Abstract
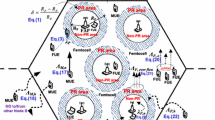
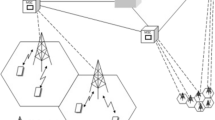
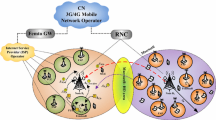
In this paper a dynamic channel reservation and call admission control scheme is proposed to provide QoS guarantees in a mobile wireless network using the concept of influence curve. The basic idea behind the proposed scheme is that a moving user, in addition to its requirements in the current cell, exerts some influence on the channel allocation in neighboring cells. Such an influence is related to the moving pattern of the users and is calculated statistically. Furthermore we developed a general analytical model to calculate the corresponding blocking probabilities for wireless networks with multiple platforms, which removes the commonly used assumption that new calls and handoff calls have same channel holding time. The numerical results demonstrate that our scheme outperforms traditional channel reservation schemes and can effectively adapt to the real time network conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Boumerdassi and A. Beylot, Adaptive channel allocation for wireless PCN, Mobile Networks and Applications 4 (1999) 111–116.
M. Cheung and J.W. Mark, Effect of mobility on QoS provisioning in wireless communication networks, in: Proceedings of IEEE WCNC'99, New Orleans, September 1999.
S. Choi and K.G. Shin, Predictive and adaptive bandwidth reservation for hand-offs in QoS-sensitive cellular networks, in: Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM'98, September 1998.
Y. Fang and I. Chlamtac, Teletraffic analysis and mobility modeling for PCS networks, IEEE Transactions on Communications 47(7) (1999) 1062–1072.
Y. Fang, I. Chlamtac and Y.B. Lin, Modeling PCS networks under general call holding times and cell residence time distribution, IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 5(6) (1997) 893–906.
C. Ho and C. Lea, Improving call admission policies in wireless networks, Wireless Networks 5 (1999) 257–265.
D. Hong and S.S. Rappaport, Traffic model and performance analysis for cellular mobile radio telephone systems with prioritized and nonprioritized handoff procedures, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 35 (1986) 77–92.
J. Hou and Y. Fang, Mobility-based call admission control schemes for wireless mobile networks, Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing 1(3) (2001) 269–282.
J. Hou and S. Papavassiliou, Influence-based channel reservation scheme for mobile cellular networks, in: Proceedings of IEEE ISCC 2001, July 2001, pp. 218–223.
D.A. Levine, I.F. Akylidiz and M. Naghshineh, A resource estimation and call admission algorithm for wireless multimedia networks using the shadow cluster concept, IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 5(1) (1997).
C. Oliveira, J.B. Kim and T. Suda, An adaptive bandwidth reservation scheme for high-speed multimedia wireless network, IEEE Journal on Selected Area in Communications 16(6) (1998) 858–874.
L. Ortigoza-Guerrero and A.H. Aghvami, A prioritized handoff dynamic channel allocation strategy for PCS, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 48(4) (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, J., Papavassiliou, S. A Dynamic Reservation-Based Call Admission Control Algorithm for Wireless Networks Using the Concept of Influence Curve. Telecommunication Systems 22, 299–319 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023407424369
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023407424369