Abstract
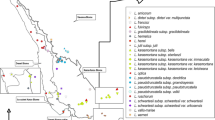
Eight German populations of the land snail Balea biplicata(Mollusca: Clausiliidae) were studied using the randomly amplified polymorphic DNA-polymerase chain reaction and morphometrics (principal component and discriminant analysis) to examine population structure and gene flow patterns in a fragmented landscape mosaic along the Elster/Saale riparian system, Germany. A variety of population genetic analyses targeting either more on the geographic scale of gene flow (genetic distances, F statistics, Mantel test) or on local genotypic structure (heterozygosity, linkage disequilibrium, bottleneck probability) showed that (1) the population system in total is governed by high gene flow independent of geographic distance, (2) genetic structure on the narrower sampling scale is mainly determined by stochastic processes due to genetic drift in small isolated and frequently recolonized populations, and (3) the morphometrical variation of the populations was related neither to habitat nor to genetic heterogeneity. The potentials for active and passive dispersal capacity of the snails and possible environmental impacts on their population structure are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apostol, B. L., Black, W. C., IV, Reiter, P., & Miller, B. (1996). Population genetics with RAPD-PCR markers: The breeding structure of Aedes aegypti in Puerto Rico. Heredity 76:325–334.
Armbruster, G. (1997). Genetische Verarmung aufgrund von Populationseinbrüchen: Eine Analyse bei der seltenen Landschneckenart Cochlicopa nitens (Gallenstein, 1848). Natur und Landschaft 72:444–446.
Armbruster, G. (1998). Bei einer verbreiteten Landschnecke, Cochlicopa lubrica (O.F. Müller), wird die Frequenz von molekularen Phänotypen durch Selbstbefruchtung und habitatspezifische Selektion beeinflußt. Laufener Seminarbeiträge 2/98 der Bayerischen Akademie für Naturschutz und Landschaftspflege (ANL), p. 39–43.
Bahl, A., Pfenninger, M., Bamberger, H., Frye, M., & Streit, B. (1996). Survival of snails in fragmented landscapes. In Settele, J., Margules, C., Poschlod, P., & Henle, K. (eds.), Species Survival in Fragmented Landscapes, Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 329–343.
Black, W. C. IV (1995). FORTRAN programs for the analysis of RAPD-PCR markers in populations, Colorado State University, Ft. Collins.
Boileau, M. G., Hebert, P. D. N., & Schwartz, S. S. (1992). Non-equilibrium gene frequency divergence: Persistent founder effects in natural populations. J. Evol. Biol. 5:25–39.
Cornuet, J. M., & Luikart, G. (1997). Description and power analysis of two tests for detecting recent population bottlenecks from allele frequency data. Genetics 144:2001–2014.
De Wolf, H., Backeljau, T., & Verhagen, R. (1998). Congruence between allozyme and RAPD data in assessing macrogeographical genetic variation in the periwinkle Littorina striata (Mollusca, Gastropoda). Heredity 81:486–492.
Felsenstein, J. (1995). PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package), University of Washington, Washington, DC.
Fischer, S., Poschlod, P., & Beinlich, B. (1996). Experimental studies on the dispersal of plants and animals by sheep in calcareous grasslands. J. Appl. Ecol. 33:1206–1222.
Fisz, M. (1970). Wahrscheinlichkeitsrechnung und mathematische Statistik. 5, Auflage, Deutscher Verlag der Wissenschaften, Berlin.
Frankham, R. (1995). Inbreeding and extinction: A threshhold effect. Conserv. Biol. 9:729–799.
Gibbs, H. L., Prior, K. A., & Weatherhead, P. J. (1994). Genetic analysis of populations of threatened snake species using RAPD markers. Mol. Ecol. 3:329–337.
Gustincich, S., Manfioletti, G., Del Sal, C., Schneider, C., & Carninci, C. (1991). A fast method for high-quality genomic DNA extraction from whole human blood. BioTechniques 11:298–302.
Heller, J., & Dolev, A. (1994). Biology and population dynamics of the crevice-dwelling land snail, Cristataria genezarethana (Clausiliidae). J. Mol. Stud. 60:33–46.
Henle, K., Poschlod, P., Margules, C., & Settele, J. (1996). Species survival in relation to habitat quality, size, and isolation: Summary conclusions and future directions. In Settele, J., Margules, C., Poschlod, P., & Henle, K. (eds.), Species Survival in Fragmented Landscapes, Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, The Netherlands pp. 373–381.
Huff, D. R., Peakall, R., & Smouse, P. E. (1993). RAPD variation within and among natural populations of outcrossing buffalograss [Buchloe dactyloides (Nutt.) Engelm.]. Theor. Appl. Genet. 86:927–934.
Johnson, M. S., & Black, R. (1995). Neighbourhood size and the importance of barriers to gene flow in an intertidal snail. Heredity 75:142–154.
Kartavtsev, Y. F., Sitnikow, A. V., Nikiforov, S. M., & Chichvarkhin, A. V. (1998). Allozyme and morphometric variation in the predatory mollusk Nucella heyseana (Mollusca, Gastropoda) in normal and polluted environments. Russ. J. Genet. 34:1209–1216.
Kempermann, T. C. M. (1992). Systematics and evolutionary history of the Albinaria species from the Ionian islands of Kephallinia and Ithaka (Gastropoda Pulmonata: Clausiliidae). Universal Book Services, Leiden, The Netherlands.
Kerney, M. P., Cameron, R. A. D., & Jungbluth, J. H. (1983). Die Landschnecken Nord-und Mitteleuropas, Paul Parey, Hamburg, Germany.
Kimberling, D. N., Ferreira, A. R., Shuster, S. M., & Keim, P. (1996). RAPD marker estimation of the genetic structure among isolated northern leopard frog populations in the south-western USA. Mol. Ecol. 5:521–529.
Liao, L. C., & Hsiao, J. Y. (1998). Relationship between population genetic structure and riparian habitat as revealed by RAPD analysis of the rheophyte Acorus gramineus Soland. (Araceae) in Taiwan. Mol. Ecol. 7:1275–1281.
Lynch, M., & Milligan, B. G. (1994). Analysis of population genetic structure with RAPD markers. Mol. Ecol. 3:91–99.
Manly, B. F. J. (1993). RT—A program for randomization testing. The Centre for Application of Statistics and Mathematics, University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand.
Mantel, N. (1967). The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res. 27:209–220.
McCauley, D. E. (1991). Genetic consequences of local population extinction and recolonization. Trends Ecol. Evol. 6:5–8.
Nei, M. (1978). Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics 89:583–590.
Nurbaev, S. D., & Balanovskaya, E. V. (1998). Interpopulation diversity of the gene pool: Beta-distribution of Wright's FST Statistics. Russ. J. Genet. 34:837–847.
Ohta, T. (1982a). Linkage disequilibrium with the island model. Genetics 101:139–155.
Ohta, T. (1982b). Linkage disequilibrium due to random genetic drift in finite subdivided populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79:1940–1944.
Pascual, M., Balanya, J., Latorre, A., & Serra, L. (1997). Analysis of the variability of Drosophila azteca and D. athabasca populations revealed by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 35:159–164.
Pfenninger, M., & Bahl, A. (1997). Influence of habitat size on the viability of spatially structured populations of the land snail Trochoidea geyeri. Verh. Ges. ökol. 27:469–473.
Pfenninger, M., Bahl, A., & Streit, B. (1996). Isolation by distance in a population of a small land snail Trochoidea geyeri: Evidence from direct and indirect methods. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 263:1211–1217.
Piry, S., Luikart, G., & Cornuet, J. M. (1999). BOTTLENECK: A computer programm for detecting recent reductions in the effective population size using allele frequency Data. J. Hered. 90:502–503.
Pulliam, H. R. (1988). Sources, sinks, and population regulation. Am. Nat. 132:652–661.
Schäfer, M. A., Hille, A., & Uhl, G. B. (2001). Geographical patterns of genetic subdivision in the cellar spider Pholcus phalangioides (Araneae). Heredity 86:94–102.
Schilthuizen, B. (1994). Reproductive isolation in snails of the genus Albinaria (Gastropoda: Clausiliidae). Biol. J. Linnean Soc. 52:317–324.
Schilthuizen, B., & Gittenberger, E. (1996). Allozyme variation in some Cretan Albinaria (Gastropoda): Paraphyletic species as natural phenomena. In Taylor, J. (ed.), Origin and Evolutionary Radiation of the Mollusca, Oxford University Press, London, pp. 301–311.
Schilthuizen, B., & Lombaerts, M. (1994). Population structure and levels of gene flow in the Mediterranean land snail Albinaria corrugata (Pulmonata: Clausiliidae). Evolution 48:577–586.
Slatkin, M. (1985). Gene flow in natural populations. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 16:393–430.
Sokal, R. R., & Rohlf, F. J. (1981). Biometry, Freeman, San Francisco.
Stothard, J. R., Mgeni, A. F., Alawi, K. S., Savioli, L., & Rollinson, D. (1997). Observations on shell morphology, enzymes and random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) in Bulinus africanus group snails (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) in Zanzibar. J. Mol. Stud. 63:489–503.
Swofford, D. L., & Selander, R. B. (1981). BIOSYS-1: A FORTRAN program for the comprehensive analysis of electrophoretic data in population genetics and systematics. J. Hered. 72:286–293.
Tenzer, C. (2000). Die passive Ausbreitung terrestrischer Wirbelloser über Fließgewässer unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Landgehäuseschnecken. Verh. Ges. ökol. 30:74.
Van de Peer, Y, and De Wachter, R. (1994). TREECON for Windows: A software package for the construction and drawing of evolutionary trees for the Microsoft Windows environment. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 10:569–570.
Vernon, J.G., Jones, C., & Noble, L. R. (1995). Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers reveal cross-fertilisation in Biomphalaria glabrata (Pulmonata: Basommatophora). J. Mol. Stud. 61:455–465.
Wahlund, S. (1928). Zusammensetzung von Populationen und Korrelationserscheinungen vom Standpunkt der Vererbungslehre aus betrachtet. Hereditas 11:65–106.
Weir, B. S., & Cockerham, C. C. (1984). Estimationg F-statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evolution 38:1358–1370.
Welsh, J., & McClelland, M. (1990). Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 18:7213–7218.
West, D. F., & Black, W. C., IV (1998). Breeding structure of three snow pool Aedes mosquito species in northern Colorado. Heredity 81:371–380.
Williams, J. G. K., Kubelik, A. R., Livak, K. J., Rafalski, J. A., & Tingey, S. V. (1990). DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 18:6531–6535.
Wirth, T., Baur, A., & Baur, B. (1997). Mating system and genetic variability in the simultaneously hermaphroditic terrestrial gastropod Balea perversa on the Baltic island of ödland, Sweden. Hereditas 126:199–209.
Wright, S. (1978). Variability Within and Among Natural Populations, Vol. 4: Evolution and the Genetics of Populations, University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hille, A., Liebal, K., Mosch, B. et al. An RAPD (Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA) Analysis of Genetic Population Structure of Balea biplicata (Gastropoda: Clausiliidae) in Fragmented Floodplain Forests of the Elster/Saale Riparian System. Biochem Genet 41, 175–199 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023329711209
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023329711209