Abstract
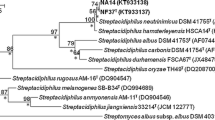
The taxonomic position of acidophilic actinomycetes selectively isolated from acidic soils and litter was examined using a polyphasic approach. The distinct 16S rDNA phyletic branch formed by representative strains was equated with related monophyletic clades that corresponded to the genera Kitasatospora and Streptomyces. The acidophilic isolates also exhibited a distinctive pH profile, a unique 16S rDNA signature, and contained major amounts of LL-diaminopimelic acid, galactose and rhamnose in whole-organism hydrolysates. It is proposed that these acidophilic actinomycetes be assigned to a new genus, Streptacidiphilus gen. nov., on the basis of genotypic and phenotypic differences. Three species were defined on the basis of DNA:DNA pairing and phenotypic data, namely, Streptacidiphilus albus sp. nov., the type species, Streptacidiphilus neutrinimicus sp. nov. and Streptacidiphilus carbonis sp. nov. Members of the genera Kitasatospora, Streptacidiphilus and Streptomyces share a number of key characteristics and form a stable monophyletic branch in the 16S rDNA tree. It is, therefore, proposed that the description of the family Streptomycetaceae be emended to account for properties shown by Kitasatospora and Streptacidiphilus species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brosius J., Palmer M.L., Kennedy P.J. and Noller H.F. 1978. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75: 4801–4805.
Chun J. 1995. Computer-assisted classification and identification of actinomycetes, PhD University of Newcastle, Newcastle upon Tyne.
Corke C.T. and Chase F.E. 1964. Comparative studies of actinomycete populations in acid podzolic and neutral mull forest soils. Proc. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 28: 68–70.
Felsenstein J. 1981. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 17: 368–376.
Felsenstein J. 1985. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39: 783–791.
Felsenstein J. 1993. PHYLIP (phylogenetic inference package), version 3.5c. Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle.
Fitch W.M. and Margoliash E. 1967. Construction of phylogenetic trees: a method based on mutation distances as estimated from cytochrome c sequences is of general applicability. Science 155: 279–284.
Flowers T.H. and Williams S.T. 1977. Nutritional requirements of acidophilic streptomycetes. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 9: 225–226.
Goodfellow M. and Dawson D. 1978. Qualitative and quantitative studies of bacteria colonizing Picea sitchensis litter. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 10: 303–307.
Goodfellow M. and Simpson K.E. 1987. Ecology of streptomycetes. Frontiers Appl. Microbiol. 2: 97–125.
Goodfellow M. and Williams S.T. 1983. Ecology of actinomycetes. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 37: 189–216.
Hagedorn C. 1976. Influences of soil acidity on Streptomyces populations inhabiting forest soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 32: 368–375.
Jensen H.L. 1928. Actinomyces acidophilus n. sp. – a group of acidophilus actinomycetes isolated from the soil. Soil Sci. 25: 225–236.
Jones K.L. 1949. Fresh isolates of actinomycetes in which the presence of sporogenous aerial mycelia is a fluctuating characteristic. J. Bacteriol. 57: 141–145.
Jukes T.H. and Cantor C.R. 1969. Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro H.N. (ed.), Mammalian Protein Metabolism Vol. 3. Academic Press, New York, pp. 21–213.
Kelly K.L. 1958. Centroid notations for the revised ISCC-NBS color name blocks. J. Res. Nat. Bur. Standards USA 61: 427.
Khan M.R. and Williams S.T. 1975. Studies on the ecology of actinomycetes in soil-VIII. Distribution and characteristics of acidophilic actinomycetes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 7: 345–348.
Kim B., Sahin N., Minnikin D.E., Zakrzewska-Czerwinska J., Mordarski M. and Goodfellow M. 1999. Classification of thermophilic streptomycetes, including the description of Streptomyces thermoalcalitolerans sp nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49: 7–17.
Kim D., Chun J., Sahin N., Hah Y.C. and Goodfellow M. 1996. Analysis of thermophilic clades within the genus Streptomyces by 16S ribosomal DNA sequence comparisons. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 46: 581–587.
Kim S.B. and Goodfellow M. 1999. Reclassification of Amycolatopsis rugosa Lechevalier (1986) as Prauserella rugosa gen. nov., comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49: 507–512.
Kim S.B., Falconer C., Williams E. and Goodfellow M. 1998. Streptomyces thermocarboxydovorans sp. nov. and Streptomyces thermocarboxydus sp. nov., two moderately thermophilic carboxydotrophic species from soil. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 48: 59–68.
Kim S.B., Brown R., Oldfield C., Gilbert S.C. and Goodfellow M. 1999. Gordonia desulfuricans sp. nov., a benzothiophene-de-sulphurizing actinomycete. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49: 1845–1851.
Kluge A.G. and Farris F.S. 1969. Quantitative phyletics and the acevolution of anurans. Syst. Zool. 18: 1–32.
Kroppenstedt R.M. 1985. Fatty acid and menaquinone analysis of actinomycetes and related organisms. In: Goodfellow M. and Minnikin D.E. (eds), Chemical Methods in Bacterial Systematics. Academic Press, London, pp. 173–199.
Labeda D.P. 1988. Kitasatosporia mediocidica sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 38: 287–290.
Labeda D.P. 1993. DNA relatedness among strains of the Streptomyces lavendulae phenotypic cluster group. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 43: 822–825.
Labeda D.P. 1998. DNA relatedness among the Streptomyces fulvissimus and Streptomyces griseoviridis phenotypic cluster groups. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 48: 829–832.
Lechevalier M.P., de Biévre C. and Lechevalier H.A. 1977. Chemotaxonomy of aerobic actinomycetes: phospholipid composition. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 5: 249–260.
Lonsdale J.T. 1985. Aspects of the biology of acidophilic actinomycetes, PhD University of Newcastle, Newcastle upon Tyne.
Mikami Y., Miyashita K. and Arai T. 1982. Diaminopimelic acid profiles of alkalophilic and alkaline-resistant strains of actinomycetes. J. Gen. Microbiol. 128: 1709–1712.
Minnikin D.E., Hutchinson I.G., Caldicott A.B. and Goodfellow M. 1980. Thin layer chromatography of methanolysates of mycolic acid-containing bacteria. J. Chromatogr. 188: 221–233.
Minnikin D.E., O'Donnell A.G., Goodfellow M., Alderson G., Athalye M., Schaal A. et al. 1984. An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J. Microbiol. Methods 2: 233–241.
Nakagaito Y., Yokota A. and Hasegawa T. 1992. Three new characspecies of the genus Streptomyces:Streptomyces cochleatus sp. nov., Streptomyces paracochleatus sp. nov., and Streptomyces azaticus sp. nov. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 38: 105–120.
National Bureau of Standards 1964. The ISCC-NBS Color Manual Charts Illustrated with Centroid Colours. Supplement to NBS, Circular 553.
O'Donnell A.G., Falconer C., Goodfellow M., Ward A.C. and Williams E. 1993. Biosystematics and diversity amongst novel carboxydotrophic actinomycetes. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 64: 325–340.
Ōmura S., Takahashi Y., Iwai Y. and Tanaka H. 1982. Kitasatosporia, a new genus of the order Actinomycetales. J. Antibiotics 35: 1013–1019.
Ōmura S., Takahashi Y. and Iwai Y. 1989. Genus Kitasatosporia Ōmura et al. (1983), 672VP. In: Williams S.T., Sharpe M.E. and Holt J.G. (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology Vol. 4. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp. 2594–2598.
Park Y.-H., Yim D.-G., Kim E., Kho Y.-H., Mheen T.-I., Lonsdale J. et al. 1991. Classification of acidophilic, neutrotolerant and neutrophilic streptomycetes by nucleotide sequencing of 5S ribosomal RNA. J. Gen. Microbiol. 137: 2265–2269.
Sahin N. 1995. Selective isolation, characterisation and classification of novel thermotolerant streptomycetes, PhD University of Newcastle, Newcastle upon Tyne.
Saitou N. and Nei M. 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4: 406–425.
Sembiring L., Ward A.C. and Goodfellow M. 2000. Selective isolation and characterisation of members of the Streptomyces violaceusniger clade associated with the roots of Paraserianthes falcataria. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 78: 353–366.
Seong C.N., Goodfellow M., Ward A.C. and Hah Y.C. 1993. Numerical classification of acidophilic actinomycetes isolated from acid soil in Korea. Kor. J. Microbiol. 31: 355–363.
Seong C.N., Park S.K., Goodfellow M., Kim S.B. and Hah Y.C. 1995. Construction of probability identification matrix and selective medium for acidophilic actinomycetes using numerical classification data. J. Microbiol. 33: 95–102.
Shirling E.B. and Gottlieb D. 1966. Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 16: 313–340.
Shirling E.B. and Gottlieb D. 1976. Retrospective evaluation of International Streptomyces Project taxonomic criteria. In: Arai T. (ed.), Actinomycetes: The Boundary Microorganisms. University Park Press, Baltimore, pp. 9–41.
Staneck J.L. and Roberts G.D. 1974. Simplified approach to identification of aerobic actinomycetes by thin-layer chromatography. Appl. Microbiol. 28: 226–231.
Stackebrandt E., Rainey F.A. and Ward-Rainey N.L. 1997. Proposal for a new hierarchic classification system, Actinobacteria classis nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47: 479–491.
Takahashi Y., Iwai Y. and Ōmura S. 1983. Relationship between cell morphology and the types of diaminopimelic acid in Kitasatosporia setalba. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 29: 459–465.
Takahashi Y., Iwai Y. and Ōmura S. 1984. Two new species of the genus Kitasatosporia, Kitasatosporia phosalacinea sp. nov. and Kitasatosporia griseola sp. nov. J. Gen. Microbiol. 30: 377–387.
Tamura T., Suzuki S. and Hatano K. 2000a. Arcocarpospora gen. nov., a new genus of the order Actinomycetales. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50: 1163–1171.
Tamura T., Liu Z., Zhang Y. and Hatano K. 2000b. Actinoalloteichus cyanogriseus gen. nov., sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50: 1435–1440.
Waksman S.A. and Henrici A.T. 1943. The nomenclature and classification of the actinomycetes. J. Bacteriol. 46: 337–341.
Wayne L.G., Brenner D.J. and Colwell R.R., & 9 other authors 1987. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 37: 463–464.
Wellington E.M.H., Stackebrandt E., Sanders D., Wolstrup J. and Jorgensen N.O.G. 1992. Taxonomic status of Kitasatosporia and proposed unification with Streptomyces on the basis of phenotypic and 16S rRNA analysis and emendation of Strep tomycesWaksman and Henrici (1943), 339AL. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 42: 156–160.
Williams S.T. and Khan M.R. 1974. Antibiotics – a soil microbiologist's viewpoint. Post. Hig. I. Med. Dosw. 28: 395–408.
Williams S.T. and Flowers T.H. 1978. The influence of pH on starch hydrolysis by neutrophilic and acidophilic actinomycetes. Microbios 20: 99–106.
Williams S.T. and Robinson C.S. 1981. The role of streptomycetes in decomposition of chitin in acidic soils. J. Gen. Microbiol. 127: 55–63.
Williams S.T., Davies F.L., Mayfield C.I. and Khan M.R. 1971. Studies on the ecology of actinomycetes in soil II. The pH requirements of streptomycetes from two acid soils. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 3: 187–195.
Williams S.T., Goodfellow M., Alderson G., Wellington E.M.H., Sneath P.H.A. and Sackin M.J. 1983. Numerical classification of Streptomyces and related genera. J. Gen. Microbiol. 129: 1743–1813.
Williams S.T., Lanning S. and Wellington E.M.H. 1984. Ecology of actinomycetes. In: Goodfellow M., Mordarski M. and Williams S.T. (eds), The Biology of the Actinomycetes. Academic Press, London, pp. 481–528.
Williams S.T., Goodfellow M. and Alderson G. 1989. Genus Streptomyces Waksman and Henrici (1943), 339AL. In: Williams S.T., Sharpe M.E. and Holt J.G. (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology Vol. 4. Williams Wilkins, Baltimore, pp. 2594–2598.
Zhang Z., Wang Y. and Ruan J. 1997. A proposal to revive the genus Kitasatospora (Ōmura et al. 1982). Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47: 1048–1054.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.B., Lonsdale, J., Seong, CN. et al. Streptacidiphilus gen. nov., acidophilic actinomycetes with wall chemotype I and emendation of the family Streptomycetaceae (Waksman and Henrici (1943)AL) emend. Rainey et al. 1997. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 83, 107–116 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023397724023
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023397724023