Abstract
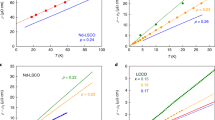
The superconducting T c of cuprates have been modeled on a linear scaling with hole concentration per CuO2 plane and a deleterious influence of bond resonance with the apical system (effective hole formalism). In cases where distribution between various hole reservoirs is not trivial, Knight shift can provide actual hole concentrations. It is shown here that when Knight shift data are used in an effective hole algorithm, satisfactory T c predictions can be made, corroborating the deleterious influence on T c of apical O and earlier assumptions concerning hole distributions. For the case of stacking of more than two CuO2 planes, the inner plane has to be treated as an infinite layer analog in the effective hole model. A separation into inner and outer planes with different dopings is indeed observed by Knight shift, with higher doping in the latter. This is explained here as being due to a tendency to equalize an effective doping degree, as the outer planes lose holes in resonance of bonding with the apical system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Oshima and K. Motida, J. Supercond. 15, 165–167 (2002).
M. R. Presland and J. L. Tallon, Physica C 176, 95(1991).
G. V. M. Williams and J. L. Tallon Physica C 258, 41(1996).
Y. J. Uemura, Phys. Rev. Lett. 62, 2317(1989).
J. M. Tranquada, S. M. Heald, A. R. Moodenbaugh, and Y. Xu, Phys. Rev. 38, 8893(1988).
B. O. Wells, Science 277, 1067(1997).
D. Ko and H. Oesterreicher, Physica C 277, 95(1997).
H. Oesterreicher, J. Alloys Comd. 270, L1(1998).
H. Oesterreicher, J. Low Temp. Phys. 177, 993(1999).
H. Oesterreicher, J. Supercond. 15, 511, (2002).
H. Oesterreicher, J. Solid State Chem. 163, 390(2002).
C. Park and R. L. Snyder J. Am. Cer. Soc. 78, 3171(1995).
H. Kotegawa, Y. Tokunaga, K. Ishida, G.-Q. Zhang, Y. Kitaoka, H. Kito, A. Iyo, K. Tokiwa, T. Watanabe, and H. Ihara, Phys. Review B 64, 064515(2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oesterreicher, H. Knight Shift Data and Superconducting T c Modeling Based on an Effective Hole Model. Journal of Superconductivity 16, 507–512 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023817003653
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023817003653