Abstract
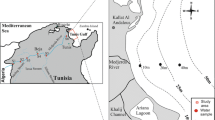
In situ benthic flux chamber experiments were performed during late austral spring and early summer of 1996 at eleven nearshore locations in the southern Patos Lagoon, Brazil. The Patos Lagoon is the largest lagoonal system in South America and is a very important nursery ground for local fin fish and shell fish fisheries. These are the first benthic flux measurements made in Patos Lagoon and they suggest that remineralizationwithin the sediments may dominate the recycling of organic matter and nutrients in thelagoon. Measured oxygen benthic fluxes (45–160 mmol m-2 d-1) are sufficientto remineralize reported mean water column carbon fixation while phosphate and fixednitrogen benthic fluxes (-0.4–2 and -1.1–4.2 mmol m-2 d-1, respectively)are sufficient to supply 100% and 25% of the required water column nutrient demand,respectively. Although of limited areal and temporal coverage, these initial studiesdemonstrate that sediments play a major role in the metabolism and nutrient cyclingwithin the Patos Lagoon Estuary and that future studies of lagoonal biogeochemistrymust consider exchange with the bottom.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu P. C., Biddanda B. and Odebrecht C. (1992) Bacterial dynamics of the Patos Lagoon estuary, southern Brazil (32°S, 52°W): relationship with phytoplankton production and suspended material. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 6, 621–635.
Abreu P. C., Odebrecht C. and Gonzales A. (1994) Particulate and dissolved phytoplankton production of the Patos Lagoon estuary, southern Brazil: comparison of methods and influencing factors. Journal of Plankton Research 16, 737–753.
Aller R. C. (2001) Transport and reactions in the bioirrigated zone. In The Benthic Boundary Layer (eds. B. P. Boudreau and B. B. Jorgensen) pp. 269–301. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Baumgarten M. G. Z., Niencheski L. F. and Kuroshima K. (1995) Qualidade das guas estuarinas que margeiam a cidade do Rio Grande (RS). Atlantica 17, 19–36.
Bemvenuti C. E. (1997) Environment and Biota of the Patos Lagoon Estuary: Benthic invertebrates. In Subtropical Convergence Environments. The Coast and Sea in the Southwestern Atlantic (eds. U. Seeliger, C. Odebrecht and J. P. Castello) pp. 43–46. Springer.
Bergesh M. (1990) Variacoes de biomassa e composicao do fitoplancton na area estuarina rasa da Lagoa dos Patos e suas relacoes com fatores de influencia. M.Sc. Thesis, Universidade do Rio Grande-FURG, RS, Brazil.
Boynton W. R., Kemp W.M., Osborne C. G., Kaumeyer K. R. and Jenkins M. C. (1981) Influence of water circulation rate on in situ measurements of benthic community respiration. Marine Biology 65, 185–190.
Buchholtz-ten Brink M. R., Gust G. and Chavis D. (1989) Calibration and performance of a stirred benthic chamber. Deep-Sea Research 36, 1083–1101.
Castello J. P. (1985) La ecologia de los consumidores del estuario da Lagoa dos Patos, Brazil. In Fish Community Ecology in Estuaries and Coastal Lagoons: Towards an Ecosystem Integration (ed. A. Yanes-Arancibia) pp. 383–406. Dr (R) Unam Press, Mexico.
Castello J. P. and Müller O. O. (1978) On the relationship between rainfall and shrimp production in the estuary of Patos Lagoon (Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil). Atlantica 3, 67–74.
Costa C. S. B. (1997) Environment and Biota of the Patos Lagoon Estuary: Tidal marsh and wetland plants. In Subtropical Convergence Environments. The Coast and Sea in the Southwestern Atlantic (eds. U. Seeliger, C. Odebrecht and J. P. Castello) pp. 24–26, Springer.
Costa C. S. B., Seeliger U. and Kinas P. G. (1988) The effect of wind velocity and direction on the salinity regime in the lower Patos Lagoon estuary. Ciencia e Cultura 40, 909–912.
Grasshoff K., Ehrhardt M. and Kremling K. (1983) Methods of seawater analysis. [second ed.] Verlag Chemie, Weinheim.
Herz R. (1977) Circulacao das aguas de superficie da Lagoa dos Patos. Ph.D. Thesis. Universidade de Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil.
Huettel M. and Gust G. (1992) Solute release mechanisms from confined sediment cores in stirred benthic chambers and flume flows. Marine Ecology Progress Series 82, 187–197.
Jahnke R. A. (2001) Constraining organic matter cycling with benthic fluxes. In The Benthic Boundary Layer: Transport Processes and Biogeochemistry (eds. B. P. Boudreau and B. B. Jorgensen) pp. 302–319, Oxford.
Jahnke R. A., Nelson J. R., Marinelli R. L. and Eckman J. E. (2000) Benthic flux of biogenic elements on the Southeastern U.S. continental shelf: Influence of pore water advective transport and benthic microalgae. Continental Shelf Research 20, 109–127.
Kjerfve, B. (1986) Comparative oceanography of coastal lagoons. In Estuarine Variability (ed. D. A. Wolde) pp. 63–81, Academic Press, New York.
Li Y. H. and Gregory S. (1974) Diffusion of ions in seawater and deep-sea sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 38, 703–714.
Muelbert J. H. and Weiss G. (1991) Abundance and distribution of fish larvae in the channel area of the Patos Lagoon estuary, Brazil. NOAA Technical Report NMFS 95, 43–54.
Niencheski L. F. and Baumgarten M. G. (1997) Environment and Biota of the Patos Lagoon Estuary: Environmental Chemistry. In Subtropical Convergence Environments. The Coast and Sea in the Southwestern Atlantic (eds. U. Seeliger, C. Odebrecht and J. P. Castello) pp. 20–23, Springer.
Niencheski L. F. and Windom H. L. (1994) Nutrient flux and budget in Patos Lagoon estuary. The Science of the Total Environment 149, 53–60.
Niencheski L. F., Windom H. L. and Smith R. (1994) Distribution of particulate trace metal in Patos Lagoon Estuary (Brazil). Marine Pollution Bulletin 28, 96–102.
Redfield A. C. Ketchum B. H. and Richards F. A. (1963) The influence of organisms on the composition of seawater. In The Sea (ed. M. N. Hill). Vol. 2, Interscience Pub., New York.
Seeliger U. (1997) Environment and Biota of the Patos Lagoon Estuary: Benthic macroalgae. In Subtropical Convergence Environments. The Coast and Sea in the Southwestern Atlantic (U. Seeliger, C. Odebrecht and J. P. Castello) pp. 30–33, Springer.
Vieira E. F. and Rangel S. R. S. (1988) Planicie Costeira do Rio Grande do Sul. Sagra. Porto Alegre. p. 256.
Windom H. L., Niencheski L. F. and Smith R. (1999) Biogeochemistry of nutrients and trace metals in the estuarine region of the Patos Lagoon (Brazil). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 48, 113–123.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niencheski, L.F., Jahnke, R.A. Benthic Respiration and Inorganic Nutrient Fluxes in the Estuarine Region of Patos Lagoon (Brazil). Aquatic Geochemistry 8, 135–152 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024207220266
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024207220266