Abstract
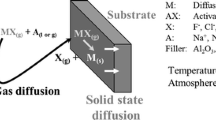
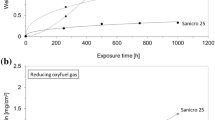
Corrosion of A210 C carbon steel was investigated under three different conditions: (1) using synthetic gas mixtures with varying amounts of O2, SO2, and HCl; (2) in the flue gas introduced from a coal-fired fluidized-bed combustor (FBC), with and without a deposit cover; and (3) within the freeboard of the FBC firing two different coals. Generally, the oxide scale formed in the temperature range of 370–560°C was mainly Fe2O3. The oxidation rate was significantly increased with an increase in temperature. In the synthetic gas mixtures SO2 and HCl caused scale damage by weakening of the scale-metal interface. The combination of the gases can greatly accelerate the metal corrosion. In the FBC flue gas (condition 2), deposit additions exerted a significant effect on accelerating the metal corrosion. In the FBC freeboard tests (condition 3), the atmospheres containing a higher content of SO2 and HCl increased the metal corrosion in comparison to corrosion in low-SO2 and HCl-containing atmospheres. In the former case, an S-enriched phase or pits formed in the residual wastage at or near the metal. This may be the cause of wastage spallation. The HCl effect is discussed but is not conclusive. Moreover, in the FBC system, erosion and deposition appeared to play important roles in exaggerating metal recession.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
E. A. Rogers, J. C. Holder, J. Minchener, A. J. Page, R. D. Lanauze, and G. G. Thurlow, Materials Problems in Fluidized-Bed Combustion Systems, EPRI Report No.CS-1449, May, 1980.
J. Stringer and I. G. Wright, J. Mater. Energy System 8, 319(1986).
J. Minchener and A. V. Levy, eds., Proceedings, Conf. on Corrosion-Erosion-Wear of Materials at Elevated Temperature. NACE, Houston, TX. 1987, p. 152.
K. Nakagawa, Proc. High Temp. Corros. (III), Les Embiez, France, May, 1992;K. Nakagawa, J. De Physique 4, 787(1993).
P. Y. Hou, S. MacAdam, H. Zhang and J. Stringer, Mat. High Temp. 14, 255(1997).
W. T. Bakker, R. A. Perkins, and J. van Liere, Mat. Perf. 1, 59(1985).
K. Natesan, Corrosion 41, 655(1985).
H. J. Grabke and Meadowcroft, eds. Guideline for Methods of Testing and Research in High-Temperature Corrosion. European Federation of Corrosion Publication, No. 14, Institute of Materials, 1995.
F. H. Stott and J. F. Norton, Mat. High Temp. 14, 219(1997).
J. R. Nicholls, Mat. High Temp. 14, 255(1997).
K. Liu, W.P. Pan, and J. T. Riley, Corrosion 56, 298(2000).
X. Peng, W. P. Pan, and J. T. Riley, Mater. Sci. Eng. 332, 270(2002).
W. Xie, W.P. Pan, and J. T. Riley, Energy and Fuel, 13, 585(1999).
E. A. Gulbransen, Mem. Scient. Rev. Met. 62, 253(1965).
R. L. Tallman and E. A. Gulbransen, J. Electrochem. Soc. 115, 770(1968).
J. C. Yang, E. Schumann, I. Levin and M. Rühle, Acta Mater. 46, 2195(1998).
W. J. Bottega and A. J. Maewal, Appl. Mech. 50, 184(1983).
M. Spiegel, and H. J. Grabke, Mater. Corros. 46, 121(1995).
H. J. Grabke, E. Reese and M. Spiegel, Corros. Sci. 37, 1023(1995).
Z. Suo, Mech. Phys. Solids., 43, 829(1995).
W. Xie, K. Liu, W.P. Pan, and J. T. Riley, Fuel, 78, 1425(1999).
R. Q. Vincent, and A. M. Manaker, in Chlorine in Coal, J. Stringer, and D. D. Banerjee, (eds.), Elsevier Science Publishers B. V., Amsterdam, 1991, p. 389.
X. Peng, K. Liu, W.P. Pan, and J. T. Riley, (work to be published).
D. T. Liang, E. J. Antony, B. K. Leowin, and K. J. Yates, Proceedings, 11th International Conference on FBC, Montreal, Canada, 1991, Vol. 2, p. 917.
P. L. Daniel, in Chlorine in Coal, J. Stringer, and D. D. Banerjee, (eds.), Elsevier Science Publishers B. V., Amsterdam, 1991, p. 207.
P. Seifert and M. Born, Effect of fuel composition on chloride corrosion in furnaces, VGB Tech. Ver. Grosskraftsverksbetr., [Tech. Ber.] VGB-TP 1995, Paper 9, p. 21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, X., Liu, K., Pan, WP. et al. High-Temperature Corrosion of A210-C Carbon Steel in Simulated Coal-Combustion Atmospheres. Oxidation of Metals 60, 117–135 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024621514635
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024621514635