Abstract
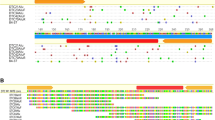
A complete mariner-like element has been identified in the lepidopteran Mamestra brassicae. This element, called Mbmar, represents a new type of mariner transposon. It has a transposase similar to that of other insect mariner coding sequences but its inverted terminal repeats differ from typical mariner ones. This observation is unique since generally both mariner coding region and ITRs are evolutionarily conserved in insects. Mbmar is detectable by FISH only in the heterochromatic regions of both the sex chromosomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auge-Gouillou C, Bigot Y, Pollet N, Hamelin MH, Meunier-Rotival M, Periquet G (1995) Human and other mammalian genomes contain transposons of the marinerfamily.FEBS Lett 368: 541-546.
Boyle AL, Ballard SG, Ward DC (1990) Differential distribution of long and short interspersed element sequences in the mouse genome-chromosome karyotyping by fluorescent in-situ hybridisation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA87: 7757-7761.
Capy P, Langin T, Bigot Y et al. (1994) Horizontal transmission versus ancient origin: mariner in the witness box. Genetica 93:161-170.
Dimitri P, Junakovic N (1999) Revising the selfish DNA hypothesis: new evidences on accumulation of transposable elements in heterochromatin. Trends Genet 15: 123-124.
Mandrioli M (2000) Mariner-like transposable elements are interspersed within the rDNA-associated heterochromatin of the pufferfish Tetraodon fluviatilis.Chromosome Res 8: 177-179.
Mandrioli M (2002) Cytogenetic characterization of telomeres in the holocentric chromosomes of the lepidopteran Mamestra brassicae. Chromosome Res 9:279-286.
Mandrioli M, Bizzarro D, Giusti M, Manicardi GC, Bianchi U (1999a) NORheteromorphism within a parthenogenetic lineage of the aphid Megoura viciae. Chromosome Res 7: 157-162.
Mandrioli M, Bizzaro D, Gionghi D, Bassoli L, Manicardi GC, Bianchi U (1999b) Molecular cytogenetic characterization of a highly repeated DNA sequence in the peach potato aphid Myzus persicae. Chromosoma 108: 436-442.
Mandrioli M, Manicardi GC, Marec F (2003) Cytogenetic and molecular characterization of the MBSAT1 satellite DNA in holokinetic chromosomes of the cabbage moth, Mamestra brassicae(Lepidoptera). Chromosome Res 11:51-56.
Marec F (1996)Synaptonemal complexes in insects. Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 25: 205-233.
Martin VJJ, Mohn WW (1999) An alternative inverse PCR method to amplify DNA sequences flanking Tn5 transposon insertions. J Microbiol Meth 35: 163-166.
Pimpinelli S, Berlocco M, Fanti M et al. (1995) Transposable elements are stable structural components of Drosophila melanogasterheterochromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 3804-3808.
Robertson HM (1993) The mariner transposable element is widespread in insects.Nature 362:241-245.
Steinemann M, Steinemann S, (1992) Degenerating Y chromosome of Drosophila miranda: a trap for retrotransposons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 7591-7595.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandrioli, M. Identification and chromosomal localization of mariner-like elements in the cabbage moth Mamestra brassicae (Lepidoptera). Chromosome Res 11, 319–322 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024035706192
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024035706192