Abstract
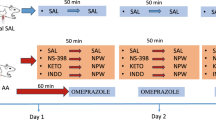
Until recently, the secretion of gastric acid, which plays an important role in the pathogenesis of peptic ulcer, was thought to be controlled by diet, the autonomic nerves and gut hormones. However, peptic ulcer is now known to be caused by the infection with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), so it is possible that inflammation modifies the secretion of gastric acid. We used gastric-lumen-perfused rats to first examine the effect of interleukin-8 (IL-8) on acid secretion and then the involvement of free radicals and neutrophils in the action of IL-8. IL-8 enhanced tetragastrin-stimulated acid secretion and free radical scavengers or inhibitors and the pretreatment with anti-rat neutrophil serum inhibited this effect, which indicates that IL-8 enhances gastrin-stimulated acid secretion and that neutrophil-derived hydroxyl radicals mediate the IL-8-induced increase in acid secretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blaser MJ: Gastric Campylobacter-like organisms, gastritis and peptic ulcer disease. Gastroenterology 93:371-383, 1987
Blair AJ, Feldman M, Barnett C, Walsh JH, Richardson T: Detailed comparison of basal and food-stimulated gastric acid secretion rates and serum gastrin concentrations in duodenal ulcer patients and normal subjects. J Clin Invest 79:582-587, 1987
El-Omar E, Penman I, Ardill JES, Chittajallu RS, Howie C, McColl KEL: Helicobacter pylori infection and abnormality of acid secretion in patients with duodenal ulcer disease. Gastroenterology 109:681-691, 1995
Crabtree JE, Peichl P, Wyatt JI, Stachl U, Lindley IJD: Gastric interleukin-8 and IgA IL-8 autoantibodies in Helicobacter pylori infection. Scand J Immunol 37:65-70, 1993
Crabtree JE, Shallcross TM, Heatley RV, Wyatt JI: Mucosal tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 in patients with Helicobacter pylori associated gastritis. Gut 32:1473-1477, 1991
Noach LA, Bosma NB, Jansen J, Hoek FJ, van Deventer SJH, Tytgat GNJ: Mucosal tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, and interleukin-8 production in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection. Scand J Gastroenterol 29:425-429, 1994
Wallece JL, Cucala M, Mugridge K, Porente L: Secretagogue-specific effects of interleukin-1 on gastric acid secretion. Am J Physiol 261:G559-G564, 1991
Nakatsuji K, Fujitani B, Ito T: General pharmacology of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor. First communication: effect on cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, renal and blood function, Arzneimittelforshung 40:218-225, 1990
Beals I, Calam J, Post L, Srinivasan S, Yamada T, Del Valle J: Effect of trransforming growth factor-α and interleukin-8 on somatostatin release from canine fundic D cells. Gastroenterology 112:136-143, 1997
Beales I, Blaser MJ, Srinivasan S, Calam J, Perez-Perez GI, Yamada T, Scheiman J, Post L, Del Valle J: Effect of Helicobacter pylori products and recombinant cytokines on gastrin release from cultured canine G cells. Gastroenterology 113:465-471, 1997
Chiba T, Yamada T: Gut somatostatin. In Gut Peptide. J, Alsh, G Dockray (eds). New York, Raven Press, 1664, pp 123-146
Kovacs TOG, Walsh JH, Maxwell V, Wong HC, Azuma T, Katt E: Gastrin is a major mediator in dogs:proof by monoclonal antibofy neutralization. Gastroenterology 97:1406-1413, 1987
Yakabi K, Mimura H, Iwabuchi H, Ro S, Nakamura T: Interleukin-8 enhances tetragastrin-stimulated acid secretion in vivo. Dig Dis Sci 43:2317-2321, 1998
Baggiolini M, Walz A, Kunkel SL: Neutrophil-activating peptide 1/interleukin-8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest 84:9233-9237, 1989
Mooney C, Keenan J, Munster D, Wilson I, Allardyce R, Bagshaw P, Chapman B, Chadwick V: Neutrophil activation by Helicobacter pylori. Gut 32:853-857, 1991
Itoh M, Guth P: Role of oxgen-derived free radicals in hemorrhagic shock-induced gastric lerosion in the rat. Gastroenterology 88:1162-1167, 1985
Smith SM, Grisham MB, Manci EA, Granger DN, Russell JM: Gastric mucosal injury in the rat. Gastroenterology 92:950-956, 1987
Yoshikawa T, Yoshida N, Naito Y, Takemura T, Miyagawa H, Tanigawa T, Kondo M: Role of oxygen radicals in the pathogenesis of gastric mucosal lesions induced by water-immersion restraint stress and burn stress in rats. J Clin Biochem Nutr 8:227-234, 1990
Johnston D, Jepson K: the use of pentagastrin in a test of gastric acid secretion. Lancet 2:585-588, 1967
El-Omar E, Oien K, El-Nujumini A, Wirz A, Gillen D, Williams C, Fullerton G, McColl K: Helicobacter pylori infection and chronic gastric acid hyposecretion. Gastroenterology 113:15-24, 1996
Iijima K, Ohara S, Sekine H, Koike T, Asaki S, Shimosegawa T, Toyota T: Changes in gastric acid secretion assayed by endoscopic gastrin test before and after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Gut 46:20-26, 2000
Dixon MF: Helicobacter pylori and peptic ulcerarion: histopathological aspects. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 6:125-130, 1991
Nompleggi D, Beinborn M, Roy A, Wolfe MM: The effect of re-combinant cytokines on [14C]aminopyrine accumulation by isolated canine parietal cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:440-445, 1994
Prinz C, Neumayer N, Mahr S, Classen M, Schepp W: Functional impairment of rat enterochromaffin-like cells by interleukin-1β. Gastroenterology 112:364-375, 1997
Babior BM, Kipnes RS, Curnutte JT: Biological defence mechanisms. The production by leucocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest 52:741-744, 1973
McCord JM, Fridovich I: Superoxide dismutase. An enzymatic function for erythro-cuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem 244:6049-6055, 1969
Haber A, Weiss J: The catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by iron salts. Proc R Soc Lond A 147:332-351, 1934
Grisham MB, Jefferson MM, Melton DF, Thomas EI: Chrorination of endogenous amines by isolated neutrophils. Ammonia-dependent bactericidal, cytotoxic, and cytolytic activities of chloramines. J Biol Chem 259:10404-10413, 1984
Grisham MB, Jefferson MM, Thomas EL: Role of monochloramine in the oxidation of erythrocyte hemoglobin by stimulated neutrophils. J Biol Chem 259:6757-6765, 1984
Harrison JE, Schultz J: Studies on the chlorinating activity of myeloperoxidase. J Biol Chem 251:1371-1374, 1976
Weiss J: Oxygen, ischemia and inflammation. Acta Physiol Scand 126(suppl 548):9-37, 1986
Parks DA, Granger DN: Role of xanthine oxydase and hydroxyl radicals in ischemia-induced vascular changes. Am J Physiol 245(Gastrointest. Liver Physiol 8):G285-G289, 1983
Granger DN, McCord JM, Parks DA, Hollwarth ME: Xanthine oxydase inhibitors attenuate ischemia-induced vascular permeability changes in the cat intestine. Gastroenterology 90:80-84, 1986
Hille R, and Massey V: Tight binding inhibitors of xanthine oxydase. Pharmacol Ther 14:249-263, 1981
Keberle H: The biochemistry of desferrioxamine and its relation to iron metabolism. Ann NY Acad Sci 119:758-768, 1964
Del Maestro RF, Bjork J, Arfors KE: Increase in microvascular permeability induced by enzymatically generated free radicals. II. Role of superoxide anion radical, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radical. Microvasc Res 22:255-270, 1981
Ro S, Yakabi K, Nakamura T: Interleukin-8 increases gastrin-stimulated histamine release from thre isolated rat stomach. Gastroenterology 120(suppl 2):A-159, 2001
Fridovich J: The biology of oxygen radicals. Science 201:875-850, 1978
Brown K, Fridovich J: Superoxide radical and superoxide dismutase: threat and defense. Acta Physiol Scand 492:9-18, 1980
McCord JM: Free radicals and inflammation: protection of synovial fluid by superoxide dismutase. Science 185:529-531, 1974
Levi S, Beardshall K, Haddad G, Playford R, Ghosh P, Calam J: Campylobacter pylori and duodenal ulcer: The gastrin link. Lancet 27:1167-1168, 1989
Harris AW, Gummentt PA, Misiewicz JJ, Baron JH: Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in patients with duodenal ulcer lowers basal and peak acid outputs to gastrin releasing peptide and pentagastrin. Gut 38:663-667, 1996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yakabi, K., Mimura, H., Iwabuchi, H. et al. Neutrophil-Derived Hydroxyl Radicals Mediate Interleukin-8-Induced Increases in Tetragastrin-Stimulated Acid Secretion in Rats. Dig Dis Sci 48, 1081–1087 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023708511116
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023708511116