and Farid M 1994 Optimization of culture conditions for indole-3-pyruvic acid production by Streptomyces griseoflavus. Can. J. Microbiol. 40, 754–760.
El-Tarabily K A, Hardy G E St J, Sivasithamparam K, Hussein A M and Kurtböke I D 1997 The potential for the biological control of cavity spot disease of carrots caused by Pythium coloratum by streptomycete and non-streptomycete actinomycetes in Western Australia. New Phytol. 137, 495–507.
El-Tarabily K A, Soliman M H, Nassar A H, Al-Hassani H A, Sivasithamparam K, McKenna F and Hardy G E St J 2000 Biological control of Sclerotinia minor using a chitinolytic bacterium and actinomycetes. Plant Pathol. 49, 573–583.
El-Tarabily K A, Sykes M L, Kurtböke D I, Hardy G E St J, Barbosa A M and Dekker R F H 1996 Synergistic effects of a cellulase-producing Micromonospora carbonacea and an antibiotic-producing Streptomyces violascens on the suppression of Phytophthora cinnamomi root-rot of Banksia grandis. Can. J. Bot. 74, 618–624.
Emino E R 1981 Effectiveness of fish soluble nutrients as fertilizers on container-grown plants. HortScience 16, 338.
Frankland B and Wareing P F 1960 Effect of some gibberellic acid on hypocotyl growth of lettuce seedlings. Nature (London) 185, 225–226.
Gaines T P and Mitchell G A 1979 Boron determination in plant tissue by the azomethine-H method. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 10, 1099–1108.
Guinn G, Brummett D L and Beier R C 1986 Purification and measurement of abscisic acid and indole-acetic acid by high performance liquid chromatography. Plant Physiol. 81, 997–1002.
Gunstone F D and Wijesundera R C 1978 The component acids of the lipids in four commercial fish meals. J. Sci. Food Agr. 29, 28–32.
Gutierrez-Manero F J, Ramos-Solano B, Probanza A, Mehouachi J, Tadeo F R and Talon M 2001 The plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria Bacillus pumilus and Bacillus licheniformis produce high levels of physiologically active gibberellins. Physiol. Plant. 111, 206–211.
Hoitink H A and Boehm M J 1999 Biocontrol within the context of soil microbial communities: A substrate-dependent phenomenon. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 37, 427–446.
Katznelson H and Cole S E 1965 Production of gibberellin-like substances by bacteria and actinomycetes. Can. J. Microbiol. 11, 733–741.
Kloepper J W, Lifshitz R and Schroth M N 1988 Pseudomonas inoculants to benefit plant production. ISI Atlas Sci. Anim. Plant Sci. 1, 60–64.
Kloepper J W, Lifshitz R and Zablotowicz R M 1989 Free-living bacterial inocula for enhancing crop productivity. Trends Biotechnol. 7, 39–43.
Kloepper J W, Schroth M N and Miller T D 1980 Effects of rhizosphere colonization by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on potato development and yield. Phytopathology 70, 1078–1082.
Kortemaa H, Rita H, Haahtela K and Smolander A 1994 Root colonization ability of antagonistic Streptomyces griseoviridis. Plant Soil 163, 77–83.
Landry J and Delhaye S 1994 Suitability of the linear relationships for predicting tryptophan of feedstuffs from nitrogen content. A critical study of literature data. J. Sci. Food Agr. 66, 521–525.
Lewis J A, Lumsden R D and Locke J C 1996 Biocontrol of damping-off diseases caused by Rhizoctonia solani and Pythium ultimum with alginate prills of Gliocladium virens, Trichoderma hamatum and various food bases. Biocontrol Sci. Techn. 6, 163–173.
Li Y C, Stoffella P J and Bryan H H 2000 Management of organic amendments in vegetable crop production systems in Florida. Soil Crop Sci. Soc. Fl. 59, 17–21.
Libbert E and Silhengst P 1970 Interactions between plants and epiphytic bacteria regarding their auxin metabolism. VIII. Transfer of 14C-indoleacetic acid from epiphytic bacteria to corn coleoptiles. Physiol. Plant. 23, 480–487.
Locci R 1989 Streptomycetes and related genera. In Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Volume 4. Eds. S T Williams, M E Sharpe and J G Holt. pp 2451–2508. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, MD.
Machàckovà I, Krekule J, Eder J, Seidlovà F and Strnad M 1993 Cytokinins in photoperiodic induction of flowering Chenopodium species. Physiol. Plant. 87, 160–166.
MacMilan J and Suter P J 1963 Thin layer chromatography of the gibberellins. Nature (London) 97, 790.
McQuaker N R, Brown D F and Kluckner P D 1979 Digestion of environmental materials for analysis by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 51, 1082–1084.
Miller E L, Juritz J M, Barlow S M and Wessels J P H 1989 Accuracy of amino acid analysis of fish meals by ion-exchange and gas chromatography. J. Sci. Food Agr. 47, 293–310.
Misaghi I J 1990 Screening bacteria for root colonizing ability by a rapid method. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 22, 1085–1088.
Ndiaye M, Yamoah C F and Dick R P 2000 Fish by-products as a soil amendment for millet and groundnut cropping systems in Senegal. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 17, 329–338.
Nieto K F and Frankenberger W T Jr 1989 Biosynthesis of cytokinins in soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 53, 735–740.
Noel T C, Sheng C, Yost C K, Pharis R P and Hynes M F 1996 Rhizobium leguminosarum as a plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria: Direct growth promotion of canola and lettuce. Can. J. Microbiol. 42, 279–283.
O'Sullivan D J and O'Gara F 1992 Traits of fluorescent Pseudomonas spp. involved in suppression of plant root pathogens. Microbiol. Rev. 56, 662–676.
Okot M W 1995 The chemical composition of Haplochromis and Rastraneobola argenta fish meals. Discov. Innovat. 7, 107–109.
Palleroni N J 1984 Gram-negative aerobic rods and cocci. In Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Volume 1. Eds. N R Kreig and J G Holt. pp 140–219. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, MD.
Regier L W, Jangaard P M, Power H E, March B E and Biely J 1974 Composition and nutritive characteristics of Atlantic Canadian white fish meals. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 31, 201–204.
Sadiq M and Hussain G 1993 Effect of chelate fertilizers on metal concentrations and growth of corn in a pot experiment. J. Plant Nutr. 16, 699–711.
Sarwar M and Frankenberger W T Jr 1994 Influence of L-tryptophan and auxins applied to the rhizosphere on the vegetative growth of Zea mays L. Plant Soil 160, 97–104.
Schnurer J and Rosswall T 1982 Fluorescein diacetate hydrolysis as a measure of total microbial activity in soil and litter. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 6, 1256–1261.
Seear J, Bradfute O E and McLaren A D 1968 Uptake of proteins by plant roots. Physiol. Plant. 21, 979–989.
Seesahai A and Ferguson T U 1998 The yield response of two sweet potato cultivars grown in bags using different soil amendments. Trop. Agr. 75, 29–34.
Shindy W W and Smith O E 1975 Identification of plant hormones from cotton ovules. Plant Physiol. 55, 550–554.
Sneath P H A 1986 Endospore-forming Gram positive rods and cocci. In Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Volume 2. Eds. P H A Sneath, N S Mair, M E Sharpe and J G Holt. pp 1104–1207. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, MD.
Soares J H Jr, Miller D, Cuppett S and Bauerfeld P 1973 A review of the chemical and nutritive properties of condensed fish solubles. Fish Bul. (US) 71, 255–265.
Srinivasan M, Petersen D J and Holl F B 1996 Influence of indoleacetic acid-producing Bacillus isolates on the nodulation of Phaseolus vulgaris by Rhizobium etli under gnotobiotic conditions. Can. J. Microbiol. 42, 1006–1014.
Stephens P M, Crowley J J and Oconnell C 1993 Selection of pseudomonad strains inhibiting Pythium ultimum on sugarbeet seeds in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 25, 1283–1288.
Strain H H, Cope B T and Svec W A 1971 Analytical procedures for isolation, identification, estimation and investigation of the chlorophylls. Method Enzymol. 23, 452–478.
Surico G, Evidente A, Iacobellis N and Randazzo G 1985 A cytokinin from the culture filtrate of Pseudomonas syringae pv. savastanoi. Phytochemistry 24, 1499–1502.
Sweeney R A and Rexroad P R 1987 Comparison of LECO FP-228 ‘nitrogen determinator’ with AOAC copper catalyst Kjeldahl method for crude protein. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 70, 1028–1030.
Tien T M, Gaskings M H and Hubbell D H 1979 Plant growth substances produced by Azospirillum brasilense and their effect on the growth of pearl millet (Pennisetum americanum L.). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 37, 1016–1024.
Wellington E M H and Williams S T 1978 Preservation of actinomycete inoculum in frozen glycerol. Microbios Lett. 6, 151–157.
Wheeler A W 1972 Changes in growth-substances contents during growth of wheat grains. Ann. Appl. Biol. 72, 327–334.
Whipps J M 1997 Developments in the biological control of soil-borne plant pathogens. Adv. Bot. Res. 26, 1–134.
Whipps J M 2001 Microbial interactions and biocontrol in the rhizosphere. J. Exp. Bot. 52, 487–511.
Zall D M, Fisher D and Garner M Q 1956 Photometric determination of chlorides in water. Anal. Chem. 28, 1665–1668.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Tarabily, K.A., Nassar, A.H., Hardy, G.E. et al. Fish emulsion as a food base for rhizobacteria promoting growth of radish (Raphanus sativus L. var. sativus) in a sandy soil. Plant and Soil 252, 397–411 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024729620154
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024729620154