Abstract
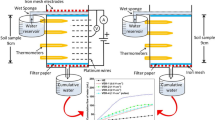
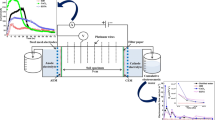
Recently, electrokinetic injection has been applied in bioremediationto provide nutrients and TEAs in low permeable soil. However, an effective pH control system and a uniform injection system have yet to be developed. This study investigated an enhanced EK injection system, which is combined with electrolyte circulation and electrode polarity reversal on kaolinite. Soil pH was maintained continuously only by circulation of electrolytes in each chamber without any buffering solutions. Existing ions were distributed more uniformly in soil by electrodepolarity reversal. In view of microbiological degradation, the polarity reversal system resulted in better ion injection. Therefore, the novel electrokinetic nutrient and TEAs injectionsystem can be applied to in situ biodegradation more effectively than the conventional technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar, Y. B. and Alshawabkeh, A. N.: 1996, ‘Electrokinetic remediation. II: Theoretical model’, J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Engineer. 122(3), 186-196.
Acar, Y. B., Rabbi, M. F. and Ozsu, E. E.: 1997, ‘Electrokinetic injection of ammonium and sulfate ions into sand and kaolinite beds’, J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Engineer. 123(3), 239-249.
Acar, Y. B., Gale, R. J., Putnam, G. and Hamed, J.: 1989, ‘Electrochemical Processing of Soil: Its Gradients’, 2nd International Symposium on Environmental Geotechnology, Shanghai, China, Envo Publishing, Bethlehem, PA, Vol. 1, pp. 25-38.
Berry, K. A. T. and Burton, D. C.: 1997, ‘Natural attenuation of diesel fuel in heavy clay soil’, Can. J. Soil Sci. 77, 469-477.
Chappell, B. A. and Burton, P. L.: 1974, ‘Electro-osmosis applied to unstable embankment’, J. Geotech. Engineer. 101(8), 733-741.
Charbeneau, R. J., Bedient, P. B. and Loehr, R. C.: 1992, Groundwater Remediation, Technomic Publishing Co., Inc., Lancaster, PA
Demque, D. E., Biggar, K.W. and Heroux, J. A.: 1997, ‘Land treatment of diesel contaminated sand’, Can. Geotech. J. 34, 421-431.
Elektorowicz, M. and Boeva, V.: 1996, ‘Electrokinetic supply of nutrients in soil bioremediation’, J. of Environ. Technol. 17, 1333-1349.
Eykholt, G. R. and Daniel, D. E.: 1994, ‘Impact of system chemistry on electro-osmosis in contaminated soil’, J. Geotech. Engineer. 120(5), 797-815.
Gray, D. H. and Somogyi, F.: 1977, ‘Electro-osmotic dewatering with polarity reversals’,J. Soil Mech. Found. 103(1), 51-54.
Rabbi, M. F., Clark, B. and Gale, R. J.: 2000, ‘In situ TCE bioremediation study using electrokinetic cometabolite injection’, Waste Manage. 20, 279-286.
Sujan, K. B.: 1996, Sufactant Enhanced Electrokinetic Remediation of Gasoline Contaminated Soil (Ground Water Contamination), University of Wyoming.
Wan, T. Y. and Mitchell, J. K.: 1976, ‘Electro-osmotic consolidation of soils’, J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Engineer. 102(5), 473-491.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.S., Han, S.J. Application of an Enhanced Electrokinetic Ion Injection System to Bioremediation. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 146, 365–377 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023934518049
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023934518049