Abstract
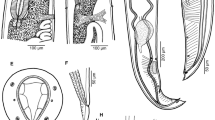
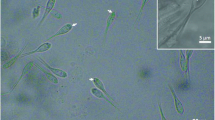
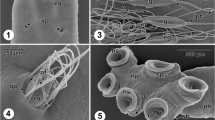
Fishing tentacle nematocysts of the hydrozoan, Physalia utriculus, from Hawaiian coastal waters, were examined by light microscopy, as well as by scanning and transmission electron microscopy (SEM and TEM). Hawaiian P. utriculus has been assumed to be conspecific with the Australian morph based on general macroscopic descriptions. Ultrastructural examination using SEM and TEM revealed that the cnidome was composed of two sizes of heterotrichous anisorhizas as well as rare rhopoloids (less than one observed per 1000 nematocysts). Beyond classification of the cnidome of Hawaiian P. utriculus, an unprecedented morphological structure was observed. Specifically, SEM revealed fibers (<1 μm in diameter) along the spiral crest of spines of some discharged tubules of P. utriculus anisorhizas. A hypothetical model of spine morphogenesis was formulated based on comparative analysis of hundreds of discharged tubules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam, J. M. & R. Qasim, 1991. Toxicology of Physalia's (Portuguese man-o'-war) venom. Pakistan J. Pharmaceut. Sci. 4: 159–168.
Alam, J. M. & R. Qasim, 1992. Preliminary studies on the biological and hazardous marine toxins from Karachi coast: (1) biochemical and biological properties of Physalia venom. Toxicon 30: 532.
Alam, J. M. & R. Qasim, 1996. Isolation and physiopharmacological properties of three high molecular weight lethal proteins from a coelenterate (Physalia utriculus) venom. Pakistan J. Zool. 28: 245–252.
Arneson, A. C. & C. E. Cutress, 1976. Life history of Carybdea alata Reynaud, 1830 (Cubomedusae). In Mackie G. O. (ed.), Coelenterate Ecology and Behaviour. Plenum Publishing, New York: 227–236.
Auerbacha P. S. & J. Taylor Hays, 1987. Erythema nodosum following a jellyfish sting. J. Emerg. Med. 5: 487–491.
Baker, H., 1743. An attempt towards a natural history of the polype. In Hessinger, D. A. & H. M. Lenhoff (eds), 1988, The Biology of Nematocysts. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego: 1–19.
Baxter, E. H. & A. G. M. Marr, 1969. Seawasp venom–lethal hemolytic and dermonecrotic properties. Toxicon 7: 195–210.
Blake, A. S., R. S. Blanquet & G. B. Chapman, 1988. Fibrillar ultrastructure of the capsular wall and intracapsular space in developing nematocysts of Aiptasia pallida (Cnidaria: Anthozoa). Trans. am. Microsc. Soc. 107: 217–231.
Blanquet R. S., 1988. The chemistry of cnidae. In Hessinger, D. A. & H. A. Lenhoff (eds), The Biology of Nematocysts. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego: 407–425.
Bloom, D. A., J. W. Burnett & P. Alderslade, 1998. Partial puri-fication of box jellyfish (Chironex fleckeri) nematocyst venom isolated at the beachside. Toxicon 36: 1075–1085.
Burnett, J. W., 1992. Immunological aspects of jellyfish envenomations. In Gopalakrishnakone, P. & C. K. Tan (eds), Recent Advances in Toxinology Research. Venom and Research Group, Singapore: 333–349.
Burnett, J. W. & G. J. Calton, 1977. The chemistry and toxicology of some venomous pelagic coelenterates. Toxicol 15: 177–196.
Burnett, J. W. & W. D. Gable, 1989. A fatal jellyfish envenomation by Portuguese man-o'-war. Toxicon 27: 823–824.
Burnett, J. W., J. V. Ordonez & G. J. Calton, 1986. Differential toxicity of Physalia physalis (Portuguese Man-of-War) nematocysts separated by flow cytometry. Toxicon 24: 514–518.
Chung, J. J., L. A. Ratnapala, I. M. Cooke & A. A. Yanagihara, 2001. Partial purification and characterization of a hemolysin (CAH1) from Hawaiian box jellyfish (Carybdea alata) venom. Toxicon 39: 981–990.
Clausen, C., 1991. Differentiation and ultrastructure of nematocysts in Halammohydra intermedia (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria). Hydrobiologia 216/217: 623–628.
Cleland, J. B. & R. V. Southcott, 1965. Injuries to man from marine invertebrates in the Australian region. Special Report Series (No.12). National Health and Medical Research Council, Canberra, Australia: 1965.
Crone, H. D. & T. E. B. Keen, 1970. Further studies on the biochemistry of the toxins of the sea wasp Chironex fleckeri. Toxicon 9: 145–151.
Endean, R. & J. F. Rifkin, 1975. Isolation of different types of nematocysts from the cubomedusan Chironex fleckeri. Toxicon 13: 375–376.
Endean, R., C. Duchemin, D. McColm & E. Hope Fraser, 1969. A study of the biological activity of toxic material derived from nematocysts of the cubomedusan Chironex fleckeri. Toxicon 6: 179–204.
Fenner, P. J., P. F. Fitzpatrick, R. J. Hartwick & R. Skinner, 1985. “Morbakka”, another cubomedusan. Med. J. Aust. 143: 550–555.
Fenner, P. J., J. Rifkin & J.A. Williamson, 1996. Physalia utriculus (Bluebottle). In Williamson, J. A., P. J. Fenner, J. W. Burnett, J. F. Rifkin (eds), Venomous and Poisonous Marine Animals. A Medical and Biological Handbook. University of New South Wales Press, Sydney, Australia: 200.
Fenner, P. J. & J. A. Williamson, 1996. Worldwide deaths and severe envenomation from jellyfish stings. Med. J. Aust. 165: 658–661.
Halstead, B.W., 1988. Poisonous and Venomous Marine Animals of the World (2nd revised edn). Darwin Press, Princeton, NJ: 1168 pp.
Hessinger, D. A., 1988. Nematocyst venoms and toxins. In Hessinger, D. A. & H. M. Lenhoff (eds), The Biology of Nematocysts. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego: 333–369.
Hessinger, D. A. & M. T. Ford, 1988. Ultrastructure of the small cnidocyte of the Portuguese Man-of-War (Physalia physalis) tentacle. In Hessinger, D. A. & H.M. Lenhoff (eds), The Biology of Nematocysts. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego: 75–94.
Hulet, W. H., J. L. Belleme, G. Musil & C. E. Lane, 1974. Ultrastructure of Physalia nematocysts. In Humm, H. J. & C. E. Lane (eds), Bioactive Compounds from the Sea. Marcel Dekker, New York: 99–114.
Hyman, L. H., 1940. The Invertebrates: Protozoa through Ctenophora, Vol I. McGraw-Hill, New York: 365–661.
Kaplan, E. H., 1982. A Field Guide to Coral Reefs of the Caribbean and Florida. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston.
Klug, M., J. Weber & P. Tardent, 1988. Direct Observation of hemolytic activity associated with single nematocysts. In Hessinger, D. A. & H. M. Lenhoff (eds), The Biology of Nematocysts. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego: 543–550.
Lane, C. E. & E. Dodge, 1958. The toxicity of Physalia nematocysts. Biol. Bull. 115: 219–226.
Lubbock, R., B. L. Gupta & T. A. Hall, 1981. Novel role of calcium in exocytosis: Mechanism of nematocyst discharge as shown by X-ray microanalysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78: 3624–3628.
Mariscal, R. N., 1971. Effect of a disulfide reducing agent on the nematocyst capsules from some coelenterates, with an illustrated key to nematocyst classification. In Lenhoff, H. M., L. Muscatine & L. V. Davis (eds), Experimental Coelenterate Biology. University of Hawaii Press, Honolulu: 157–168.
Mariscal, R. N., 1974a. Scanning electron microscopy of the sensory surface of the tentacles of sea anemones and corals. Z. Zellforsch. Mikrosk. Anat. 147: 149–156.
Mariscal, R. N., 1974b. Nematocysts. In Muscatine, L. & H. M. Lenhoff (eds), Coelenterate Biology: Reviews and New Perspectives. Academic Press, New York: 129–178.
Purcell, J. E., 1984. The functions of nematocysts in prey capture by epipelagic siphonophores (Coelenterata, Hydrozoa). Biol. Bull. 166: 310–327.
Rifkin, J. F., 1987. Studies of the structure, arrangement and mode of operation of cnidae from cnidarians belonging to the classes cubozoa, hydrozoa, scyphozoa and anthozoa. Ph.D. Thesis. University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia.
Rifkin, J. F. & R. Endean, 1983. The structure and function of the nematocysts of Chironex fleckeri Southcott 1956. Cell Tissue Res. 233: 563–577.
Skaer, R. J., 1973. The secretion and development of nematocysts in a siphonophore. J. Cell. Sci. 13: 371–393.
Skaer, R. J. & L. E. R. Picken, 1965. The structure of the nematocyst thread and the geometry of discharge in Corynactis viridis Allman. Phil. Trans. r. Soc. Ser. B. 250: 131–164.
Southcott, R. V., 1956. Studies on Australian cubomedusae, including a new genus and species apparently harmful to man. Australian. J. Marine Freshwat. Res. 7: 254–280.
Southcott, R. V., 1967. Revision of some carybdeidae (Scyphozoa: Cubomedusae), including a description of the jellyfish responsible for the “Irukandji Syndrome”. Aust. J. Zool. 15: 651–671.
Tamkun, M. M. & D. A. Hessinger, 1981. Isolation and partial characterization of a hemolytic and toxic protein from the nematocyst venom of the Portuguese man-of-war, Physalia physalis. Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 667: 87–98.
Thomas, C. & S. Scott, 1997. All Stings Considered. University of Hawaii Press, Honolulu, 231 pp.
Totton, A. K. & G. O. Mackie, 1960. Studies on Physalia physalis. Discovery Rep. 30: 301–408.
Watson, G. M., 1988. Ultrastructure and cytochemistry of developing nematocysts. In Hessinger, D. A. & H. M. Lenhoff (eds), The Biology of Nematocysts. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego: 143–164.
Watson, G. M. & R. N. Mariscal, 1984. Calcium cytochemistry of nematocyst development in catch tentacles of the sea anemone Haliplanella luciae (Cnidaria: Anthozoa) and the molecular basis for tube inversion into the capsule. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 86: 202–214.
Watson, G. M. & R. L. Wood, 1988. Colloquium on Terminology. In Hessinger, D. A. & H. M. Lenhoff (eds), The Biology of Nematocysts. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego: 21–23.
Weber, J., 1991. A novel kind of polyanions as principal components of cnidarian nematocysts. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 98A: 285–291.
Weill, R., 1934. Contribution à l'étude des cnidaires et de leurs nématocystes: (2 vols.). Trav. Sta. Zool. Wimereux I 10: 1–347; II 11: 348–701.
Williamson, J. A., P. J. Fenner & J. W. Burnett, 1996. Principles of patient care in marine envenomations and poisonings. In Williamson, J. A., P. J. Fenner, J. W. Burnett, & J. F. Rifkin (eds), Venomous and Poisonous Marine Animals: A Medical and Biological Handbook. University of New South Wales Press, Sydney: 98–117.
Yanagita, T. M. & T. Wada, 1959. Physiological mechanism of nematocyst response in sea-anemone. VI. A note on the microscopical structure of acontium, with special reference to the situation of cnidae within its surface. Cytologia (Tokyo) 24: 81–97.
Yanagihara, A. A., J. M. Y. Kuroiwa, L. M. Oliver, J. J. Chung & D. D. Kunkel, 2002. Ultrastructure of a novel eurytele nematocyst of Carybdea alata Reynaud (Cubozoa, Cnidaria). Cell Tissue Res. 308: 307–318.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yanagihara, A.A., Kuroiwa, J.M., Oliver, L. et al. The ultrastructure of nematocysts from the fishing tentacle of the Hawaiian bluebottle, Physalia utriculus (Cnidaria, Hydrozoa, Siphonophora). Hydrobiologia 489, 139–150 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023272519668
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023272519668