Abstract
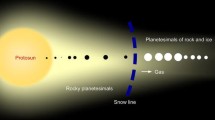
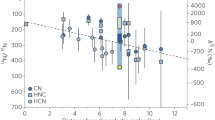
We discuss some of the major noble gas components on the Moon and their implications on the history of Moon and Sun. He, Ar, and Rn have been detected in the tenuous lunar atmosphere. The Ar and Rn abundances suggest that a sizeable fraction of the lunar interior presently loses all its freshly produced radiogenic noble gases. Part of the radiogenic Ar and Xe (the latter from now extinct radioactive isotopes of I and Pu) outgassed from the lunar interior later became retrapped in the dust grains on the lunar surface. These “parentless” gases may also be used to constrain the degassing history of the Moon, although a quantitative understanding is lacking. The dust layer on the lunar surface contains large amounts of noble gases implanted by the solar wind. The lunar regolith therefore constitutes the best available archive of the solar history of the past four billion years.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aellig, M.R., Lazarus, A.J., and Steinberg, J.T.: 2001, 'The Solar Wind Helium Abundance: Variation with Wind Speed and the Solar Cycle', Geophys. Res. Lett. 28, 2767–2770.
Benkert, J.-P., Baur, H., Signer, P., and Wieler, R.: 1993, 'He, Ne, and Ar from the Solar Wind and Solar Energetic Particles in Lunar Ilmenites and Pyroxenes', J. Geophys. Res. 98, 13147–13162.
Bernatowicz, T.J., Hohenberg, C.M., and Podosek, F.A.: 1979, 'Xenon Component Organization in 14301', Proc. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. 10th, 1587–1616.
Black, D.C.: 1972, 'On the Origins of Trapped He, Ne and Ar Isotopic Variations in Meteorites — I. Gas-rich Meteorites, Lunar Soil and Breccia', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 36, 347–375.
Bjorkholm, P.J., Golub, L., and Gorenstein, P.: 1973, 'Distribution of 222Rn and 210Po on the Lunar Surface as Observed by the Alpha Particle Spectrometer', Proc. Lunar Sci. Conf. 4th, 2793–2802.
Bochsler, P.: 2000, 'Abundances and Charge States of Particles in the Solar Wind', Rev. Geophys. 38, 247–266.
Bochsler, P., Geiss, J., and Maeder, A.: 1990, 'The Abundance of 3He in the Solar Wind — a Constraint for Models of Solar Evolution', Solar Phys. 128, 203–215.
Bodmer, R., and Bochsler, P.: 1998, 'The Helium Isotopic Ratio in the Solar Wind and Ion Fractionation in the Corona by Inefficient Coulomb Drag', Astron. Astrophys. 337, 921–927.
Bogard, D.D.: 1995, 'Impact Ages of Meteorites: A Synthesis', Meteoritics 30, 244–268.
Drozd, R., Hohenberg, C.M., and Ragan, D.: 1972, 'Fission Xenon from Extinct 244Pu in 14301', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 15, 338–346.
Eugster, O., Terribilini, D., Polnau, E., and Kramers, J.: 2001, 'The Antiquity Indicator 40Ar/36 Ar for Lunar Surface Samples Calibrated by 235U-136 Xe Dating', Met. Planet. Sci. 36, 1097–1115.
Fegley, B., and Swindle, T.D.: 1993, 'Lunar Volatiles: Implications for Lunar Resource Utilization', in J. Lewis, M. S. Matthews, and M.L. Guerrieri (eds.), Resources of Near-Earth Space, Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson AZ, pp. 367–426.
Geiss, J.: 1973, 'Solar Wind Composition and Implications About the History of the Solar System', Conf. Pap. Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 13th, 3375–3398.
Geiss, J., and Reeves, H.: 1972, 'Cosmic and Solar System Abundances of Deuterium and Helium-3', Astron. Astrophys. 18, 126–132.
Geiss, J., Gloeckler, G., and von Steiger, R.: 1994, 'Solar and Heliospheric Processes from Solar Wind Composition Measurements', Phil. Trans. Royal Soc. London A 349, 213–226.
Gorenstein, P., Golub, L., and Bjorkholm, P.J.: 1973, 'Spatial Features and Temporal Variability in the Emission of Radon from the Moon: An Interpretation of Results from the Alpha Particle Spectrometer', Proc. Lunar. Sci. Conf. 4th, 2803–2809.
Halliday, A.N.: 2000, 'Terrestrial Accretion Rates and the Origin of the Moon', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 176, 17–30.
Heber, V.S.: 2002, 'Ancient Solar Wind Noble Gases in Lunar and Meteoritic Archives and Tests for Modern Solar Wind Collection with the GENESIS Mission', PhD Thesis ETH Zürich Nr. 14579, 154 pp.
Heber, V.S., Baur, H., and Wieler, R.: 2001, 'Heavy Solar Noble Gases in Meteorites — New Insights into a Unique Archive of Solar Wind', in R.F. Wimmer-Schweingruber (ed.), Solar and Galactic Composition, AIP Conf. Proc. 598, pp. 387–392.
Hodges, R.R.: 1975, 'Formation of the Lunar Atmosphere', Moon 14, 139–157.
Hodges, R.R.: 1977, 'Release of Radiogenic Gases from the Moon', Phys. Earth Planet. Int. 14, 282–288.
Hoffman, J.H., Hodges, R.R., Johnson, F.S., and Evans, D.E.: 1973, 'Lunar Atmospheric Composition Results from Apollo 17', Proc. Lunar Sci. Conf. 4th, 2865–2875.
Kallenbach, R.: 2001, 'Isotopic Composition Measured In-situ in Different Solar Wind Regimes by CELIAS/MTOF on board SOHO', in R.F. Wimmer-Schweingruber (ed.), Solar and Galactic Composition, AIP Conf. Proc. 598, pp. 113–119.
Kallenbach, R., Ipavich, F.M., Bochsler, P., et al.: 1997, 'Isotopic Composition of Solar Wind Neon Measured by CELIAS/MTOF on Board SOHO', J. Geophys. Res. 102, 26895–26904.
Kerridge, J.F., Eugster, O., Kim, J.S., and Marti, K.: 1991, 'Nitrogen Isotopes in the 74001/74002 Double-drive Tube from Shorty Crater, Apollo 17', Proc. Lun. Planet. Sci. 21, 291–299.
Killen, R.M., and Ip, W.-H.: 1999, 'The Surface-bounded Atmospheres of Mercury and the Moon', Rev. Geophys. 37, 361–406.
Lawson, S.L., Feldman, W.C., Lawrence, D.J., Moore, K.R., Maurice, S., Belian, R.D., and Binder, A.B.: 2002, 'Maps of Lunar Radon-222 and Polonium-210', Lunar Planet. Sci., XXXIII, abstract #1835, Lunar Planet. Institute, Houston (CD-ROM).
Leich, D.A., and Niemeyer, S.: 1975, 'Trapped Xenon in Lunar Anorthositic Breccia 60015', Proc. Lunar Sci. Conf. 6th, 1953–1965.
Lightner, B.D., and Marti, K.: 1974, 'Lunar Trapped Xenon', Proc. Lunar Sci. Conf. 5th, 2023-2031.
Manka, R.H., and Michel, F.C.: 1971, 'Lunar Atmosphere as a Source of Lunar Surface Elements', Proc. Lunar Sci. Conf. 2nd, 1717–1728.
Marty, B., Hashizume, K., Chaussidon, M., and Wieler, R.: 2003, 'Nitrogen Isotopes on the Moon: Archives of the Solar and Planetary Contributions to the Inner Solar System', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Mathew, K.J., and Marti, K.: 2001, 'Lunar Nitrogen: Indigenous Signature and Cosmic-ray Production Rate', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 184, 659–669.
Megrue, G.H.: 1973, 'Spatial Distribution of 40Ar/39 Ar Ages in Lunar Breccia 14301', J. Geophys. Res. 78, 3216–3221.
Mewaldt, R.A., Ogliore, R.C., Gloeckler, G., and Mason, G.M.: 2001, 'A new Look at Neon-C and SEP-Ne', in R.F. Wimmer-Schweingruber (ed.), Solar and Galactic Composition, AIP Conf. Proc. 598, pp. 393–398.
Murer, C.A., Baur, H., Signer, P., and Wieler, R.: 1997, 'He, Ne, and Ar Abundances in the Solar Wind: in Vacuo Etching of Meteoritic Iron-nickel', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 61, 1303–1314.
Niedermann, S., and Eugster, O.: 1992, 'Noble Gases in Lunar Anorthositic Rocks 60018 and 65315: Acquisition of Terrestrial Krypton and Xenon Indicating an Irreversible Adsorption Process', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 56, 493–509.
Niemeyer, S., and Leich, D.A.: 1976, 'Atmospheric Rare Gases in Lunar Rock 60015', Proc. Lunar Sci. Conf. 7th, 587–597.
Palma, R.L., Becker, R.H., Pepin, R.O., and Schlutter, D.J.: 2002, 'Irradiation Records in Regolith Materials, II: Solar-wind and Solar-energetic-particle Components in Helium, Neon, and Argon Extracted from Single Lunar Mineral Grains and from the Kapoeta Howardite by Stepwise Pulse-heating', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 66, in press.
Pedroni, A., and Begemann, F.: 1994, 'On Unfractionated Solar Noble Gases in the H3-6 meteorite Acfer111', Meteoritics 29, 632–642.
Pepin, R.O., Nyquist, L.E., Phinney, D., and Black, D.C.: 1970a, 'Isotopic Composition of Rare Gases in Lunar Samples', Science 167, 550–553.
Pepin, R.O., Nyquist, L.E., Phinney, D., and Black, D.C.: 1970b, 'Rare Gases in Apollo 11 Lunar Material', Proc. Apollo 11 Lunar Sci. Conf., 1435–1454.
Pepin, R.O., Becker, R.H., and Rider, P.E.: 1995, 'Xenon and Krypton Isotopes in Extraterrestrial Regolith Soils and in the Solar Wind', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 59, 4997–5022.
Polnau, E., and Eugster, O.: 1998, 'Cosmic-ray Produced, Radiogenic, and Solar Noble Gases in Lunar Meteorites Queen Alexandra Range 94269 and 94281', Met. Planet. Sci. 33, 313–319.
Reynolds, J.H., Hohenberg, C.M., Lewis, R.S., Davis, P.K., and Kaiser, W.A.: 1970, 'Isotopic Analysis of Rare Gases from Stepwise Heating of Lunar Fines and Rocks', Science 167, 545–548.
Stern, S.A.: 1999, 'The Lunar Atmosphere: History, Status, Current Problems, and Context', Rev. Geophys. 37, 453–491.
Stöffler, D., and Ryder, G.: 2001, 'Stratigraphy and Isotope Ages of Lunar Geologic Units: Chronological Standard for the Inner Solar System', Space Sci. Rev. 96, 9–54.
Swindle, T.D.: 2002, 'Noble Gases in the Moon and Meteorites — Radiogenic Components and Early Volatile Chronologies', Rev. Min. Geochem. 47, in press.
Swindle, T.D., Caffee, M.W., Hohenberg, C.M., and Taylor, S.R.: 1986, 'I-Pu-Xe Dating and the Relative Ages of the Earth and Moon', in W.K. Hartmann, R.J. Phillips, and G.J. Taylor (eds.), Origin of the Moon, Lunar Planet. Institute, Houston TX, pp. 331–357.
von Steiger, R., Geiss, J., and Gloeckler, G.: 1997, 'Composition of the Solar Wind', in J.R. Jokipii, C.P. Sonett, and M.S. Giampapa (eds.), Cosmic Winds and the Heliosphere, Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson AZ, pp. 581–616.
Walter, F.M., and Barry, D.C.: 1991, 'Pre-and Main-sequence Evolution of the Solar Activity', in C.P. Sonett, M.S. Giampapa, and M.S. Matthews (eds.), The Sun in Time, Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson AZ, pp. 633–657.
Wieler, R.: 1997, 'Why are SEP Noble Gases so Abundant in Extraterrestrial Samples?', Lunar Planet. Sci. XXVIII, Lunar Planet. Inst., Houston, TX, pp. 1551–1552.
Wieler, R.: 1998, 'The Solar Noble Gas Record in Lunar Samples and Meteorites', Space Sci. Rev. 85, 303–314.
Wieler, R.: 2002, 'Noble Gases in the Solar System', Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 47, in press.
Wieler, R., and Baur, H.: 1994a, 'Krypton and Xenon from the Solar Wind and Solar Energetic Particles in two Lunar Ilmenites of Different Antiquity', Meteoritics 29, 570–580.
Wieler, R., and Baur, H.: 1994b, 'Parentless Fission Xenon in Mineral Separates of Lunar Breccia 14301 Studied by Closed System Etching', Meteoritics 29, 550.
Wieler, R., and Baur, H.: 1995, 'Fractionation of Xe, Kr, and Ar in the Solar Corpuscular Radiation Deduced by Closed System Etching of Lunar Soils', Astrophys. J. 453, 987–997.
Wieler, R., Baur, H., and Signer, P.: 1993, 'Parentless Fission and Radiogenic Xe in Lunar Breccia 14301 Studied by Closed-system Etching', Meteoritics 28, 459–460.
Wieler, R., Kehm, K., Meshik, A.P., and Hohenberg, C.M.: 1996, 'Secular Changes in the Xenon and Krypton Abundances in the Solar Wind Recorded in Single Lunar Grains', Nature 384, 46–49.
Wimmer-Schweingruber, R.F., and Bochsler, P.: 2001, 'Lunar Soils: a Long-term Archive for the Galactic Environment of the Heliosphere?', in R.F. Wimmer-Schweingruber (ed.), Solar and Galactic Composition, AIP Conf. Proc. 598, pp. 399–404.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wieler, R., Heber, V. Noble Gas Isotopes on the Moon. Space Science Reviews 106, 197–210 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024641805441
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024641805441