Abstract
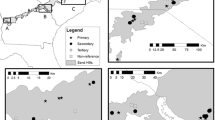
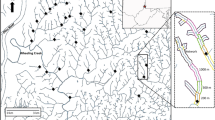
Using a probabilistic survey design, we assessed the ecologicalcondition of the Florida (U.S.A.) portion of the Escambia Riverwatershed using selected environmental and benthicmacroinvertebrate data. Macroinvertebrates were sampled at 28sites during July-August 1996, and 3414 individuals wereidentified. Taxonomic data were distilled into the 8 m ofthe Stream Condition Index (SCI), developed specifically forFlorida waterways, and sites were classified on an ordinal scaleas very good, good, poor, and very poor. The weighted cumulativedistribution function of the SCI showed that 8% (± 7) of thestream and river miles in this landscape were in very goodcondition, while 25% (± 7), 51% (± 16), and 16%(±15) were in good, poor, and very poor condition, respectively.The only environmental parameter significantly correlated withSCI was dissolved oxygen (DO), and two sites classified as verypoor had oxygen levels around or below 2 mg L-1. However, othersites exhibited similarly low SCI values without the attendantlow DO, implying that factors determining site condition werecomplex and multivariate. The results of this survey corroborateFederal and state assessments demonstrating that many locationswithin this watershed exhibit significant degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Barbour, M. T., Stribling, J. B. and Karr, J. R.: 1995, "Multimetric Approach for Establishing Biocriteria and Measuring Biological Condition', in W. S. Davis and T. P. Simon (eds), Biological Assessment and Criteria: Tools for Water Resource Planning and Decision Making, Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Florida, pp. 63-77.
Barbour, M. T., Gerritsen, J., Griffith, R. G. E., Frydenborg, R., McCarron, E., White, J. S. and Bastian, M. L.: 1996, "A framework for biological criteria for Florida streams using benthic macroinvertebrates', J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 15, 185-211.
Berg, M. B. and Hellenthal, R. A.: 1990, "Data Variability and the use of Chironomids in Environmental Studies: the Standard Error of the Midge', in W. S. Davis (ed.), Proceedings of the 1990 Midwest Pollution Control Biologists Meeting. U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, Chicago, IL, EPA-905-9-90/005, pp. 1-8.
Carpenter, S. R., Caraco, N. F., Correll, D. L., Howarth, R. W., Sharpley, N. and Smith, V. H.: 1998, "Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen', Ecol. App. 8, 559-568.
Clements, W. H.: 1999, "Metal tolerance and predator-prey interactions in benthic macroinvertebrate stream communities', Ecol. App. 9, 1073-1084.
Cochran, W. G.: 1977, Sampling Techniques, 3rd ed. John Wiley, New York.
Collard, S. B.: 1991, Surface Water Improvement and Management (S.W.I.M.) Program. The Pensacola Bay system: Biological trends and current status, Water Resources Special Report 91-3, Northwest Florida Water Management District, Havana, Florida.
DeShon, J. E.: 1995, "Development and Application of the Invertebrate Community Index (ICI)', in W. S. Davis and T. P. Simon (eds), Biological Assessment and Criteria: Tools for Water Resource Planning and Decision Making, Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Florida, pp. 217-244.
Flanagan, J. F. and Rosenberg, D. M.: 1982, "Types of artificial Substrates used for Sampling Freshwater Benthic Macroinvertebrates', in J. Cairns (ed.), Artificial Substrates. Ann Arbor Science, Ann Arbor, Michigan, pp. 237-266.
Hilsenhoff, W. L.: 1987, "An improved biotic index of organic stream pollution', Great Lakes Entomol. 20, 31-39.
Hughes, R. M.: 1995, "Defining Acceptable Biological Status by Comparing with Reference Conditions', in W. S. Davis and T. P. Simon (eds), Biological Assessment and Criteria: Tools for Water Resource Planning and Decision Making, Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Florida, pp. 31-47.
Karr, J. R.: 1981, "Assessment of biotic integrity using fish communities', Fisheries 6, 21-27.
Karr, J. R. and Chu, E. W.: 1999, Restoring Life in Running Waters: Better Biological Monitoring, Island Press, Washington, DC.
Kerans, B. L. and Karr, J. R.: 1994, "A benthic index of biotic integrity (B-IBI) for rivers of the Tennessee Valley', Ecol. App. 4, 768-785.
Klemm, D. J., Lewis, P. A., Fulk, F. and Lazorchak, J. M.: 1990, Macroinvertebrate Field and Laboratory Methods for Evaluating the Biological Integrity of Surface Waters, EPA/600/4-90-030. Environmental Monitoring and Support Laboratory, US Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, OH.
Kleinbaum, D.G., Kupper, L.L., Mueller, K.E.: 1988, Applied Regression Analysis and Other Multivariable Methods, PWS-Kent Publishing, Boston, Mass.
Larsen, D. P.: 1995, "The Role of Ecological sample Surveys in the Implementation of Biocriteria', in W. S. Davis and T. P. Simon (eds), Biological Assessment and Criteria: Tools for Water Resource Planning and Decision Making, Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Florida, pp. 287-300.
Larsen, D. P.: 1997, "Sample survey design issues for bioassessment of inland aquatic ecosystems', Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 3, 979-991.
Lenat, D. R.: 1988, "Water quality assessment of streams using a qualitative collection method for benthic macro-invertebrates', J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 12, 279-290.
Long, E. R., MacDonald, D. D., Smith, S. L. and Calder, F. D.: 1995, "Incidence of adverse biological effects withing ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments', Environ. Manag. 19, 81-97.
Maxted, J. R., Barbour, M. T., Gerritsen, J., Poretti, V., Primrose, N., Silvia, A., Penrose, D., and Renfrow, R.: 2000, "Assessment framework for mid-Atlantic coastal plain streams using benthic macroinvertebrates', J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 19, 128-144.
Merritt, R. W. and Cummins, K. W.: 1996, An Introduction to the Aquatic Insects of North America, 3rd Edition. Kendall/Hunt, Dubuque, IA.
Ohio EPA (Environmental Protection Agency).: 1987, Biological Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Life, Vol. 1-3. Monitoring and Assessment Program, Surface Water Section, Division of Water Quality, Columbus, Ohio.
Olinger, L. W., Rogers, R. G., Fore, P. L., Todd, R. L., Mullins, B. L., Bisterfeld, F. T. and Wise, L. A.: 1975, Environmental and Recovery Studies of Escambia Bay and the Pensacola Bay System, Florida. EPA-904/7-76-016, Athens, Georgia.
Plafkin, J. L., Barbour, M. T., Porter, K. D., Gross, S. K. and Hughes, R. M.: 1989, Rapid Bioassessment Protocols for Use in Streams and Rivers: Benthic Macroinvertebrates and Fish, EPA/440/4-89-001. Office of Water, US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC.
Rosen, B. H.: 1995, "Use of Periphyton in the Development of Biocriteria', in W. S. Davis and T. P. Simon (eds), Biological Assessment and Criteria: Tools for Water Resource Planning and Decision Making, Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Florida, pp. 209-215.
Rosenberg, D. M. and Resh, V. H.: 1982, "The Use of Artificial Substrates in the Study of Freshwater Benthic Macroinvertebrates', in J. Cairns (ed.), Artificial Substrates. Ann Arbor Science, Ann Arbor, Michigan, pp. 175-235.
Ross, L. T. and Jones, D. A.: 1979, Biological Aspects of Water Quality in Florida, Technical Series Vol. 4, no. 3. Florida Department of Environmental Regulation. Tallahassee.
SAS: 1989, SAS/STAT® User's Guide, Version 6, 4th edn. Cary, North Carolina.
Stevens, D. L., Olsen, A. R. and White, D.: 1991, Environmental Monitoring and Assessment Program-Integrated Sampling Design, Draft report. Environmental Research Laboratory, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Corvallis, OR.
Summers, J. K.: 2000, "Ecological condition of the estuaries of the Atlantic and Gulf Coasts of the United States', Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 20, 99-106.
Wallace, J. B., Grubaugh, J. W. and Whiles, M. R.: 1996, "Biotic indices and stream ecosystem processes: results from an experimental study', Ecol. App. 6, 140-151.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DiDonato, G.T., Summers, J.K. & Roush, T.H. Assessing the Ecological Condition of a Coastal Plain Watershed Using a Probabilistic Survey Design. Environ Monit Assess 85, 1–21 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023348931931
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023348931931