Abstract
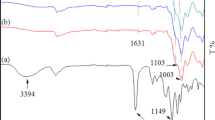
Porous organic-inorganic hybrids of poly(n-butyl acrylate) (PBA) and silica were synthesized with different polymer contents via sol-gel process. With the aim of controlling interfacial properties in hybrids, the bonding agent 3-methacryloxypropyl-trimethoxysilane (MPTS) was copolymerized with n-butyl acrylate (BA) at different proportions. Copolymers P(BA-co-MPTS) and hybrids obtained were characterized by infrared spectroscopy and thermogravimetric analysis. Nitrogen sorption analyses of hybrids determined that the increase in polymer content leads to the formation of non-porous hybrids only if bonding agent content is sufficiently large. Otherwise, hybrids with large pore volumes and sizes, nearly reaching macropore range, are obtained even for polymer content as high as 45% in the absence or low content of MPTS. Scanning electron microscopy images showed that the addition of bonding agent changes the aspect of hybrid surface from rough, with loosely bound particles with a few hundreds nanometers, to relatively smooth, with particles typically smaller than 100 nm. These results were explained considering that a more homogeneous medium provided by the presence of MPTS may lead to easier condensation of PBA-silica particles due to the smaller polymeric domains. This idea is supported by the fact that, after polymer degradation, smaller uniform-sized pores arise for hybrids with larger bonding agent contents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.A. Loy, MRS Bull. 26, 364 (2001).
C.J. Brinker and G.W. Scherer, Sol-Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing (Academic Press, San Diego, 1990), pp. 465, 524.
J.E. Mark, C.Y. Jiang, and M.Y. Tang, Macromolecules 17, 2613 (1984).
H.H. Huang, B. Orler, and G.L. Wilkes, Polym. Bull. 14, 557 (1985).
E.J.A. Pope, M. Asami, and J.D. Mackenzie, J. Mater. Res. 4, 1018 (1989).
B.M. Novak, Adv. Mater. 5, 442 (1993).
L. Mascia, Trends Polym. Sci. 3, 61 (1995).
A.B. Brennan and T.M. Miller, in Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 4 ed. (Wiley, New York, 1994), Vol. 12, p. 644.
J. Wen and G.L. Wilkes, Chem. Mater. 8, 1667 (1996).
P. Judeinstein and C. Sanchez, J. Mater. Chem. 6, 511 (1996).
A.B. Wojcik and L.C. Klein, Appl. Organometal. Chem. 11, 129 (1997).
Y. Chujo and R. Tamaki, MRS Bull. 26, 389 (2001).
C.J. Brinker, Curr. Opin. Solid Mater. Sci. 1, 798 (1996).
A. Stein, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 44–55, 227 (2001).
B. Lindlar, A. Kogelbauer, P.J. Kooyman, and R. Prins, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 44–55, 89 (2001).
Y. Lu, G. Cao, R.P. Kale, S. Prabakar, G.P. López, and C.J. Brinker, Chem. Mater. 11, 1223 (1999).
C. Yu, Y. Yu, L. Miao, and D. Zhao, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 44–55, 65 (2001).
K.A. Mauritz and C.K. Jones, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 40, 1401 (1990).
M. Motomatsu, T. Takahashi, H.Y. Nie, W. Mizutani, and H. Tokumoto, Polymer 38, 177 (1997).
W. Zhou, J.H. Dong, K.Y. Qiu, and Y. Wei, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 73, 419 (1999).
C.K. Chan, I.M. Chu, W. Lee, and W.K. Chin, Macromol. Chem. Phys. 22, 911 (2001).
S.J. Gregg and K.S.W. Sing, Adsorption, Surface Area and Porosity, 2 ed. (Academic Press, San Diego, 1982).
P.A. Webb and C. Orr, Analytical Methods on Fine Particle Technology (Micromeritcs Instrument Corporation, Norcross, 1997).
P. Bosch, F. Monte, J.L. Mateo, and D. Levy, J. Polym. Sci. A: Polym. Chem. 34, 3289 (1996).
Z.H. Huang and K.Y. Qiu, Polymer 38, 521 (1997).
R.O.R. Costa and W.L. Vasconcelos, J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 304, 84 (2002).
I.K. Varma, A.K. Tomar, and R.C. Anand, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 33, 1377 (1987).
S. Yano, K. Nakamura, M. Kodomari, and N. Yanauchi, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 54, 163 (1994).
J.C. Pouxviel, J.P. Boilet, J.C. Beloeil, and J.Y. Allemand, J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 89, 345 (1987).
R.O.R. Costa, W.L. Vasconcelos, and F.S. Lameiras, J. Mater. Sci., submitted.
T. Saegusa, J. Macromol. Sci.-Chem. A28, 817 (1991).
R. Tamaki and Y. Chujo, Appl. Organomet. Chem. 12, 775 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, R.O., Lameiras, F.S. & Vasconcelos, W.L. Structural Control in Poly(butyl acrylate)-Silica Hybrids by Modifying Polymer-Silica Interactions. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology 27, 343–354 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024029305642
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024029305642