Abstract
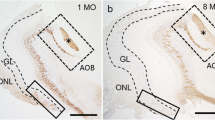
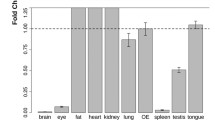
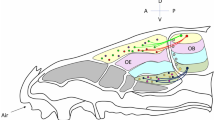
Cell surface glycoconjugates have been implicated in the growth and guidance of subpopulations of primary olfactory axons. While subpopulations of primary olfactory neurons have been identified by differential expression of carbohydrates in the rat there are few reports of similar subpopulations in the mouse. We have examined the spatiotemporal expression pattern of glycoconjugates recognized by the lectin from Wisteria floribunda (WFA) in the mouse olfactory system. In the developing olfactory neuroepithelium lining the nasal cavity, WFA stained a subpopulation of primary olfactory neurons and the fascicles of axons projecting to the target tissue, the olfactory bulb. Within the developing olfactory bulb, WFA stained the synaptic neuropil of the glomerular and external plexiform layers. In adults, strong expression of WFA ligands was observed in second-order olfactory neurons as well as in neurons in several higher order olfactory processing centres in the brain. Similar, although distinct, staining of neurons in the olfactory pathway was detected with Dolichos biflorus agglutinin. These results demonstrate that unique subpopulations of olfactory neurons are chemically coded by the expression of glycoconjugates. The conserved expression of these carbohydrates across species suggests they play an important role in the functional organization of this region of the nervous system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen WK, Akeson R (1985) Identification of a cell surface glycoprotein family of olfactory receptor neurons with a monoclonal antibody. J Neurosci 5: 284–296.
Dodd J, Solter D, Jessell TM (1984) Monoclonal antibodies against carbohydrate differentiation antigens identify subsets of primary sensory neurones. Nature 311: 469–472.
Dowsing B, Puche A, Hearn C, Key B (1997) Presence of novel N-CAM glycoforms in the rat olfactory system. J Neurobiol 32: 659–670.
Fujita SC, Mori K, Imamura K, Obata K (1985) Subclasses of olfactory receptor cells and their segregated central projections demonstrated by a monoclonal antibody. Brain Res 326: 192–196.
Key B, Giorgi PP (1986) Soybean agglutinin binding to the olfactory systems of the rat and mouse. Neurosci Lett 69: 131–136.
Key B, Akeson RA (1991) Delineation of olfactory pathways in the frog nervous system by unique glycoconjugates and N-CAM glycoforms. Neuron 6: 381–396.
Key B, Akeson RA (1993) Distinct subsets of sensory olfactory neurons in mouse: Possible role in the formation of the mosaic olfactory projection. J Comp Neurol 335: 355–368.
Key B, St John J (2002) Axon navigation in the Mammalian primary olfactory pathway: Where to next? Chem Senses 27: 245–260.
Koppe G, Bruckner G, Brauer K, Hartig W, Bigl V (1997) Developmental patterns of proteoglycan-containing extracellular matrix in perineuronal nets and neuropil of the postnatal rat brain. Cell Tissue Res 288: 33–41.
Kunzle H, Radtke-Schuller S (2000) The subrhinal paleocortex in the hedgehog tenrec:Amultiarchitectonic characterization and an analysis of its connections with the olfactory bulb. Anat Embryol (Berl) 202: 491–506.
Mahanthappa NK, Cooper DN, Barondes SH, Schwarting GA (1994) Rat olfactory neurons can utilize the endogenous lectin, L-14, in a novel adhesion mechanism. Development 120: 1373–1384.
Mombaerts P, Wang F, Dulac C, Chao SK, Nemes A, Mendelsohn M, Edmondson J, Axel R (1996) Visualizing an olfactory sensory map. Cell 87: 675–686.
Mori K, Fujita SC, Imamura K, Obata K (1985) Immunohistochemical study of subclasses of olfactory nerve fibers and their projections to the olfactory bulb in the rabbit. J Comp Neurol 242: 214–229.
Oliva AA, Jr Jiang M, Lam T, Smith KL, Swann JW (2000) Novel hippocampal interneuronal subtypes identified using transgenic mice that express green fluorescent protein in GABAergic interneurons. J Neurosci 20: 3354–3368.
Pays L, Schwarting G (2000) Gal-NCAM is a differentially expressed marker for mature sensory neurons in the rat olfactory system. J Neurobiol 43: 173–185.
Regan LJ, Dodd J, Barondes SH, Jessell TM (1986) Selective expression of endogenous lactose-binding lectins and lactoseries glycoconjugates in subsets of rat sensory neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 2248–2252.
Ressler KJ, Sullivan SL, Buck LB (1994) Information coding in the olfactory system: Evidence for a stereotyped and highly organized epitope map in the olfactory bulb. Cell 79: 1245–1255.
Royal SJ, Key B (1999) Development of P2 olfactory glomeruli in P2-internal ribosome entry site-tau-LacZ transgenic mice. J Neurosci 19: 9856–9864.
Saito S, Nii Y, Taniguchi K (1999) Heterogeneous expression of glycoconjugates among individual glomeruli of the hamster main olfactory bulb. Chem Senses 24: 509–515.
Schwarting GA, Crandall JE (1991) Subsets of olfactory and vomeronasal sensory epithelial cells and axons revealed by monoclonal antibodies to carbohydrate antigens. Brain Res 547: 239–248.
St John JA, Key B (1999) Expression of galectin-1 in the olfactory nerve pathway of rat. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 117: 171–178.
St John JA, Key B (2001) Chemically and morphologically identifiable glomeruli in the rat olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol 436: 497–507.
St John JA, Clarris HJ, Key B (2002) Multiple axon guidance cues establish the olfactory topographic map: How do these cues interact? Int J Dev Biol 46: 639–647.
Tisay KT, St John JA, Key B (2002) Expression of specific glycoconjugates in both primary and secondary olfactory pathways in BALB/C mice. J Comp Neurol 443: 213–225.
Vassar R, Ngai J, Axel R (1993) Spatial segregation of odorant receptor expression in the mammalian olfactory epithelium. Cell 74: 309–318.
Vassar R, Chao SK, Sitcheran R, Nunez JM, Vosshall LB, Axel R (1994) Topographic organization of sensory projections to the olfactory bulb. Cell 79: 981–991.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
St John, J.A., Key, B. Heterogeneity in Olfactory Neurons in Mouse Revealed by Differential Expression of Glycoconjugates. Histochem J 34, 281–289 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023374407724
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023374407724