Abstract
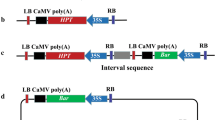
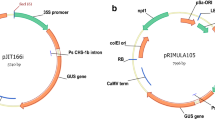
A simple strategy to identify and isolate new promoters suitable for driving the expression of selectable marker genes is described. By employing a Brassica napus hypocotyl transformation protocol and a promoterless gus::nptII tagging construct, a series of 20 kanamycin-resistant tagged lines was produced. Most of the regenerated plants showed hardly any GUS activity in leaf, stem and root tissues. However, expression was readily restored in callus tissue induced on in vitro leaf segments. Genomic sequences upstream of the gus::nptII insertions were isolated via plasmid rescue. Three clones originating from single copy T-DNA lines were selected for further evaluation. The rescued plasmids were cloned as linear fragments in binary vectors and re-transformed to Brassica napus hypocotyl and Solanum tuberosum stem segments. The new sequences maintained their promoter activity, demonstrated by transient and stable GUS activity after transformation. Furthermore, the promoters provided sufficient expression of the nptII gene to yield transgenic plants when using kanamycin as selective agent. Database searching (BLASTN) revealed that the promoters have significant homology with three Arabidopsis BAC clones, one Arabidopsis cDNA and one Brassica napus cDNA. The results presented in this paper illustrate the strength of combined methods for identification, isolation and testing of new plant promoters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altenbach, S.B., Kuo, C.C., Staraci, L.C., Pearson, K.W., Wainwright, C., Georgescu, A. and Townsend, J. 1992. Accumulation of a brazil nut albumin in seeds of transgenic canola results in enhanced levels of seed protein methionine. Plant Mol. Biol. 18: 235–245.
André, D., Colau, D., Schell, J., Van Montagu, M. and Hernalsteens, J.-P. 1986. Gene tagging in plants by a T-DNA insertion that generates APH(3')II plant gene fusions. Mol. Gen. Genet. 204: 512–518.
Bade, J.B. and Damm, B. 1995. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of rapeseed (Brassica napus). In: I. Potrykus and G. Spangenberg (Eds.) Gene Transfer to Plants, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 32–38.
Baumann, K., De Paolis, A., Costantino, P. and Gualberti, G. 1999. The DNA binding site of the Dof protein NtBBF1 is essential for tissue-specific and auxin-regulated expression of the rolB oncogene in plants. Plant Cell 11: 323–333.
Charest, P.J., Caléro, N., Lachance, D., Datla, R.S.S., Duchêsne, L.C. and Tsang, E.W.T. 1993. Microprojectile-DNA delivery in conifer species: factors affecting assessment of transient gene expression using the β-glucuronidase reporter gene. Plant Cell Rep. 12: 189–193.
Datla, R.S.S., Hammerlindl, J.K., Pelcher, L.E., Crosby, W. and Selvaraj, G. 1991. A bifunctional fusion between β-glucuronidase and neomycin phosphotransferase: a broad-spectrum marker enzyme for plants. Gene 101: 239–246.
De Block, M., Debrouwer, D. and Tenning, P. 1989. Transformation of Brassica napus and Brassica oleracea using Agrobacterium tumefaciens and the expression of the bar and neo genes in the transgenic plants. Plant Physiol. 91: 694–701.
de Groot, M.J., Offringa, R., Groet, J., Does, M.P., Hooykaas, P.J. and van den Elzen, P.J. 1994. Non-recombinant background in gene targeting: illegitimate recombination between a hpt gene and a defective 5' deleted nptII gene can restore a Kmr phenotype in tobacco. Plant Mol. Biol. 4: 721–733.
Firek, S., Ozcan, S., Warner, S.A.J. and Draper, J. 1993. A wound-induced promoter driving nptII expression limited to dedifferentiated cells at wound sites is sufficient to allow selection of transgenic shoots. Plant Mol. Biol. 22: 129–142.
Flavell, R.B., Dart, E., Fuchs, R.L. and Fraley, R.T. 1992. Selectable marker genes: safe for plants? Bio/technology 10: 141–144.
Fobert, P.R., Miki, B.L. and Iyer, V.N. 1991. Detection of gene regulatory signals in plants revealed by T-DNA-mediated fusions. Plant Mol. Biol. 17: 837–851.
Fobert, P.R., Labbé, H., Cosmopoulos, J., Gotlob-McHugh, S., Ouellet, T., Hattori, J., Sunohara, G., Iyer, V.N. and Miki, B.L. 1994. T-DNA tagging of a seed coat-specific cryptic promoter in tobacco. Plant J 6: 567–577.
Foster, E., Hattori, J., Labbe, H., Ouellet, T., Fobert, P.R., James, L.E., Iyer, V.N. and Miki, B.L. 1999. A tobacco cryptic constitutive promoter, tCUP, revealed by T-DNA tagging. Plant Mol. Biol. 41: 45–55.
Fristensky, B., Balcerak, M., He, D. and Zhang, P. 1999. Expressed sequence tags from the defence response of Brassica napus to Leptosphaeria maculans. Mol. Plant Path. On-Line http://www.bspp.org.uk/mppol/1999/0301FRISTENSKY
Goddijn, O.J.M., Lindsey, K.,, van der Lee, F.M., Klap, J.C. and Sijmons, P.C. 1993. Differential gene expression in nematodeinduced feeding structures of transgenic plants harbouring promoter gusA fusion constructs. Plant J 4: 863–873.
Grison, R., Grezesbesset, B., Schneider, M., Lucante, N., Olsen, L., Leguay, J.J. and Toppan, A. 1996. Field tolerance to fungal pathogens of Brassica napus constitutively expressing a chimeric chitinase gene. Nature Biotechnol. 14: 643–646.
Herman, L., Jacobs, A., Van Montagu, M. and Depicker, A. 1990. Plant chromosome/marker gene fusion assay for study of normal and truncated T-DNA integration events. Mol. Gen. Genet. 224: 248–256.
Hood, E.E., Gelvin, S.B., Melchers, L.S. and Hoekema, A. 1993. New Agrobacterium helper plasmids for gene transfer to plants. Transgenic Res. 2: 208–218.
Jefferson, R.A. 1987. Assaying chimaeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 5: 387–405.
Jiang, C., Langridge, W.H.R. and Szalay, A.A. 1992. Identification of plant genes in vivo by tagging with T-DNA border-linked luciferase genes followed by inverse polymerase chain reaction amplification. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 10: 345–361.
Kang, H.G. and Singh, K.B. 2000. Characterization of salicylic acid-responsive Arabidopsis Dof domain proteins: overexpression of OBP3 leads to growth defects. Plant J. 21: 329–339.
Kertbundit, S., De Greve, H., Deboeck, F. and Van Montagu, M. 1991. In vivo random β-glucuronidase gene fusions in Arabidopsis thaliana. Botany 88: 5212–5216.
Kertbundit, S., Linacero, R., Rouze, P., Galis, I., Macas, J., Deboeck, F., Renckens, S., Hernalsteens, J.P. and De Greve, H. 1998. Analysis of T-DNA-mediated translational β-glucuronidase gene fusions. Plant Mol. Biol. 36: 205–217.
Koncz, C., Martini, N., Mayerhofer, R., Koncz-Kalman, Z., Körber, H., Redei, G.P. and Schell, J. 1989. High-frequency T-DNAmediated gene tagging in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 8467–8471.
Lindsey, K., Wei, W.B., Clarke, M.C., Mcardle, H.F., Rooke, L.M. and Topping, J.F. 1993. Tagging genomic sequences that direct transgene expression by activation of a promoter trap in plants. Transgenic Res. 2: 33–47.
Mandal, A., Lang, V., Orczyk, W. and Palva, E.T. 1993. Improved efficiency for T-DNA-mediated transformation and plasmid rescue in Arabidopsis thaliana. Theor. Appl. Genet. 86: 621–628.
Mariani, C., De Beuckeleer, M., Truettner, J., Leemans, J. and Goldberg, R.B. 1990. Induction of male sterility in plants by a chimaeric ribonuclease gene. Nature 347: 737–741.
Mudge, S.R. and Birch, R.G. 1998. T-DNA tagging and characterisation of a novel meristem-specific promoter from tobacco. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 25: 637–643.
Pineiro, M., Garcia-Olmedo, F. and Diaz, I. 1994. Redox modulation of the expression of bacterial genes encoding cysteine-rich proteins in plant protoplasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 3867–3871.
Ponstein, A.S., Bade, J.B., Verwoerd, T.C., Molendijk, L., Storms, J., Beudeker, R.F., and Pen, J. 2002. Stable expression of Phytase (phyA) in canola (Brassica napus) seeds: towards a commercial product. Molecular Breeding 10: 31–44.
Poulsen, G.B. 1996. Genetic transformation of Brassica. Plant Breed. 115: 209–225.
Quaedvlieg, N.E.M., Schlaman, H.R.M., Admiraal, P.C., Wijting, S.E., Stougaard, J. and Spaink, P. 1998. Fusions between green fluorescent protein and β-glucuronidase as sensitive and vital bifunctional reporters in plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 37: 715–727.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. and Maniatis, T. 1989. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview, NY.
Selker, E.U. 1999. Gene silencing: repeats that count. Cell 97: 157–160.
Sijmons, P.C.M., Dekker, B.M.M., Schrammeijer, B., Verwoerd, T.C., van den Elzen, P.J.M. and Hoekema, A. 1990. Production of correctly processed human serum albumin in transgenic plants. Bio/technology 8: 217–221.
Suntio, T.M. and Teeri, T.H. 1994. A new bifunctional reporter gene for in-vivo tagging of plant promoters. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 12: 43–57.
Teeri, T.H., Herrera-Estrella, L., Depicker, A., Van Montagu, M. and Palva, E.T. 1986. Identification of plant promotors in situ by T-DNA-mediated transcriptional fusions to the nptII gene. EMBO J. 5: 1755–1760.
Teeri, T.H., Lehväslaiho, H., Franck, M., Uotila, J., Heino, P., Palva, E.T., Van Montagu, M. and Herrera-Estrella, L. 1989. Gene fusions to lacZ reveal new expression patterns of chimeric genes in transgenic plants. EMBO J. 8: 343–350.
Thompson, D. and Henry, R. 1995. Single-step protocol for preparation of plant tissue for analysis by PCR. Biotechniques 19: 394–400.
Topping, J.F. and Lindsey, K. 1995. Insertional mutagenesis and promoter trapping in plants for the isolation of genes and the study of development. Transgenic Res. 4: 291–305.
Topping, J.F. and Lindsey, K. 1997. Promoter trap markers differentiate structural and positional components of polar development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 9: 1713–1725.
Topping, J.F., Wei, W.B. and Lindsey, K. 1991. Functional tagging of regulatory elements in the plant genome. Development 112: 1009–1019.
van der Graaff, E. and Hooykaas, P.J.J. 1996. Improvements in the transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana C24 leaf discs by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Rep. 15: 572–577.
Vancanneyt, G., Schmidt, R., O'Connor-Sanchez, A., Willmitzer, L. and Rocha-Sosa, M. 1990. Construction of an intron-containing marker gene: splicing of the intron in transgenic plants and its use in monitoring early events in Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Mol. Gen. Genet 220: 245–250.
van der Kop, D.A.M., Schuyer, M., Pinas, J.E., van der Zaal, B.J. and Hooykaas, P.J.J. 1999. Selection of Arabidopsis mutants over-expressing genes driven by the promoter of an auxininducible glutathione S-transferase gene. Plant Mol. Biol. 39: 979–990.
Vieira, J. and Messing, J. 1982. The pUC plasmids, an M13MP7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene 19: 259–268.
Voelker, T.A., Worrell, A.C., Anderson, L., Bleibaum, J., Fan, C., Hawkins, D.J., Radke, S.E. and Davies, H.M. 1992. Fatty acid biosynthesis redirected to medium chains in transgenic oilseed plants. Science 257: 72–73.
Yanagisawa, S. and Sheen, J. 1998. Involvement of maize Dof zinc finger proteins in tissue-specific and light-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 10: 75–89.
Zaccomer, B., Cellier, F., Boyer, J.C., Haenni, A.L. and Tepfer, M. 1993. Transgenic plants that express genes including the 3' untranslated region of the turnip yellow mosaic virus (TYMV) genome are partially protected against TYMV infection. Gene 136: 87–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bade, J., van Grinsven, E., Custers, J. et al. T-DNA tagging in Brassica napus as an efficient tool for the isolation of new promoters for selectable marker genes. Plant Mol Biol 52, 53–68 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023980326336
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023980326336