Abstract
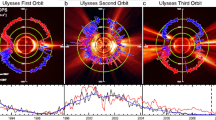
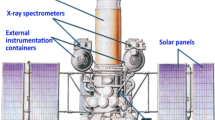
The Genesis Discovery mission will return samples of solar matter for analysis of isotopic and elemental compositions in terrestrial laboratories. This is accomplished by exposing ultra-pure materials to the solar wind at the L1 Lagrangian point and returning the materials to Earth. Solar wind collection will continue until April 2004 with Earth return in Sept. 2004. The general science objectives of Genesis are to (1) to obtain solar isotopic abundances to the level of precision required for the interpretation of planetary science data, (2) to significantly improve knowledge of solar elemental abundances, (3) to measure the composition of the different solar wind regimes, and (4) to provide a reservoir of solar matter to serve the needs of planetary science in the 21st century. The Genesis flight system is a sun-pointed spinner, consisting of a spacecraft deck and a sample return capsule (SRC). The SRC houses a canister which contains the collector materials. The lid of the SRC and a cover to the canister were opened to begin solar wind collection on November 30, 2001. To obtain samples of O and N ions of higher fluence relative to background levels in the target materials, an electrostatic mirror (‘concentrator’) is used which focuses the incoming ions over a diameter of about 20 cm onto a 6 cm diameter set of target materials. Solar wind electron and ion monitors (electrostatic analyzers) determine the solar wind regime present at the spacecraft and control the deployment of separate arrays of collector materials to provide the independent regime samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anders, E., and Grevesse, N.: 1989, 'Abundances of the Elements: Meteoritic and solar', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 53, 197–214.
Barraclough, B. L., Dors, E. E., Abeyta, R. A., Alexander J. F., Ameduri, F. P. Baldonado, J. R. Bame, S. J., Casey, P. J., Dirks, G., Everett, D. T., Gosling, J. T., Grace, K. M., Guerrero, D. R., Kolar, J. D., Kroesche, J., Lockhart, W., McComas, D. J., Mietz D. E., Roese, J., Sanders, J., Steinberg, J. T., Tokar, R. L., Urdiales, C., and Wiens, R. C.: 2003, 'The Plasma Ion and Electron Instruments for the Genesis Mission', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Bochsler, P.; 2000, 'Abundances and Charge States of Particles in the SolarWind.' Rev. Geophys. 38, 247–266.
Burnett, D. S., Woolum, D. S., Benjamin, T. M., Rogers, P. S. Z., Duffy, C. J., and Maggiore, C.: 1989, 'A Test of the Smoothness of the Elemental Abundances of Carbonaceous Chondrites.' Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 53, 471–481.
Clayton, R. N.: 1993, 'Oxygen Isotopes in Meteorites', Ann. Rev. Earth Planetary Sci. 31, 115–149.
Clayton, R. N.: 2002, 'Self-Shielding in the Solar Nebula', Nature 415, 860–861.
Clayton, R. N. and Mayeda, T. K.: 1984, 'The O Isotope Record in Murchison and Other Carbonaceous Chondrites', Earth Planetary Sci. Lett. 67, 151–161.
Collier, M. R., Hamilton, D. C., Gloeckler, G., Ho, G., Bochsler, P., Bodmer, R., and Sheldon, R.: 1998, 'Oxygen 16 to Oxygen 18 Abundance Ratio in the SolarWind Observed by Wind/MASS', J. Geophys. Res. 103, 7–13.
Fisk, L. A., Schwadron, N. A., and Zurbuchen, T. H.: 1998, 'On the Slow Solar Wind', Space Sci. Rev. 86, 51–60.
Geiss, J., Buehler F., Cerutti H., Eberhardt P., and Filleux C.: 1972, 'Solar Wind Composition Experiment,' Apollo 16 Preliminary Science Report, NASA SP-315, pp. 14–1–14–10.
Hashizume, K., Chaussidon, M., Marty, B., and Robert, F.: 2000, 'Solar Wind Record on the Moon: Deciphering Presolar from Planetary Nitrogen', Science 290, 1142–1145.
Hong, P. E., Carlisle, G., and Smith N. G.: 2002, 'Look, Ma, No HANS', Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE Aerospace Conference, to appear.
Jurewicz, A. J. G., Burnett, D. S., Wiens, R. C., Friedmann, T. A., Hays, C. C., Hohlfelder, R. J., Nishiizumi, K., Stone, J. A., Woolum, D. S., Becker, R., Butterworth, A. L., Campbell, A. J., Ebihara, M., Franchi, I. A., Heber, V., Hohenberg, C. M., Humayun, M., McKeegan, K. D., McNamara, K., Meshik, A., Pepin, R. O., Schlutter, D., and Wieler, R.: 2003, 'Overview of the Genesis Solar-Wind Collector Materials', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Kallenbach, R.: 2001, 'Isotopic Composition Measured in-situ in Different Solar Wind Regimes by CELIAS/MTOF on SOHO', in R. F. Wimmer-Schweingruber (ed.), Solar and Galactic Composition Am. Inst. of Physics, pp. 113–119.
Kallenbach, R., Ipavich, F. M., Kucharek, H., Bochsler, P., Galvin, A. B., Geiss, J., Gliem, F., Gloeckler, G., Grünwaldt, H., Hefti, S., Hilchenbach, M., and Hovestadt, D.: 1998a, 'Fractionation of SI, NE and MG Isotopes in the Solar Wind as Measured by SOHO/CELIAS/MTOF', Space Sci. Rev. 85, 357–370.
Kallenbach, R., Geiss, J., Ipavich, F. M., Gloeckler, G., Bochsler, P., Gliem, F., Hefti, S., Hilchenbach, M., and Hovestadt, D.: 1998b, 'Isotopic Composition of Solar Wind Nitrogen: First in situ Determination with the CELIAS/MTOF Spectrometer on Board SOHO', Astrophys. J. 507, L185-L188.
Kallenbach, R., Ipavich, F. M., Kucharek, H., Bochsler, P., Galvin, A. B., Geiss, J., Gliem, F., Gloeckler, G., Grünwaldt, H., Hilchenbach, M., and Hovestadt, D.: 1999, 'Solar Wind Isotopic Abundance Ratios of Ne, Mg and Si Measured by SOHO/CELIAS/MTOF as Diagnostic Tool for the Inner Corona', Phys. Chem. Earth (C) 24, 415–419.
Kerridge, J. F.: 1989, 'What Has Caused the Secular Increase in 15N?', Science 245, 480–486.
Kerridge, J. F.: 1995, 'Nitrogen and its Isotopes in the Early Solar System', in K. A. Farley (ed.), Volatiles in the Earth and Solar System Conf. Proc. 341, Am. Inst. of Physics, pp. 167–174.
Marsch, E., von Steiger, R., and Bochsler, P.: 1995, 'Element Fractionation by Diffusion in the Solar Chromosphere', Astron. Astrophys. 301, 261–276.
McSween, H. Y.: 1993, 'Cosmic or Cosmuck?', Meteoritics 28, 3–4.
Neugebauer, M.: 1991, 'The Quasi-Stationery and Transient States of the Solar Wind', Science 252, 404–409.
Neugebauer, M., Steinberg, J. T., Tokar, R. L., Barraclough, B. L., Dors, E. E., Wiens, R. C., Gingerich, D. E., Luckey, D., and Whiteaker, D. B.: 2003, 'Genesis On-Board Determination of the Solar Wind Flow Regime', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Nordholt, J. E., Wiens, R. C., Abeyta, R. A., Baldonado, J. R., Burnett, D. S., Casey, P., Everett, D. T., Kroesche, J., Lockhart, W., McComas, D. J., Mietz, D. E., MacNeal, P., Mireles, V., Moses, R. W. Jr., Neugebauer, M., Poths, J., Reisenfeld, D. B., Storms, S. A., and Urdiales, C.: 2003, 'The Genesis Solar Wind Concentrator', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Owen, T., Mahaffy, P. R., Niemann, H. B., Atreya, S., and Wong, M: 2001, 'Protosolar Nitrogen', Astrophys. J. Lett. 553, L77-L79.
Ozima, M., Wieler, R., Marty, B., and Podosek, F. A.: 1998, 'Comparative Studies of Solar, Q-Gases and Terrestrial Noble Gases, and Implications on the Evolution of the Solar Nebula', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acata 62, 301–314.
Pepin, R. O.: 1991, 'On the Origin and Evolution of Terrestrial Planet Atmospheres and Meteoritic Volatilies', Icarus 92, 2–79.
von Steiger, R., Schwadron, N. A., Fisk, L. A., Geiss, J., Gloeckler, G., Hefti, S., Wilken, B., Wimmer-Schweingruber, R. F., and Zurbuchen, T. H.: 2000, 'Composition of Quasi-Stationary Solar Wind Flows from Ulysses/Solar Wind Ion Composition Spectrometer', J. Geophys. Res. 105, 27217–27238.
Wieler, R., Kehm, K., Meshik., A. P., and Hohenberg, C. M.: 1996, 'Secular Changes in the Xenon and Krypton Abundances in the Solar Wind Recorded in Single Lunar Grains', Nature 384, 46–49.
Wiens, R. C., Huss, G. R., and Burnett, D. S.: 1999, 'The Solar Oxygen-Isotopic Composition: Predictions and Implications for Solar Nebula Processes', Met. Planetary Sci. 34, 99–107.
Wiens, R. C., Neugebauer, M., Reisenfeld, D. B., Moses, R. W. Jr., and Nordholt, J. E.: 2003, 'Genesis Solar Wind Concentrator: Computer Simulations of Performance under Solar Wind Conditions', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Wimmer-Schweingruber, R. F. and Bochsler, P.: 2001, 'The Isotopic Composition of Oxygen in the Fast Solar Wind: ACE/SWIMS', Geophys. Res. Lett. 28, 2763–2766.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burnett, D., Barraclough, B., Bennett, R. et al. The Genesis Discovery Mission: Return of Solar Matter to Earth. Space Science Reviews 105, 509–534 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024425810605
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024425810605