Abstract
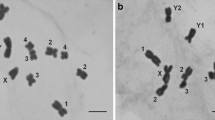
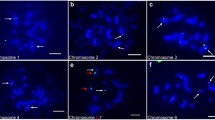
Hop (Humulus lupulus L.) waskaryotyped by Fluorescence In SituHybridization (FISH) with probes 18S-25Sand 5S rDNA as well as DAPI banding andmeasurements of lengths of chromosome.Irrespective of the sex of the plants theseprobes revealed one signal near thetelomere of chromosome 6 and two signalseach on chromosomes 2 and 5.The shortest chromosome in a metaphaseplate of a male plant was designated to bechromosome Y. It displayed neither signalswith FISH nor DAPI bands. A middle sizedmetacentric chromosome with no telomericbut with an interstitial DAPI band on theshort arm was designated as X. Allautosomes displayed telomeric DAPI-positivebands. For the first time all mitotic hopchromosomes including the sex chromosomeswere identified by methods of molecularcytogenetics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartlett, M.S., 1937. Properties of sufficiency and statistical tests. Proc Roy Soc A 160: 268-282.
Campell, B.R., Y. Soung, T.E. Posch, C.A. Cullis & C.D. Town, 1992. Sequence and organization of 5S ribosomal RNA-encoding genes of Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene 112: 225-228.
Fisher, R.A., 1925. Statistical Methods for Research Workers. Oliver and Boyd, Edinburgh, UK.
Flavell R.B., 1986. The structure and control of expression of ribosomal RNA genes. Oxf Surv PlantMol Cell Biol 3: 252-274.
Fleischer, R., C. Horlemann, C. Kling & G. Weber, 2003. AFLP fingerprinting in hop: analysis of the genetic variability of the Tettnang variety. Genet Res Crop Evol, in press.
Galasso, I., T. Schmidt and D. Pignone, 2001. Identification of Lens culinaris ssp culinaris chromosomes by physical mapping of repetitive DNA sequences. Chromosome Res 9: 199-209.
Gerlach, W.L., J.R. Bedbrook, 1979. Cloning and characterization of ribosomal RNA genes from wheat and barley. Nucleic Acids Res 7: 1869-1885.
Haunold, A., 1991. Cytology and cytogenetics of Hops. In: T. Tsuchiya and P.K. Gupta (Eds.), Chromosome Engineering in Plants: Genetics, Breeding, Evolution, pp. 251-563. Elsevier, New York.
ISCN, 1978. An international system for human cytogenetic nomenclature. Cytogenet Cell Genet 21: 318-320.
Jacobsen, P., 1957. The sex chromosomes in Humulus. Hereditas 43: 357-370.
Jewell, D.C. & I. Islam-Faridi, 1994. A technique for somatic chromosome preparation and C-banding of maize. In: M. Freeling & V. Walbot (Eds.), The Maize Handbook, pp. 484-493. Springer-Verlag, New York, USA.
Kamstra, A.S., A.G.J. Kuipers, J.M. de Jeu, M.S. Ramanna, E. Jacobsen, 1997. Physical localisation of repetitive DNA sequences in Alstroemeria: karyotyping of two species with species-specific and ribosomal DNA. Genome 40: 652-658.
Khrustaleva, L.I. & C. Kik, 2001. Localization of single-copy TDNA insertion in transgenic shallots (Allium cepa L.) by using ultra-sensitive FISH with tyramide signal amplification. Plant J 25: 699-707.
Kohlman, H. & A. Kastner, 1976. Der Hopfen. Hopfenverlag Wolnzach.
Leitch, I.J., A.R. Leitch & J.S. Heslop-Harrison, 1991. Physical mapping of plant DNA sequences by simultaneous in situ hybridization of two differently labelled fluorescent probes. Genome 34: 329-333.
Leitch, I.J. & J.S. Heslop-Harrison, 1992. Physical mapping of the 18S-5.8S-26S rRNA genes in barley by in situ hybridization. Genome 35: 1013-1018.
Levan, A., K Fredga & A. Sandberg, 1964. Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas 52: 201-220.
Linares, C., J. Gonzales, E. Ferrer & A. Fomonaya, 1996. The use of double fluorescence in situ hybridization to physically map the positions of 5S rDNA genes in relation to the chromosomal location of 18S-5/8S-26S rDNA and a C genome specific DNA sequence in the genus Avena. Genome 39: 535-542.
Lubaretz, O., J. Fuchs, R. Ahne, A. Maister & I. Schubert, 1996. Karyotyping of three Pinaceae species via fluorescent in situ hybridization and computer-aided chromosome analysis. Theor Appl Genet 92: 411-416.
Meinkoth, J. & G. Wahl, 1984. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilised on solid supports. Ann Biochem 138: 267-284.
Mukai, Y., T.R. Endo & B.S. Gill, 1990. Physical mapping of the 5S rRNA multigene family in common wheat. J Hered 81: 290-295.
Mukai, Y., T.R. Endo & B.S. Gill, 1991. Physical mapping of the 18S.25S rRNA multigene family in common wheat: identification of a new locus. Chromosoma 100: 71-78.
Neve, R.A., 1961. Sex determination in the cultivated hop Humulus lupulus. PhD thesis. Univ. of London.
Neve, R.A., 1991. Hops. Chapman and Hall, London.
Ono, T., 1955. Studies in hop. I. Chromosomes of common hop and its relatives. Bull Brew Sci 2: 1-65.
Parker, J.S. & M.S. Clark, 1991. Dosage sex-chromosome systems in plants. Plant Science 80: 79-92.
Pijnacker, L.P. & M.A. Ferwerda, 1984. Giemsa C-banding of potato chromosomes. Can J Genet Cytol 26: 415-419.
Pillay, M. & S.T. Kenny, 1996. Structure and inheritance of ribosomal DNA variants in cultivated and wild hop, Humulus lupulus L. Theor Appl Genet 93: 333-340.
Reeves, A. and J. Tear, 2000. MicroMeasure for Windows, version 3.3. Free program distributed by the authors over the Internet from Depts/ Biology/MicroMeasure.
Sadder, M.T. & G. Weber, 2001. Karyotype of maize (Zea mays L.) mitotic metaphase chromosomes as revealed by fluorescence in situ hybridization with cytogenetic DNA markers. Plant Mol Biol Reporter 19: 117-123.
Schwarzacher, T., A.R. Leitch & J.S. Heslop-Harrison, 1994. DNA-DNA in situ hybridization methods for light microscopy. In: N. Harris and K.J. Oparka (Eds.), Plant Cell Biology: A Practical Approach, pp. 127-155. IRL Press, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Seefelder, S., H. Ehrmaier, G. Schweizer & E. Seigner, 2000. Male and female genetic linkage map of hops, Humulus lupulus. Plant Breed 119: 249-255.
Shephard, H.L., J.S. Parker, P. Darby & C.C. Ainsworth, 2000. Sexual development and sex chromosomes in hop. New Pythol 148: 397-411.
Wing, O., 1929. On the nature of sex chromosomes in Humulus. Hereditas 12: 53-63.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karlov, G., Danilova, T., Horlemann, C. et al. Molecular cytogenetics in hop (Humulus lupulus L.) and identification of sex chromosomes by DAPI-banding. Euphytica 132, 185–190 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024646818324
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024646818324