Abstract
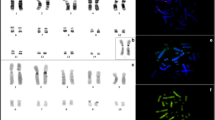
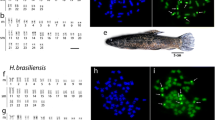
This paper presents the karyotype of Callicebus donacophilus pallescens for the first time. The analysis included G-, C-, NOR-banding techniques and FISH with chromosome painting probes from Saguinus oedipus and Homo sapiens. The results were compared with the karyotypes of Callicebus moloch donacophilus and C. moloch previously published. These three karyotypes display the same diploid number (2n=50) but diverge about the number of biarmed and acrocentric chromosomes. The acrocentrics 14 and 15 from C. m. donacophilus and C. moloch have undergone an in-tandem fusion originating a large acrocentric (pair 10) in C. d. pallescens. The major submetacentric pair (pair 1) from C. d. donacophilus and C. moloch have undergone fission originating two acrocentric pairs in C. d. pallescens (pairs 15 and 22). Herein was evidence that, in spite of the high interspecific variation among Callicebus, most of the chromosomes remained conserved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barros RMS, Pieczarka JC, Rodrigues LRR, Brigido MCO, Muniz JAPC, Nagamachi CY (1999) O cariótipo de Callicebus donacophilus pallescens (Primates). Genet Mol Biol 23: 24.
Barros RMS, Pieczarka JC, Brigido MCO, Muniz JAPC, Rodrigues LRR, Nagamachi CY (2000) A new karyotype in Callicebus torquatus (Cebidae — Primates). Hereditas 133: 55-58.
Bender MA, Chu EHY (1963) The chromosomes of primates. In: Buettner-Janusch J., ed. Evolutionary and genetic Biology of Primates. London, New York: Academic Press,pp 261-310.
Bender MA, Mettler LE (1958) Chromosomes studies of primates. Science 128: 186-190.
Benirschke K, Bogart MH (1976) Chromosomes of the tan-handed titi (Callicebus torquatus, H offmansegg, 1807). Folia Primatol 25: 25-34.
Consigliere S, Stanyon R, Koehler U, Agoramoorthy G, Wienberg J (1996) Chromosome painting defines genomic rearrangements between red howler monkey subspecies. Chromosome Res 4: 264-270.
Consigliere S, Stanyon R, Koehler U, Arnold N, Wienberg J (1998) In situ hybridisation (FISH) maps chromosomal homologies between Alouatta belzebul (Plaryrrhini, Cebidae) and other primates and reveals extensive interchromosomal rearrangements between howler monkey genomes. Am J Primatol 46: 119-133.
De Boer LEM (1974) Cytotaxonomy of the Platyrrhini (Primates). Genen Phenen 17: 1-115.
De Oliveira EHC (2001) Filogenia da subfamilia Atelinae (Primates, Platyrrhini): Anaálise comparativa por pintura cromossómica multicor. Doctoral Thesis, Universidade Federal do Paranaá, Brazil, pp 171.
De Oliveira EHC, Neusser M, Figueiredo WB et al. (2002) The phylogeny of howler monkeys (Alouatta, Platyrrhini): Reconstruction by multicolor cross-species chromosome painting. Chromosome Res 10: 669-683.
Egozcue J, Perkins EM, Hagemenas F, Ford DM (1969) The chromosomes of some Platyrrhini (Callicebus, Ateles and Saimiri). Folia Primatol 11: 17-27.
Ferguson-Smith MA, Yang, F, O'Brien PCM(1989) Comparative mapping using chromosome sorting and painting. ILAR J 39: 68-76.
Garcia F, Nogueés C, Garcia M et al. (2000) Chromosomal homologies between human and Cebus apella (Primates) revealed by ZOO-FISH. Mamm Genome 11: 399-401.
Hershkovitz P (1990) Titis, new world monkeys of the genus Callicebus (Family Cebidae, Platyrrhini): A preliminary taxonomic review. In: Fieldiana, Zool. New Series. Chicago: Field Museum of Natural History, pp 1-109.
Howell WM, Black DA (1980) Controlled silver-staining of nuclear organizer regions with protective colloidal developer: a 1-step method. Ciénc Cult 36: 1014.
Kobayashi S (1995) A phylogenetic study of titi monkeys, genus Callicebus, based on cranial measurements: I. Phyletic groups of Callicebus. Primates 36: 101-120.
Minezawa M, Borda CJV (1984) Cytogenetic study of the Bolivian titi and revision of its cytotaxonomy state. Kyoto University Overseas Res Rep New World Monkeys 4: 39-45.
Minezawa M, Jordan COC, Borda CJV (1989) Karyotypic study of titi monkeys, Callicebus moloch brunneus. Primates 30: 81-88.
Morescalchi MA, Schempp W, Wienberg J, Stanyon R (1997) Chromosome painting in the New World monkey, Ateles geoffroyi, the black handed spider monkey. Chromosome Res 5: 527-536.
Müller S, Neusser M, O'Brien PCM, Weinberg J (2001) Molecular cytogenetic characterization of the EBV producing cell line B95-8 (Saguinus Oedipus, Playrrhini) by flow cytometry and multicolour cross species chromosome painting. Chromosome Res 9: 689-693.
Nagamachi CY, Pieczarka JC, Pissinati A, Rodrigues, LRR, Goncalves ACO, Barros RMS (1999) Dados citogeneéticos apoiam a colocacáo de Callicebus personatus (Primates, Cebidae) em um grupo próprio. Presented at: IX Congresso Brasileiro de Primatologia, Santa Tereza, E.S., Brasil, pp 78.
Nagamachi CY, Rodrigues LRR, Galetti Jr PM et al. (2003) Cytogenetic studies in Callicebus personatus nigrifons (Platyrrhini, Primates). Caryologia (in press).
Neusser M (1999) Molekular Zytogenetische Untersuchungen zur Chromosomenevolution bei Neuweltaffen. München, Deutschaland, Diplomarbeit: Ludwig-Maximmilians Universität München.
Neusser M, Stanyon R, Bigoni F, Wienberg J, Müeller S (2001) Molecular cytotaxonomy of New World monkeys (Platyrrhini): Comparative analysis of five species by multi-color chromosome painting gives evidence for a classification of Callimico goeldii within the family of Callitrichidae. Cytogenet Cell Genet 94: 206-215.
Pieczarka JC, Nagamachi CY (1988) The karyotype of Callicebus moloch moloch. Rev Bras Genet 11: 653-659.
Richard F, Lombard M, Dutrillaux B (1996) ZOO-FISH suggests a complete homology between human and Capuchin monkey (Platyrrhini) euchromatin, Genomics 36: 417-423.
Rodrigues LRR, Barros RMS, Pissinati A, Pieczarka JC, Nagamachi CY (2001) Cytogenetic study of Callicebus hoffmansi (Cebidae, Primates) and comparison with C. m. moloch. Cytobios 105: 137-145.
Sherlock JK, Griffin DK, Delhanty JDA, Parrington JM (1996) Homologies between human and Marmosett (Callitrix jacchus) chromosomes revealed by comparative chromosome painting. Genomics 214-219.
Stanyon R, Consigliere S, Müller S, Morescalchi A, Neusser M, Wienberg J (2000) Fluorescence in situ hibridization (FISH) maps chromosomal homologies between the dusky titi and squirrel monkey. Am J Primatol 50: 95-107.
Stanyon R, Consigliére S, Bigoni F, Ferguson-Smith M, O'Brien PCM, Wienberg J (2001) Reciprocal chromosome painting between a NewWorld primate, the Woolly monkey, and human. Chromosome Res 9: 97-106.
Sumner AT (1972) A simple technique for distinguishing between human chromosomes. Nature N Biol 232: 31-32.
Telenius H, Carter S, Müller S, Morescalchi A, Weinberg J (1992) Degenerate oligonucleotide-primed PCR (DOPPCR): general amplification of target DNA by a single degenerate primer. Genomics 13: 718-725.
Van Roosmalen MGM, van Roosmalen T, Mittermeier RA (2002) A taxonomic review of the titi monkey, genus Callicebus Thomas 1903, with the description of two new species, Callicebus bernhardi and Callicebus stephennnashi, from Brazilian Amazonia. Neotropical Primates 10 (suppl.): 1-52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barros, R.M.S., Nagamachi, C.Y., Pieczarka, J.C. et al. Chromosomal studies in Callicebus donacophilus pallescens, with classic and molecular cytogenetic approaches: Multicolour FISH using human and Saguinus oedipus painting probes. Chromosome Res 11, 327–334 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024039907101
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024039907101