Abstract
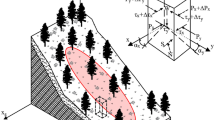
The effects of uncertainty due to the variability of soil parameters on the risk of landsliding in the Himalayan region are investigated using a random field model combined with slope stability analyses. Effects of spatial variability both in horizontal and vertical directions, number of test samples, variations in piezometric level and the influence of earthquake on the reliability of a typical slope in a slide area are investigated. The results show that the reliability of slopes in the slide area is significantly affected by the coefficients of variation of soil parameters, spatial variations of soil parameters, number of test samples and piezometric variations. The results also show that the assumption of isotropic variations to assess slope reliability isconservative. The results of the study are useful in providing guidelines and pointing to remedial measures in the form of sub-surface drainage to improve slope reliability in the area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso, E. E. (1976) Risk analysis of slopes and its application to Canadian sensitive clays, Geotechnique, 26(3), 453–472.
Ang, A. H. S. and Tang, W. H. (1975) Probability concepts in engineering planning and design, Vol. 1, Basic principles. John Wiley & Sons Inc.
Bergado, D. T. and Anderson, L. R. (1985) Stochastic analysis of pore pressure uncertainty for the probabilistic assessment of the safety of earth slopes, Soils and Foundations, 25(2), 87–105.
Calle, E. O. H. (1985) Probabilistic approach of stability of earth slopes, Proc. XIth ICSMFE, San Francisco, Vol. 2, 809–812.
Chowdhury, R. N. (1984) Recent developments in landslide studies: Probabilistic methods, State of the art report–Session VII (a), International symposium on landslides, 209–228.
Christian, J. T., Ladd, C. C. and Baecher, G. B. (1992) Reliability and probability in stability analysis, Stability and performance of slopes and embankments II, Vol. 2, STP 31, 1071–1111.
Cruden, D. M. and Fell, R. (1997) Landslide risk assessment, Proc. of International workshop on Landslide risk assessment, Honolulu, Hawaii, U.S.A.
Fell, R. and Hartford, D. (1997) Landslide risk management, In: Cruden and Fell (eds.), Landslide risk assessment, Balkema, Rotterdam, 51–109.
Griffiths, D. V. and Fenton, G. A. (2000) Influence of soil strength spatial variability on the stability of an undrained clay slope by finite elements, In: Slope Stability 2000, ASCE Geotechnical Specialty Publication No. 101, 184–193.
Griffiths, D. V. and Fenton, G. A. (2001) Bearing capacity of spatially random soil: the undrained clay Prandtl problem revisited, Geotechnique, 4, 351–359.
Hachich, W. and Vanmarcke, E. H. (1983) Probabilistic updating of pore pressure fields, Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, 109(3), 373–387.
Harr, M. E. (1987) Reliability based design in Civil Engineering, McGraw-Hill Book Company.
Jagannatha Rao, P. Sivakumar Babu, G. L. Kishor Kumar and Panigrahi. R. K. (1998) Investigation, Instrumentation and monitoring of landslide at Powari, Kinnaur District (H.P)– A case study, Journal of Indian Road Congress, 291–315.
Lee, I. K., White, W. and Ingles, O. G. (1983) Geotechnical Engineering, Pitman, London.
Li, K. S. and Lumb. P. (1987) Probabilistic design of slopes, Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 24, 520–535.
Morgenstern, N. R. (1997) Toward landslide risk assessment in practice, In: Cruden and Fell (eds.) Landslide risk assessment, Balkema, Rotterdam, 15–24.
Mostyn, G. R. and Li, K. S. (1993) Probabilistic slope analysis – State-of-Play, Proc. Of Conf. On Probabilistic Methods in Geotech. Engineering, Canberra, Australia, 89–110.
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. (1999) Risk-based analysis in geotechnical engineering for support of planning studies, Engrg. Circular. No. 1110-2-554, Department of Army, Washington, D.C.
Vanmarcke, E. H. (1977) Reliability of earth slopes, ASCE, Geotech. Engrg. Div. Journal, 103(GT11), 1227–1246.
Vanmarcke, E. H. (1992) Reliability in foundation engineering practice, Foundation Engineering, Principles and Practices, Vol. 2., (Ed. E. H. Kulhawy), 1158–1669.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babu, G.L.S., Mukesh, M.D. Risk analysis of landslides – A case study. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 21, 113–127 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023525002893
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023525002893