Abstract
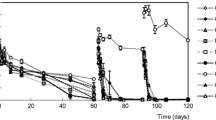
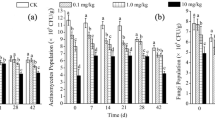
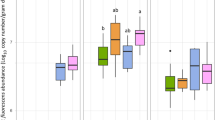
Two different microbial communities able to degrade atrazine (atz) were inoculated in four different soils. The most critical factor affecting the success of inoculation was the soil pH and its organic matter (OM) content. In two alkaline soils (pH > 7), some inoculations led immediately to a strong increase of the biodegradation rate. In a third slightly acidic soil (pH = 6.1), only one inoculum could enhance atz degradation. In a soil amended with organic matter and straw (pH = 5.7, OM = 16.5%), inoculation had only little effect on atz dissipation on the short as well as on the long-term. Nine months after the microflora inoculations, atz was added again and rapid biodegradation in all alkaline inoculated soils was recorded, indicating the long-term efficiency of inoculation. In these soils, the number of atz degraders was estimated at between 6.5 × 103 and 1.5 × 106 (g of soil)-1, using the most probable number (MPN) method. Furthermore, the presence of the atz degraders was confirmed by the detection of the gene atzA in these soils. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) analysis of the 16S rDNA genes indicated that the inoculated bacterial communities had little effect on the patterns of the indigenous soil microflora.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvey, S., Crowley and D. E.: 1996, 'Survival and activity of an atrazine-mineralizing bacterial consortium in rhizosphere soil', Environmental Science and Technology 30, 1596-1603.
Assaf, N. A., Turco and R. F.: 1994, 'Accelerated biodegradation of atrazine by a microbial consortium is possible in culture and soil', Biodegradation 5, 29-35.
Behki, R. M. and Khan, S. U.: 1994, 'Degradation of atrazine, propazine, and simazine by Rhodococcus strain B-30', Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 42, 1237-1241.
de Souza, M. L., Sadowsky, M. J., Wackett and L. P.: 1996, 'Atrazine chlorohydrolase from Pseudomonas sp. strain ADP: Gene sequence, enzyme purification, and protein characterization',Journal of Bacteriology 178, 4894-4900.
Decleire, M., De Cat, W. and Bastin, R.: 1975, 'Application de six biotests á la détection d'herbicides dans l'eau', Revue de l'Agriculture 1, 27-38.
El Fantroussi, S., Verschuere, L., Verstraete, W. and Top, E. M.: 1999a, 'Effect of phenylurea herbicides on soil microbial communities estimated by analysis of 16S rRNA gene fingerprints and community-level physiological profiles', Applied and Environmental Microbiology 65, 982-988.
El Fantroussi, S., Belkacemi, M., Top, E. M., Mahillon, J., Naveau, H. and Agathos, S. N.: 1999b, 'Bioaugmentation of a soil bioreactor designed for pilot scale anaerobic bioremediation studies', Environmental Science and Technology 33, 2992-3001.
Goux, S., Agathos, S. N. and Pussemier, L.: 1998, 'Metabolic characterisation of fifteen atrazinedegrading microbial communities', Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology 21, 254-259.
Goux, S. J., Ibanez, M., Van Hoorick, M., Debongnie, P., Agathos, S. N. and Pussemier, L.: 2000, 'Biodegradation of atrazine in sand semidments and in a sand filter', Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 54, 589-596.
Goux, S. J., Agathos, S. N. and Pussemier, L. D.: 2002, 'Towards a better understanding of enhanced pesticide biodegradation', in S. N. Agathos and W. Reineke (eds.), Biotechnology for the Environment: Strategy and Fundamentals, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 141-156.
Mandelbaum, R. T., Wackett, L. P. and Allan, D. L.: 1993, 'Mineralization of the s-triazine ring of atrazine by stable bacterial mixed cultures', Applied and Environmental Microbiology 59, 1695-17
Meynell, G. G. and Meynell, E.: 1970, Theory and Practice in Experimental Bacteriology, Cambridge University Press, London, 347 pp.
Pussemier, L., Goux, S., Van Elsen, Y. and Mariage, Q.: 1998, Biofilters for On-farm Clean-up of Pesticide Wastes, Mededelingen Faculteit Landbouwwetenschappen, Universiteit Gent 63, 243-250.
Pussemier, L., Goux, S., Vanderheyden, V., Debongnie, P., Tresinie, I. and Foucart, G.: 1997, 'Rapid dissipation of atrazine in soils taken from various maize fields', Weed Research 37, 171-179.
Radosevich, M., Traina, S. J., Hao, Y. L. and Tuovinen, O. H.: 1995, 'Degradation and mineralization of atrazine by a soil bacterial isolate', Applied and Environmental Microbiology 61, 297-302.
Radosevich, M., Traina, S. J. and Tuovinen, O. H.: 1996, 'Biodegradation of atrazine in surface soils and subsurface sediments collected from an agricultural research farm', Biodegradation 7, 137-149.
Shapir, N. and Mandelbaum, R. T.: 1997, 'Atrazine degradation in subsurface soil by indigenous and introduced microorganisms', Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 45, 4481-4486.
Struthers, J. K., Jayachandran, K. and Moorman, T. B.: 1998, 'Biodegradation of atrazine by Agrobacterium radiobacter J14a and use of this strain in bioremediation of contaminated soil', Applied and Environmental Microbiology 64, 3368-3375.
van Veen, A., van Overbeek, L. S., and van Elsas, J. D.: 1997, 'Fate and activity of microorganisms introduced in soil', Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 61, 121-135.
Van Zwieten, L. and Kennedy, I. R.: 1995, 'Rapid degradation of atrazine by Rhodococcus sp. N186/21 and by an atrazine-perfused soil', Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 43, 1377-1382.
Wenk, M., Baumgartner, T., Dobovsek, J., Fuchs, T., Kucsera, J., Zopfi, J. and Stucki, G.: 1998, 'Rapid atrazine mineralisation in soil slurry and moist soil by inoculation of an atrazinedegrading Pseudomonas sp. strain', Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 49, 624-630.
Yanze Kontchou, C. and Gschwind, N.: 1994, 'Mineralization of the herbicide atrazine as a carbon source by a Pseudomonas strain', Applied and Environmental Microbiology 60, 4297-43
Yanze Kontchou, C. and Gschwind, N.: 1995, 'Mineralization of the herbicide atrazine in soil inoculated with a Pseudomonas strain', Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 43, 2291-2294.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goux, S., Shapir, N., Fantroussi, S.E. et al. Long-Term Maintenance of Rapid Atrazine Degradation in Soils Inoculated with Atrazine Degraders. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution: Focus 3, 131–142 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023998222016
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023998222016